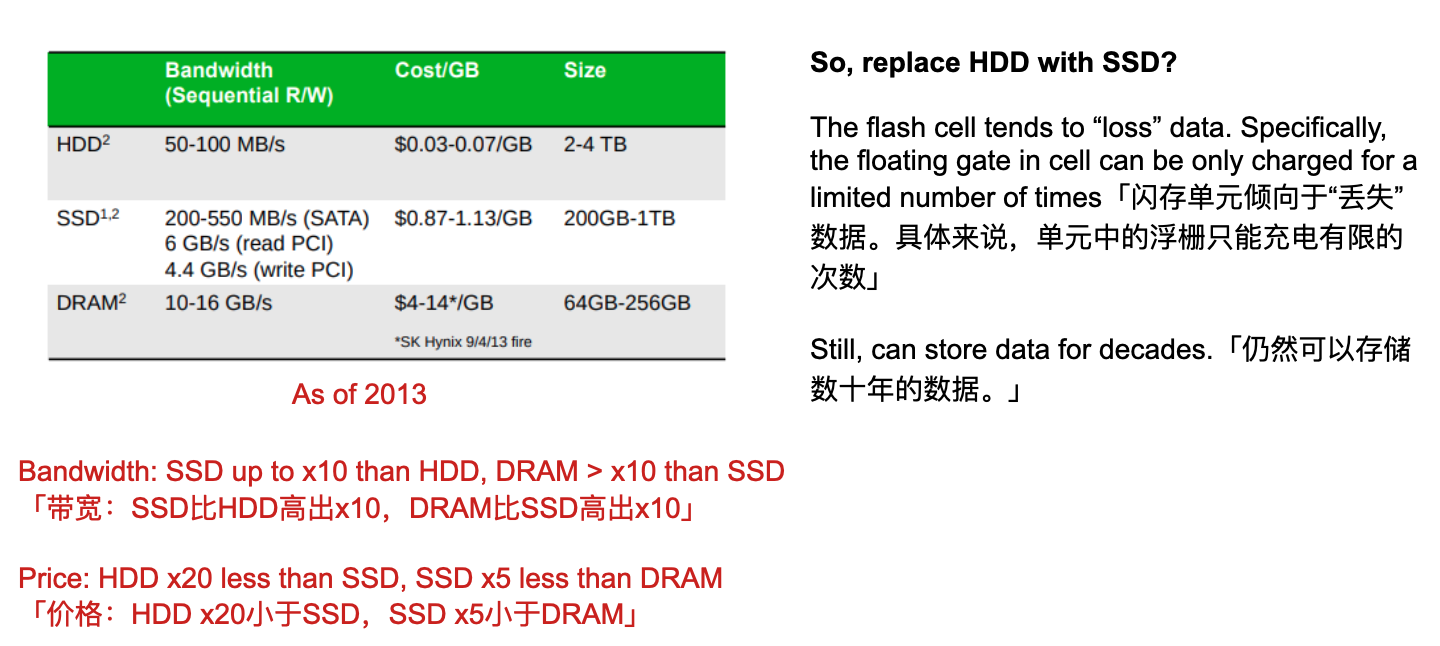
External Memory
External Memory
Magnetic Disk
The most important external memory device on almost all computer systems「几乎所有计算机系统上最重要的外部存储设备」
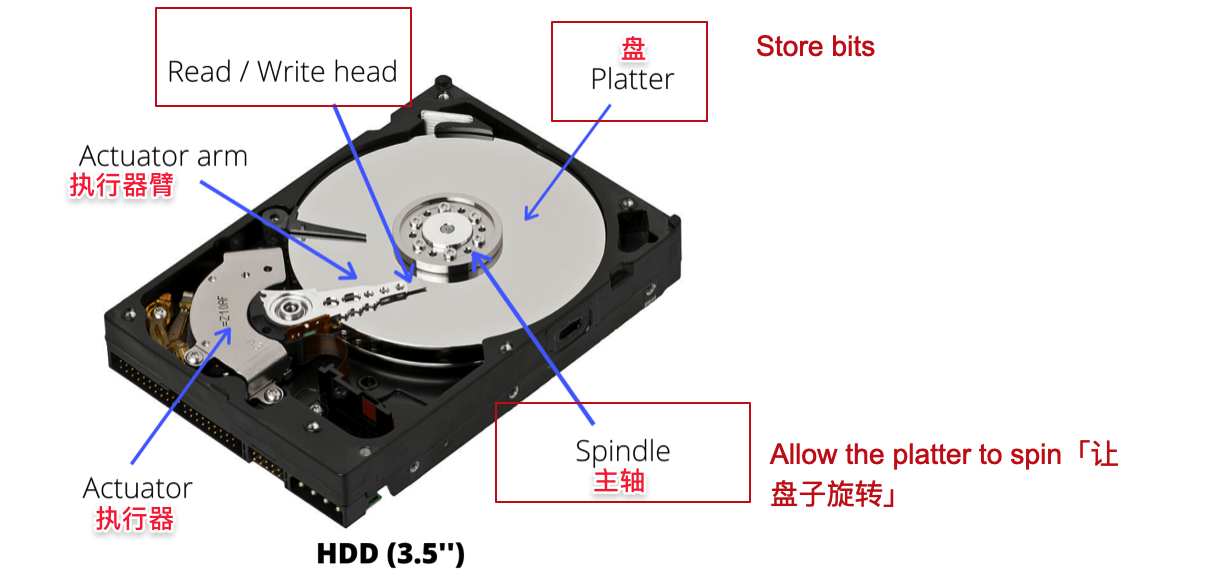
Working mechanism
How bits are read/written?
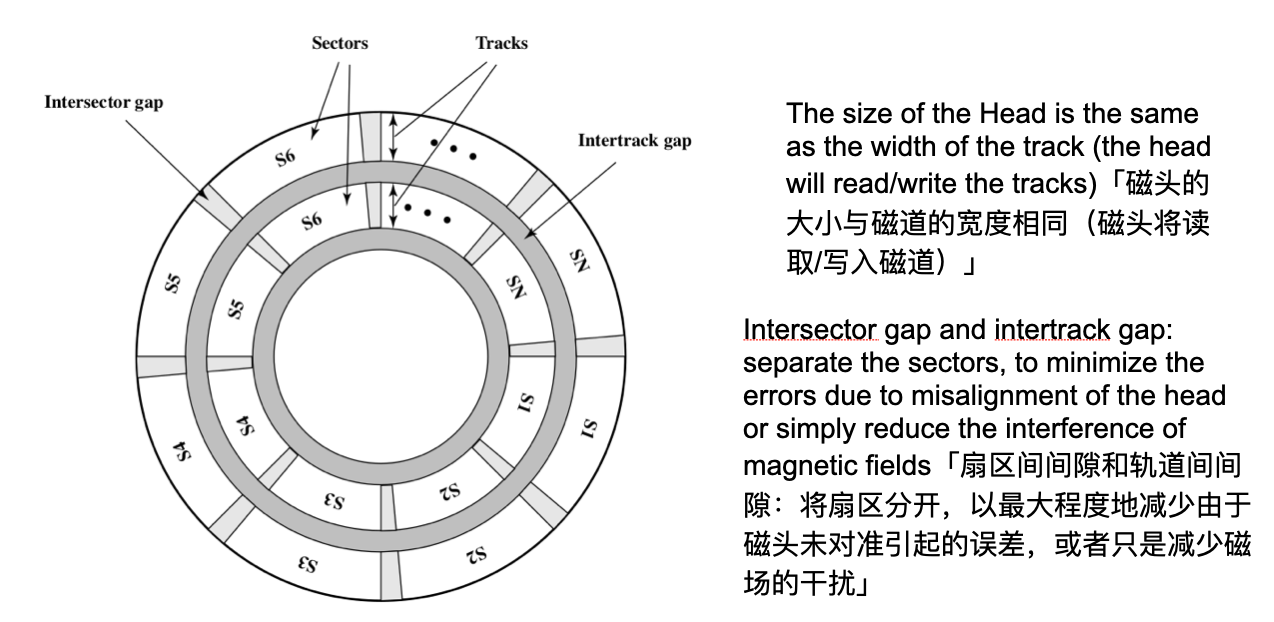
(1) Head moves to the “right position” 「(1)头部移至“正确位置”」
(2) Platter spins「(2)盘旋转」
How are the Bits stored on Platter?
Platter「盘」
- Nonmagnetic material covered with magnetic “coats”「非磁性材料覆盖有磁性“涂层”」
- On the magnetic surface, there are many magnetized「磁化的」 spots – each spot stores one bit「在磁性表面上,有许多磁化斑点–每个斑点存储一位」
- More specifically, each magnetized spot has two polarities: S and N「更具体地说,每个磁化点具有两个极性:S和N」
- The orientations (S-N or N-S) are represented as 0 or 1「方向(S-N或NS-S)表示为0或1」
- Example: 120Gb hard disk drive contains over 120 billion spots!「示例:120 Gb硬盘驱动器包含超过1200亿个斑点!」
The interaction between Head and Platter
The essence is the electromagnetic fields – the change of current will cause the change the magnetic fields, and vice versa「本质是电磁场–电流的变化将引起磁场的变化,反之亦然」
Head is covered with magnetic fields and electronic wires「头部被磁场和电线覆盖」
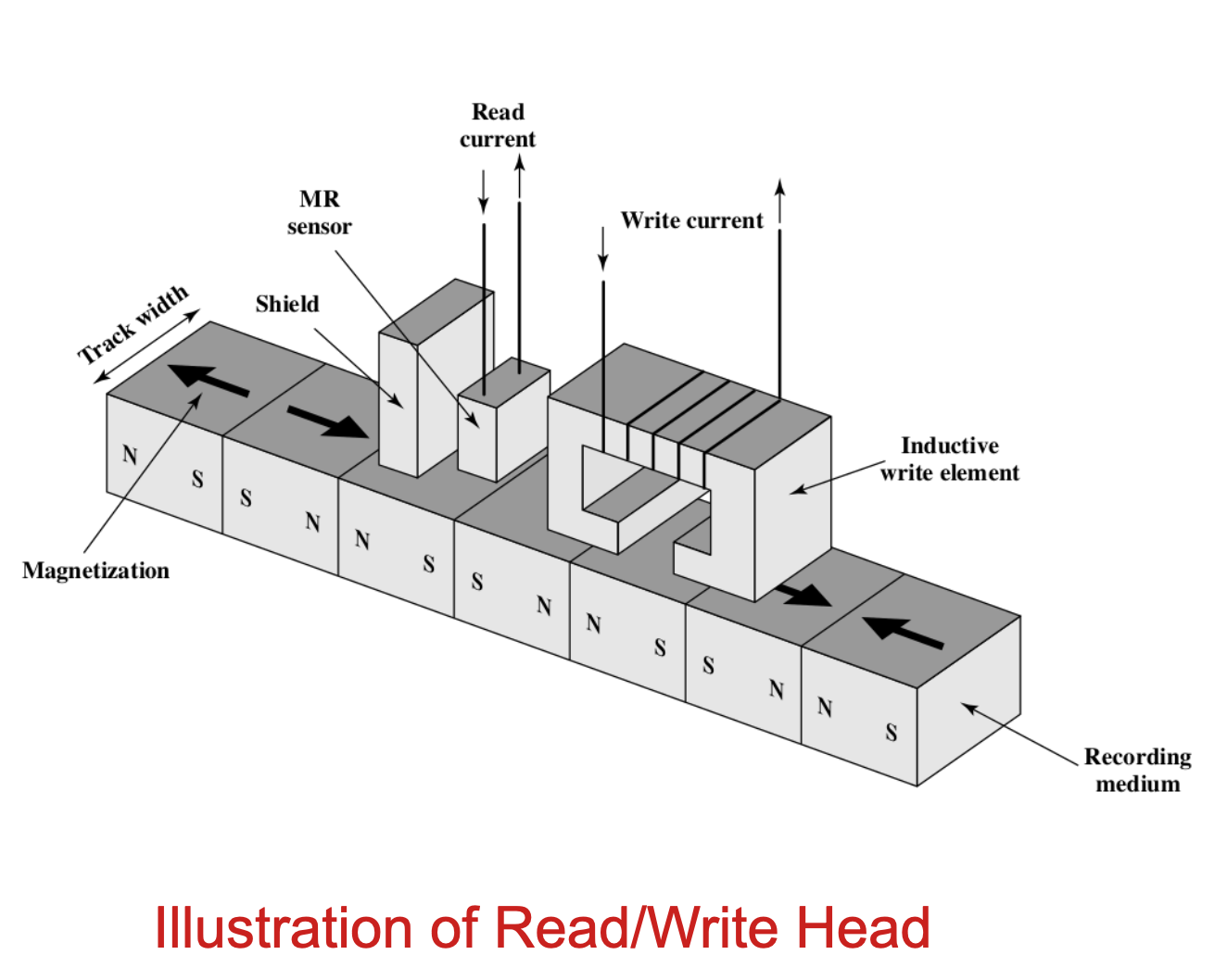
Read and write essentially have the same mechanism: the direction of the current in the Head corresponds to the orientation of the magnetized spot「读写本质上具有相同的机制:磁头中电流的方向与磁化点的方向相对应」
Two states of the directions of current = two states of the orientations (S-N or N-S) 「电流方向的两个状态=方向的两个状态(S-N或N-S)」
- Read: magnetic (Platter) → current (Head)
- Write: current (Head) → magnetic (Platter)
How are the Bits Organized on Platter
Tracks and Sectors on Platter「盘上的轨道和扇区」
- The patter contains a set of concentric rings, called tracks「图案包含一组同心环,称为轨道」
- Each track contains a number of sectors「每个轨道包含多个扇区」
- Sector = a number of magnetized spots ( a block of data)「扇区=磁化点数(数据块)」
- The size of a sector may vary「一个扇区的规模可能会有所不同」
One issue with this Organization
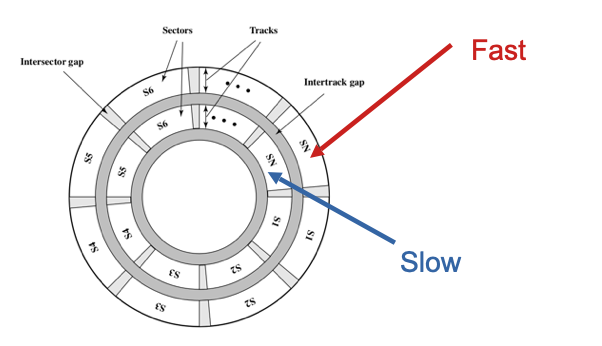
There could be different date rates for different tracks
- The head is fixed while the platter is spinning「盘旋转时,头是固定的」
- Inner and Outer tracks have different speed relatively to the head「内磁道和外磁道相对于磁头的速度不同」
- this result in different data rates when reading/writing bits stored in inner and outer tracks「读取/写入存储在内磁道和外磁道中的位时,这导致不同的数据速率」
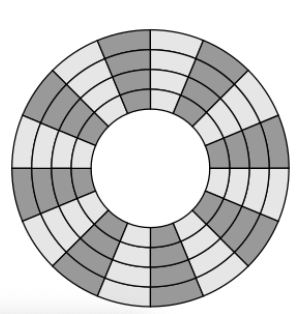
Arrangement 1: Constant Angular Velocity (CAV)
布置1:恒定角速度(CAV)
- Ideal: rotate「旋转」 the platter「盘」 at a constant speed, but the densities「密度」 of spots (bits) on different tracks「轨道」 are different「理想:以恒定的速度旋转盘子,但是不同轨道上的斑点(位)的密度不同」
- Platter is divided into a number of pie-shaped sectors「扇区」 – advantage: blocks of data can be addressed by tracks and sectors「盘片分为多个扇形扇区–优势:数据块可以通过磁道和扇区进行寻址」
- Disadvantage: amount of data can be stored on long outer tracks is only the same as what can be stored on short inner tracks (waste of space)「缺点:可以在长的外部磁道上存储的数据量与可以在短的内部磁道上存储的数据量相同(浪费空间)」
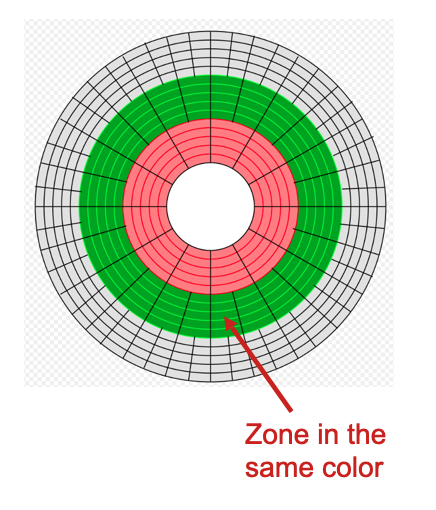
Arrangement 2: Multiple Zone Recording
Platter are organized into zones
- Each zone has multiple tracks「每个区域都有多个轨道」
- Outer track has more sectors「外轨有更多的扇区」
- The densities of the sectors are the same – increased capacity「部门的密度相同–增加容量」
- Various data transfer rate (for some disk designs, the rotation speed may change to achieve constant transfer rate)「各种数据传输速率(对于某些磁盘设计,转速可能会有所变化,以实现恒定的传输速率)」
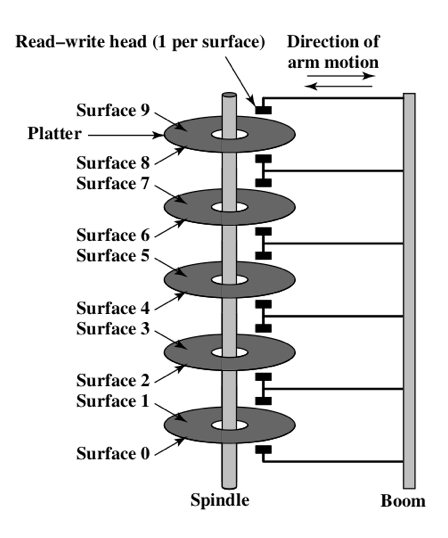
Components of Disk Drive
Data organization on Disk「磁盘上的数据组织」
- Disk – Platters – Tracks – Sectors「磁盘–盘–轨道–扇区」
- Head has the same width as that of tracks (or sectors)「磁头的宽度与磁道(或扇区)的宽度相同」
- Read/Write by sectors (one sector usually contain 512 bytes)「按扇区读/写(一个扇区通常包含512字节)」
question: how to locate「定位到」 the desired「所需」 sectors within a track?「问题:如何在轨道中找到所需的扇区?」
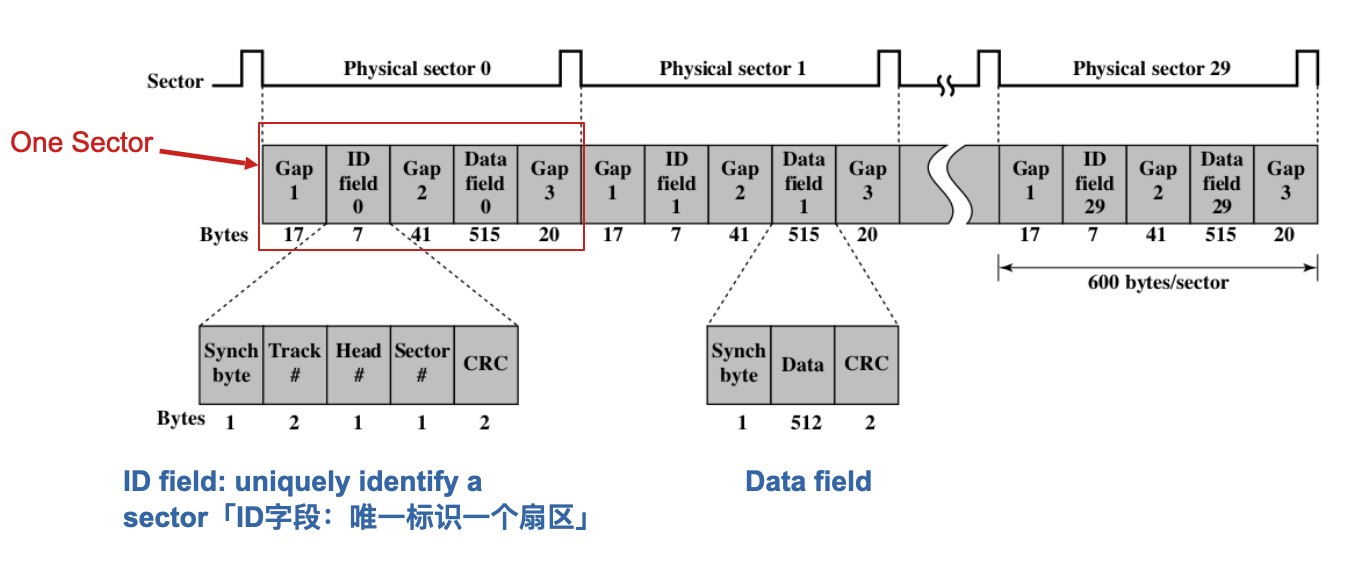
How to Locate Sector Positions within Track
Use extra control data as Marks「使用额外的控制数据作为标记」
Extra control data – used only by disk drive, not accessible by users
Format of Disk (the organization of user data and control data)「额外的控制数据–仅由磁盘驱动器使用,用户无法访问」
Example: Winchester Disk Format: each track has 30 sectors, each sector has 600 bytes (512 for data storage)「示例:温彻斯特磁盘格式:每个轨道有30个扇区,每个扇区有600字节(数据存储为512)」
How to Locate Sector Positions within Track
field「字段」
- Synch byte: the beginning「同步字节:开始」
- Head number: because there are multiple platters and heads「头数:因为有多个盘和头」
- CRC: error correction code「CRC:纠错码」
The Timing of Disk I/O Transfer
An important performance measurement「一个重要的性能指标」
The time does not just depend on how fast the disk can read/write bits – many other considerations「时间不仅仅取决于磁盘可以读取/写入位的速度–还有许多其他注意事项」
There are various queuing delays: wait for device and wait for channel「排队延迟有多种:等待设备和等待频道」
- Wait for device: when process (task) issues an I/O request, it must first wait in a queue for the device to be available「等待设备:当进程(任务)发出I / O请求时,它必须首先在队列中等待设备可用」
- Wait for channel: multiple I/O devices may share the channel between Processor and devices – need to wait for the channel to be available「等待通道:多个I / O设备可能在处理器和设备之间共享通道–需要等待通道可用」
Access time
The time for the Head to get to the right position「头部到达正确位置的时间」
It consists of two parts: seek time and rotational delay「它由两部分组成:寻道时间和旋转延迟」
- Seek time: the Head moves to the right track「搜寻时间:头部移动到正确的轨道」
- Rotational delay: the desired sector rotates to the Head「旋转延迟:所需扇区旋转到磁头」
- Factors: how compact is the platter (size of platter), rotation speed「因素:盘片的紧凑程度(盘片的大小),旋转速度」
Common example: average seek time ~ 10 ms; average rotational delay ~ 1.5 ms「常见示例:平均寻道时间~10毫秒;平均旋转延迟~1.5毫秒」
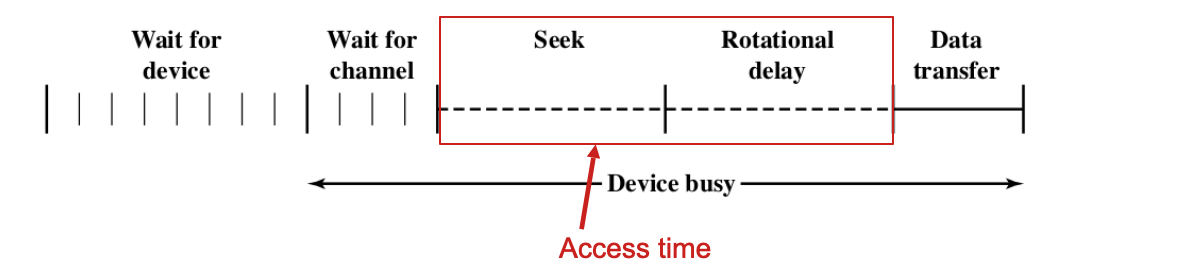
Data transfer
The actual time to read/write data as platter moves under head「当磁盘在磁头下方移动时,读取/写入数据的实际时间」
Factor: the rotation speed and the number of sectors「因素:转速和扇区数」
Typical rotation speed: 3600 – 20,000 rpm (revolutions per min)「典型转速:3600 – 20,000 rpm(每分钟转数)」
Summary
Redundant Array of Independent Disks
Redundant Array of Independent Disks (RAID)「独立磁盘冗余阵列(RAID)」
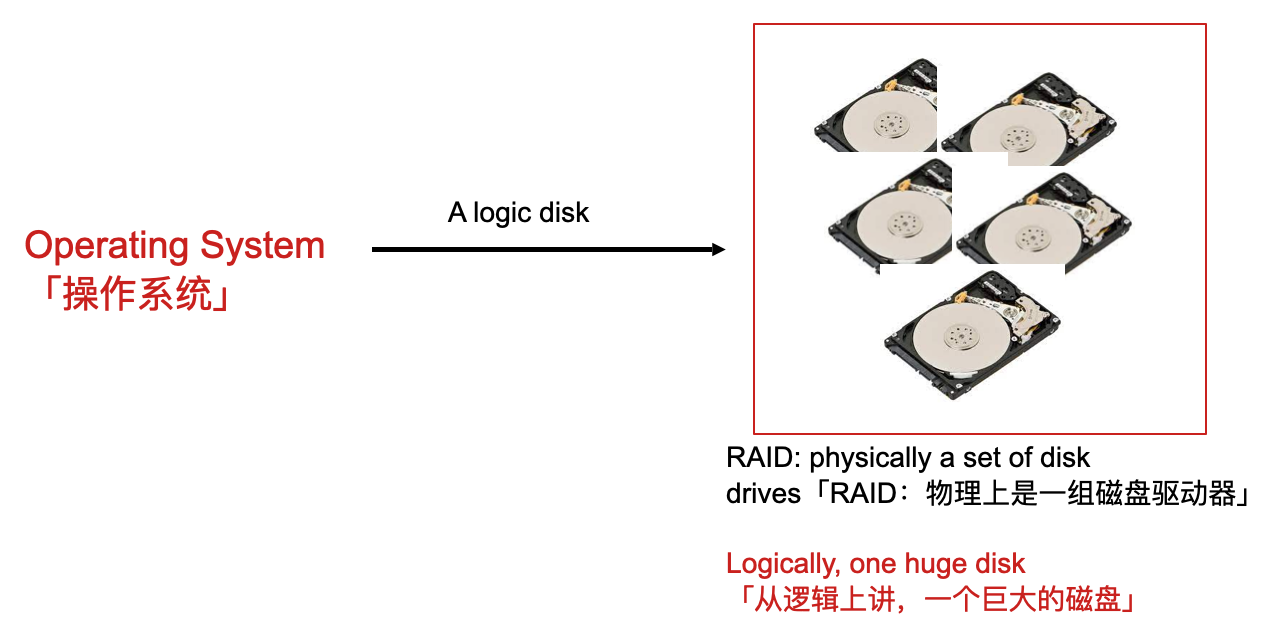
Overview
- There are 7 levels: RAID 0 to RAID 6「共有7个级别:RAID 0至RAID 6」
- These levels are NOT hierarchical, they are different designs (disks)「这些级别不是分层的,它们是不同的设计(磁盘)」
- Different levels have different characteristics「不同级别具有不同特征」
Common Characteristics
Common Characteristics「共同特征」
- A logic disk drive to the operating system「操作系统的逻辑磁盘驱动器」
- Data striping: divide logically sequential data (file) into segments (strips) and distribute them to different physical devices「数据条带化:将逻辑上顺序的数据(文件)划分为段(条)并将其分发到不同的物理设备」
- Redundant: will store some redundant data (except for RAID 0)「冗余:将存储一些冗余数据(RAID 0除外)」
RAID wants to address two main issues of single disk「RAID希望解决单个磁盘的两个主要问题」
- I/O speed: parallel the I/O operations across many disks「I / O速度:跨多个磁盘并行执行I / O操作」
- Reliability: introduce redundancy「可靠性:引入冗余」
RAID 0 – Data Distribution (NO Redundancy)
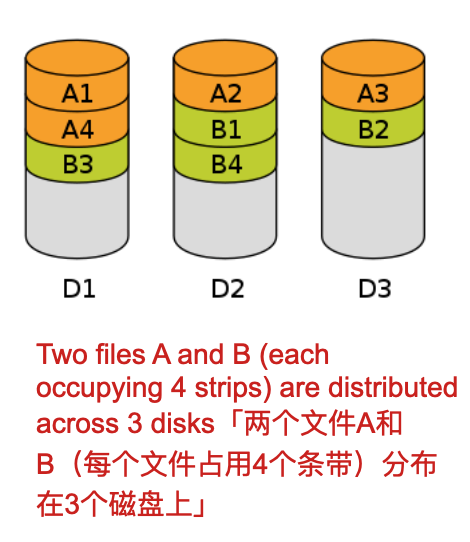
Data are segmented into strips and distributed:「数据被分割成条带并分发:」
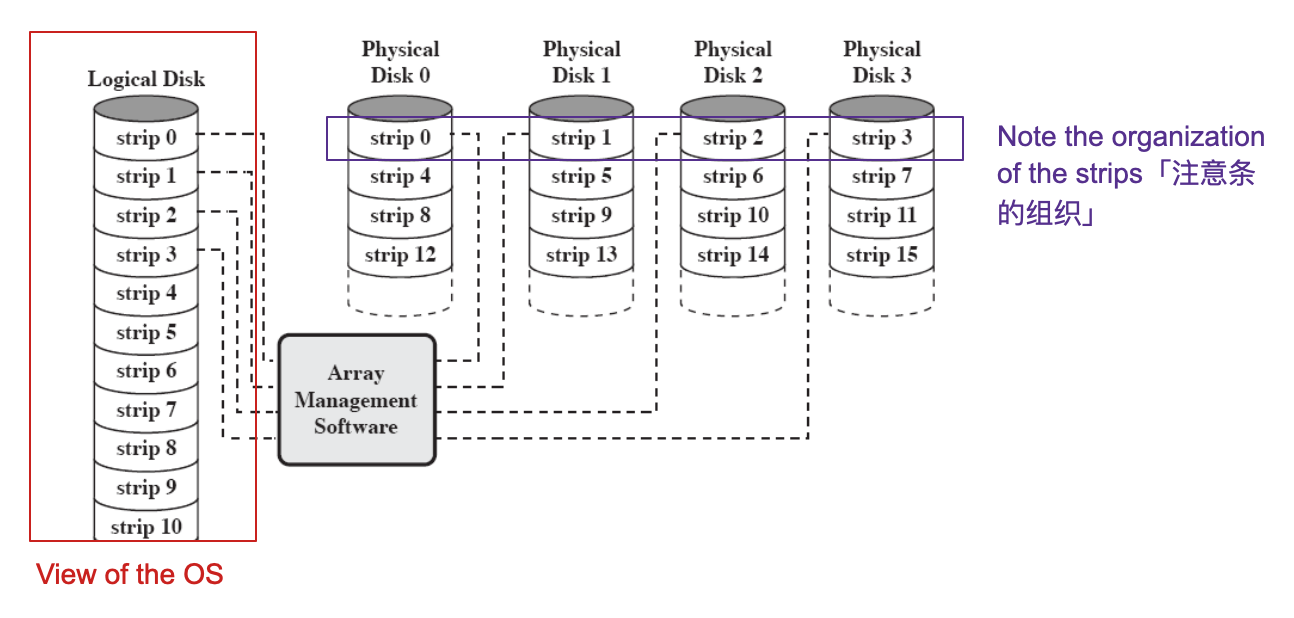
- Data are stripped across all disks「数据跨所有磁盘剥离」:Round Robin stripping「循环剥离」
- Increased speed「提高速度」
- A set of data is likely to be stripped across multiple disks 「一组数据可能会跨多个磁盘剥离」
- Disks seek in parallel「磁盘并行查找」
Failure of one disk may cause the loss of multiple files「一个磁盘发生故障可能会导致多个文件丢失」
Raid 1 Duplicated data (mirrored data)
重复数据(镜像数据)
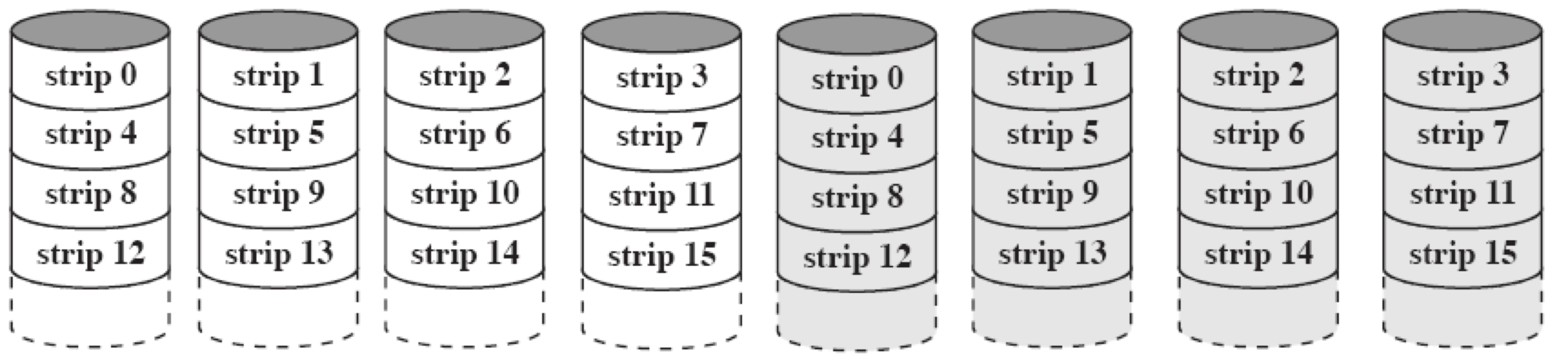
Now, a logical disk contains two same components「现在,逻辑磁盘包含两个相同的组件」
RAID 2 and RAID 3: Redundancy through Error Correction Code
RAID 2和RAID 3:通过纠错码实现冗余
- Parallel Access Technique「并行访问技术」
- The spindles of disk drives are synchronized so that each disk head is in the same position on each disk at any given time「磁盘驱动器的主轴已同步,因此每个磁盘头在任何给定时间都在每个磁盘上的相同位置」
- Read the bits in the same position in parallel「并行读取相同位置的位」
- The size of each strip is very small (e.g., a single byte or word)「并行读取相同位置的位」
RAID 2 and RAID 3 differ in error correction code used「RAID 2和RAID 3使用的纠错码不同」
RAID 2 typically uses Hamming Code
Example: (7-4) Hamming Code, the bits in the same position on each data disks are encoded, the resulting parity bits are then stored in the same position on the parity disks「示例:(7-4)汉明码,对每个数据磁盘上相同位置的位进行编码,然后将所得的奇偶校验位存储在奇偶校验磁盘上的相同位置」
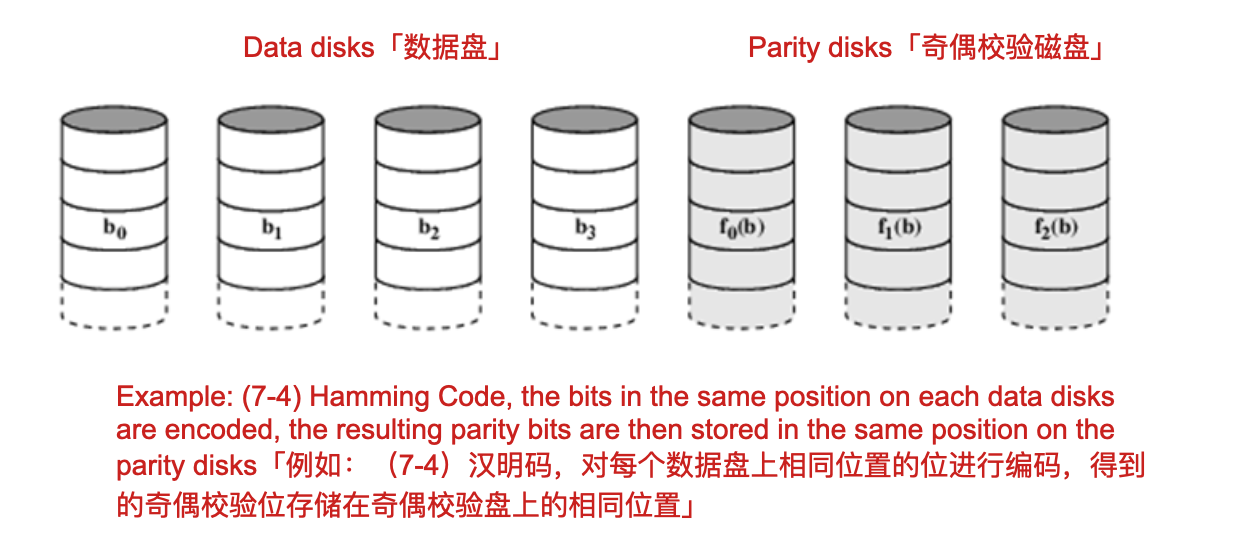
Data bits and parity bits are read/write simultaneously「同时读取/写入数据位和奇偶校验位」
- Codes are calculated “on-the-fly”「代码是“动态”计算的」
- Correct error in real time「实时纠正错误」
- Good for low quality disks which has frequent errors「适用于经常出错的低质量磁盘」
Still lots of redundancy (although better than RAID 1)「仍然有很多冗余(尽管更好,比RAID 1)」
Expensive, not commonly used「昂贵,不常用」
RAID 3 uses a single parity bit
Add a single parity bit for the data bits (b0 – b3) in the same position (bit-interleaved parity)「在同一位置为数据位(b0 – b3)添加一个奇偶校验位(比特交织奇偶校验)」
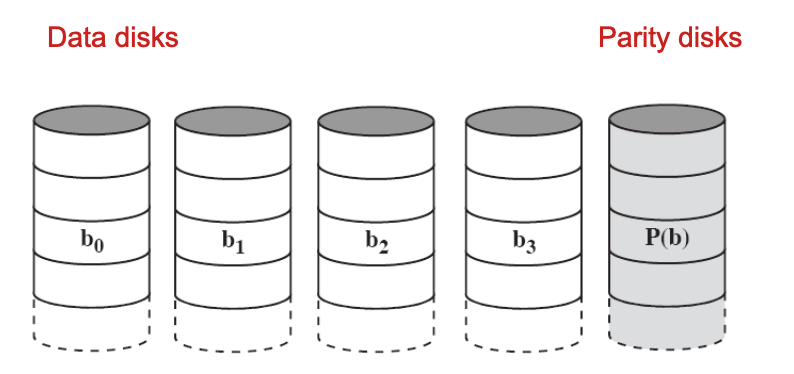
Only one redundant disk, no matter how large the array「只有一个冗余磁盘,无论阵列有多大」
Efficient than RAID 2「比RAID 2更高效」
RAID 4 - 6
Compared to RAID 3「与RAID 3相比」
- Disks are accessed independently (not in parallel)「独立访问磁盘(不是并行访问)」
- Strips have much larger size (block-level), good for high I/O read request rate (since one request can handled by one disk)「条带的大小要大得多(块级),有利于高I/O读取请求率(因为一个磁盘可以处理一个请求)」
- Also compute a single bit parity for corresponding data bits (the distribution of parity bits are different in RAID 4, 5, 6「还计算相应数据位的单位奇偶校验(奇偶校验位在RAID 4、5、6中的分布不同)」
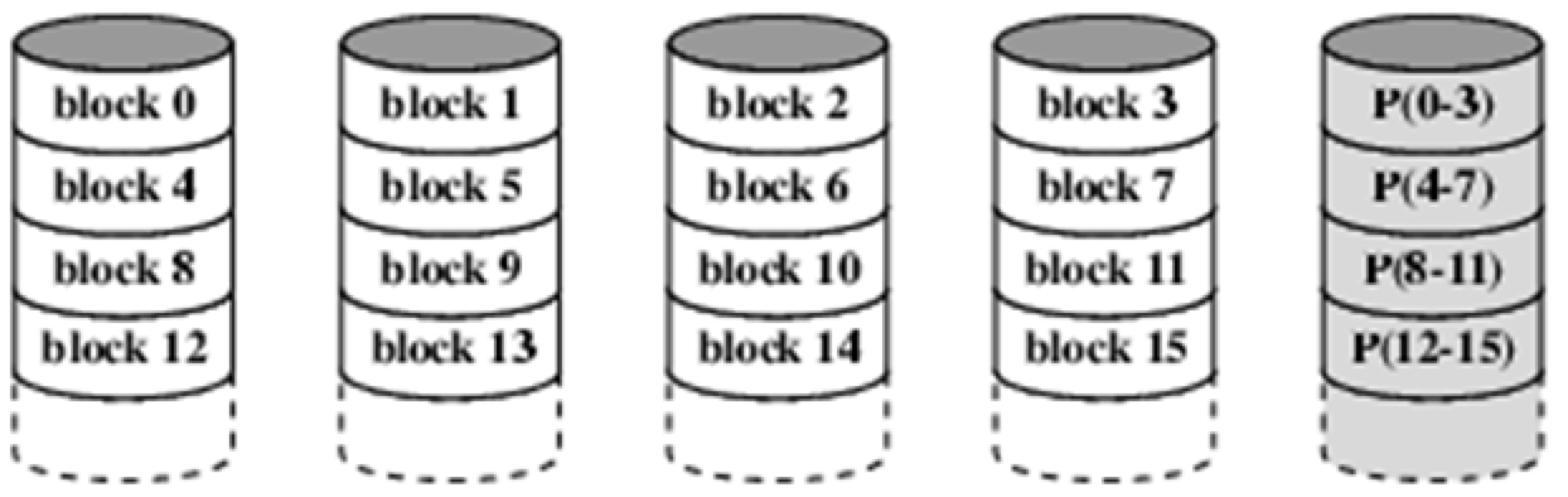
Bottleneck for data update (there is a write penalty): suppose we want to update one file in block 0, we need to read multiple blocks to also update the parity information)「数据更新瓶颈(有写惩罚):假设我们要更新块0中的一个文件,我们需要读取多个块来更新奇偶校验信息)」
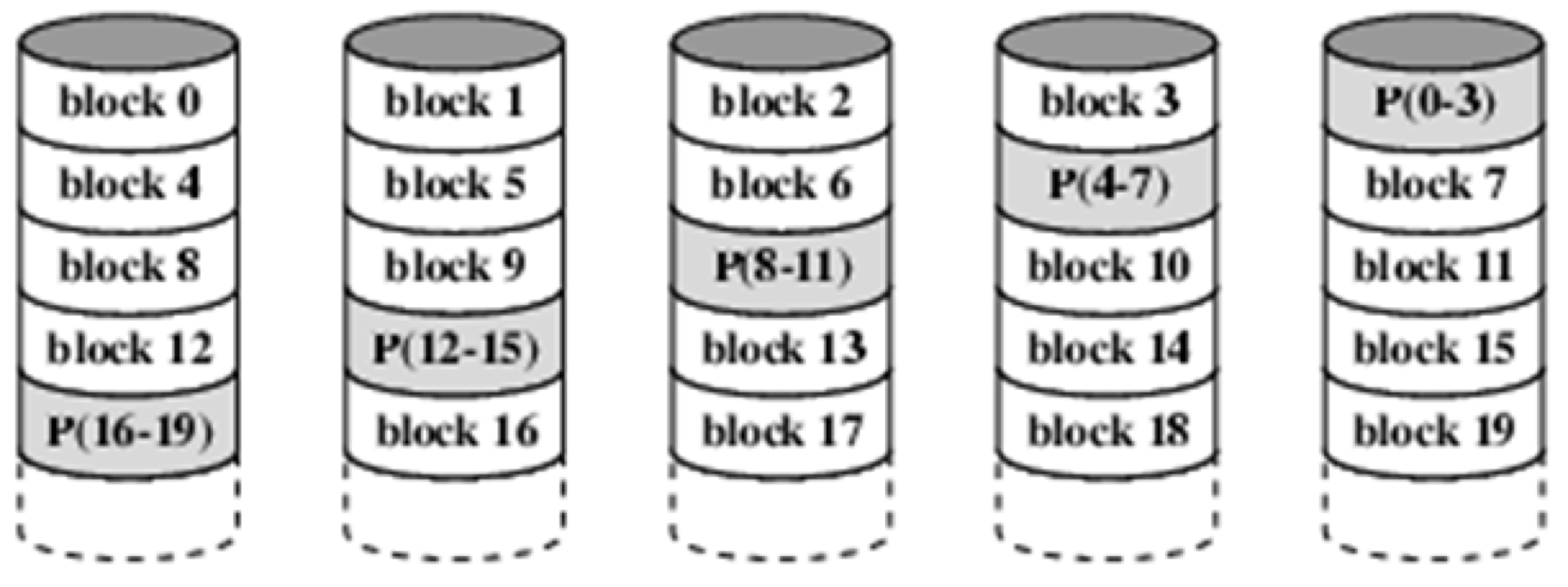
Raid 5
Almost the same as RAID 4「几乎与RAID 4相同」
- Difference: round robin allocation for parity strips, so that parity information is striped across all disks「区别:奇偶校验条带的轮询分配,从而使奇偶校验信息在所有磁盘上分条」
- Can avoid the bottleneck at parity disk in RAID 4「可以避免RAID 4中奇偶校验磁盘的瓶颈」
SSD Basics
- Previous memory devices「以前的存储设备」
- RAM: fast but volatile 「RAM:快速但易失」
- ROM: read only「ROM:只读」
- Variations of ROM (PROM, EPROM, Flash Memory, EEPROM): write at a high cost「ROM的变体(PROM,EPROM,闪存,EEPROM):写入成本高」
- Hard drive disk: mechanical parts「硬盘磁盘:机械零件」
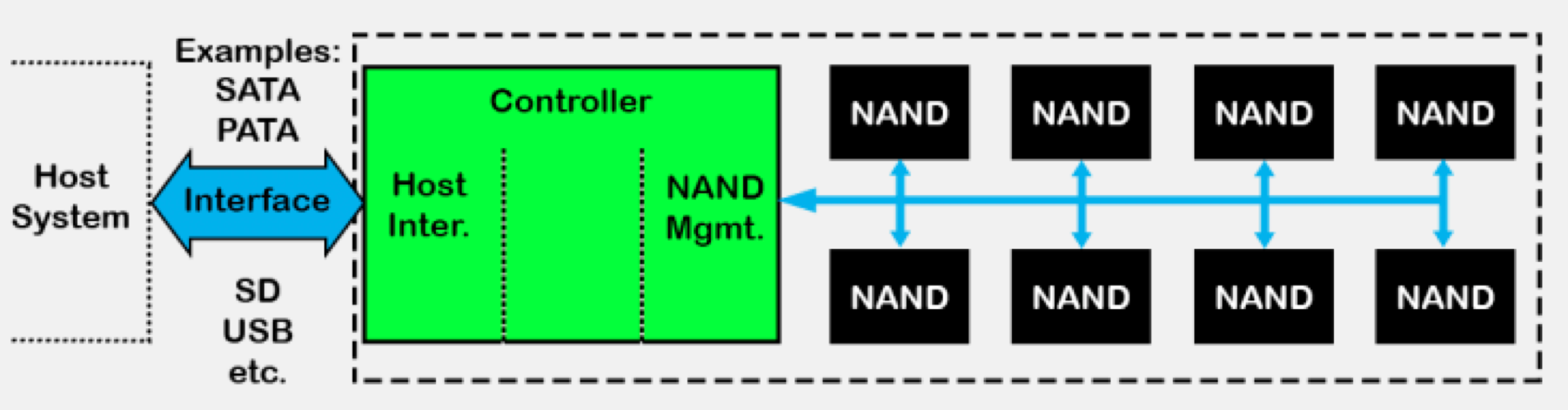
Two components:Controller + memory component「控制器+内存组件」
- Specifically, memory component uses NAND flash memory (since 1990s)「具体来说,存储组件使用NAND闪存(自20世纪90年代以来)」
- Basic element: NAND flash cell that can store 1 bit「基本元件:可存储1位的NAND闪存单元」
- Design: the organization of cells and read/write operations「设计:单元的组织和读写操作」
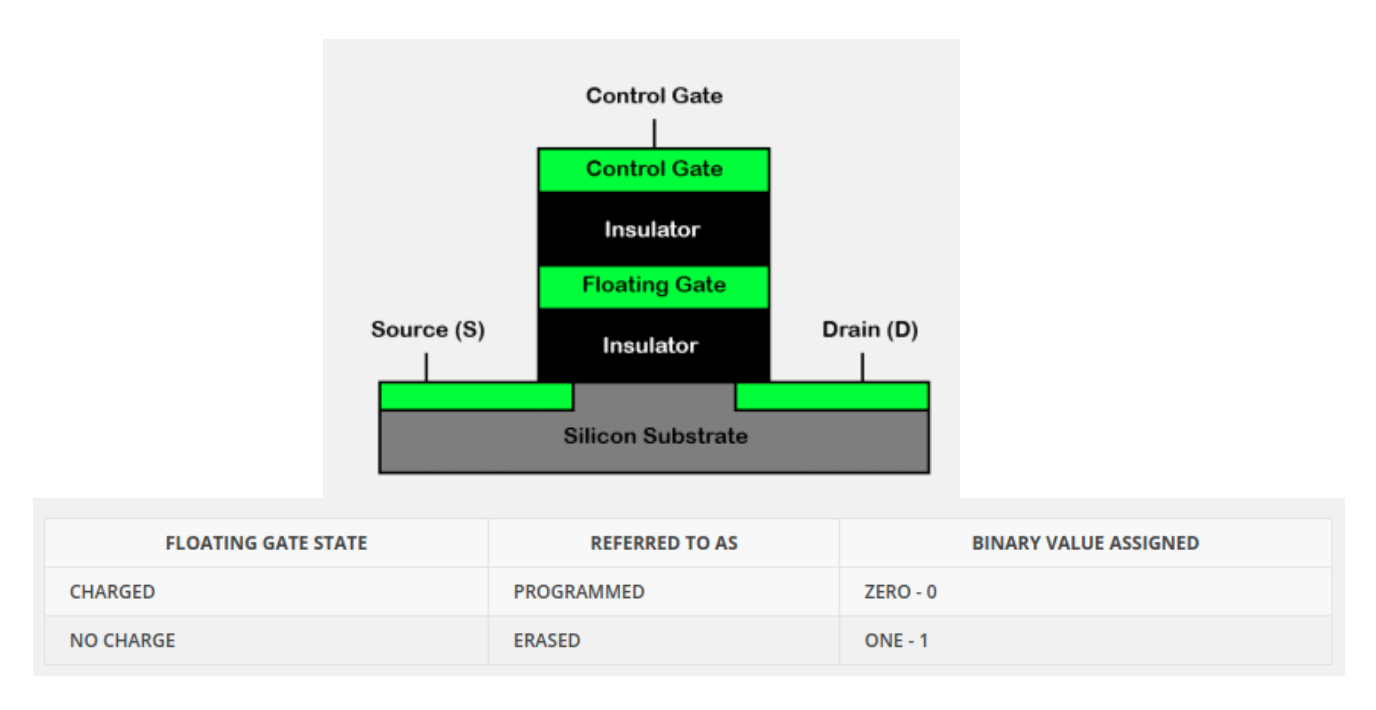
NAND Flash Cell
Surrounding circuitry can change the states of the floating gate「周围的电路可以改变浮栅的状态」
read/write though the control gate「通过控制门读/写」
Overall, this cell can store one bit「总的来说,这个单元可以存储一个位」
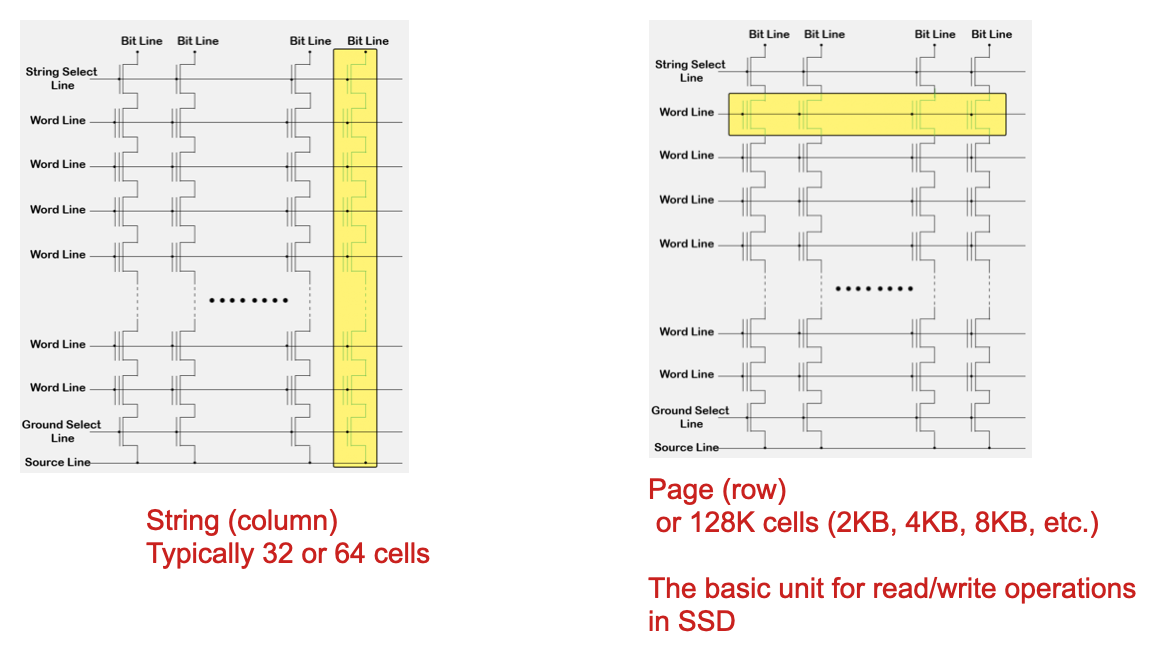
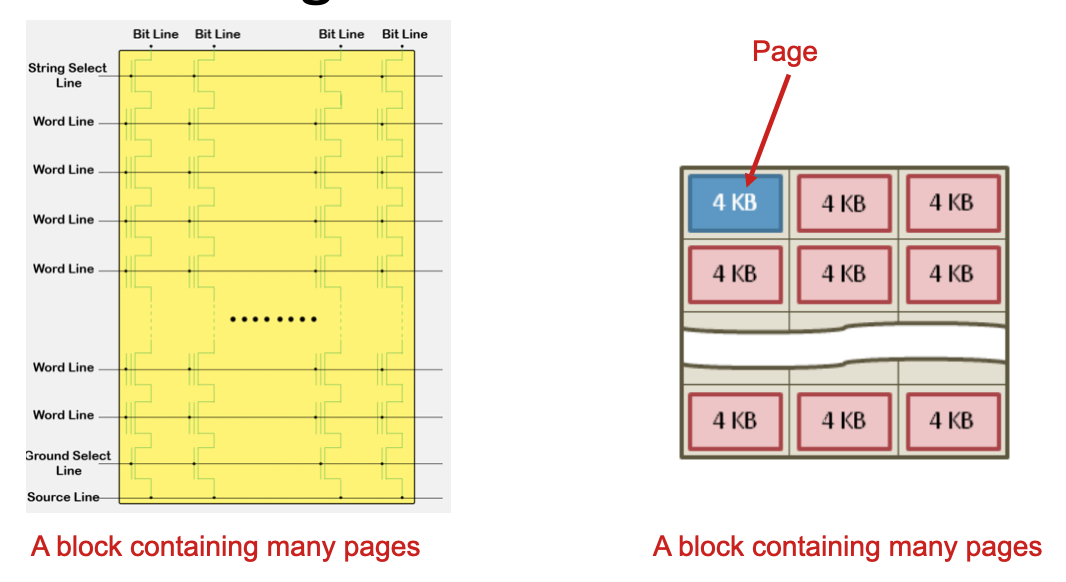
From Cells to Pages to Blocks
SSD Architecture
Read and Write Operation
Characteristics「特点」
Basic unit: read – page; write – page (when the page is empty, i.e., there is no direct over-write)「基本单位:读-页;写-页(当页为空时,即没有直接重写)」
The feature of flash memory: need to erase data before over-write (update)「闪存的特点:在重写(更新)之前需要擦除数据」
Data are erased in blocks (using high voltage, time consuming)「数据分块擦除(使用高电压,耗时)」
As a result, if we want to over-write some pages, we need to erase a block first, write pages「因此,如果我们想重写一些页面,我们需要先删除一个块,然后再写页面」

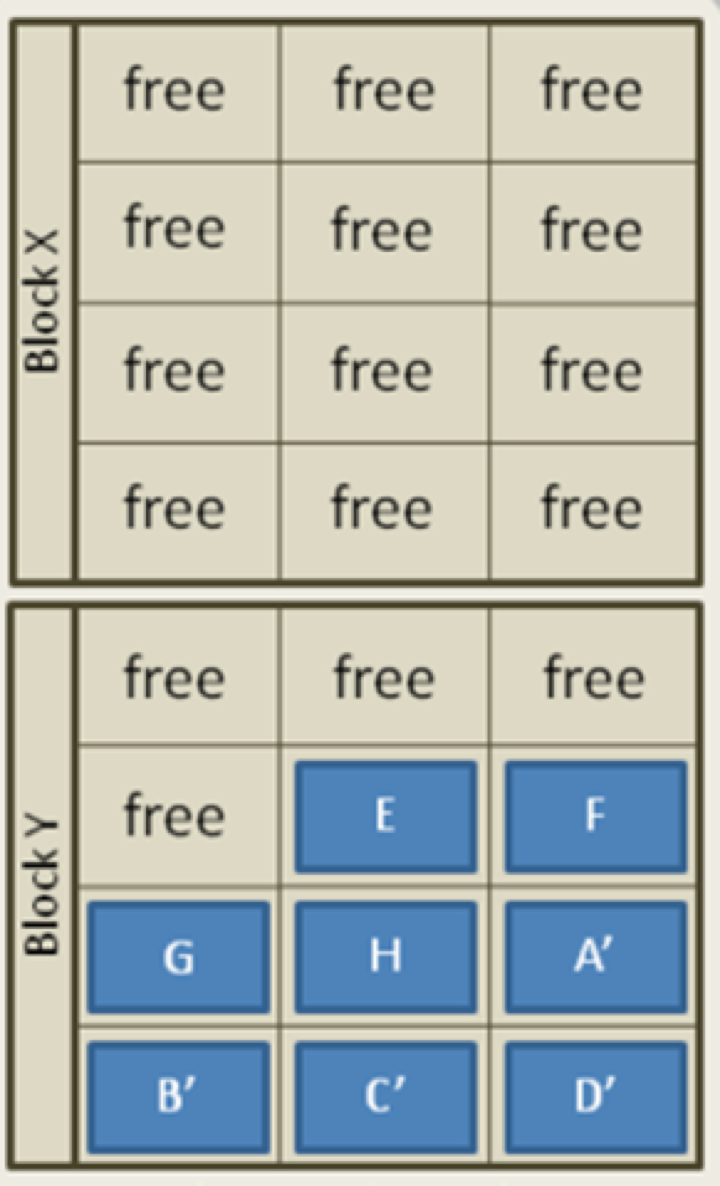
Garbage collection「垃圾收集」:
- Copy “good data” E,F,G,H and A’,B’,C’,D’ into a new empty block Y「将“好数据” E,F,G,H和A′,B′,C′,D′复制到新的空白块Y中」
- Erase block X (garbage A, B, C,D are collected – more empty pages)「擦除块X(收集了垃圾A,B,C,D –更多的空白页)」
- This is done in the background, and is controlled by the Controller component in SSD「这是在后台完成的,并由SSD中的Controller组件控制」
Comparison