Writing Functions
Writing Functions
Docstrings
def count_letter(content, letter):
"""Count the number of times `letter` appears in `content`.
Args:
content (str): The string to search.
letter (str): The letter to search for.
Returns:
int
# Add a section detailing what errors might be raised
Raises:
ValueError: If `letter` is not a one-character string.
"""
if (not isinstance(letter, str)) or len(letter) != 1:
raise ValueError('`letter` must be a single character string.')
return len([char for char in content if char == letter])
如何直接获取
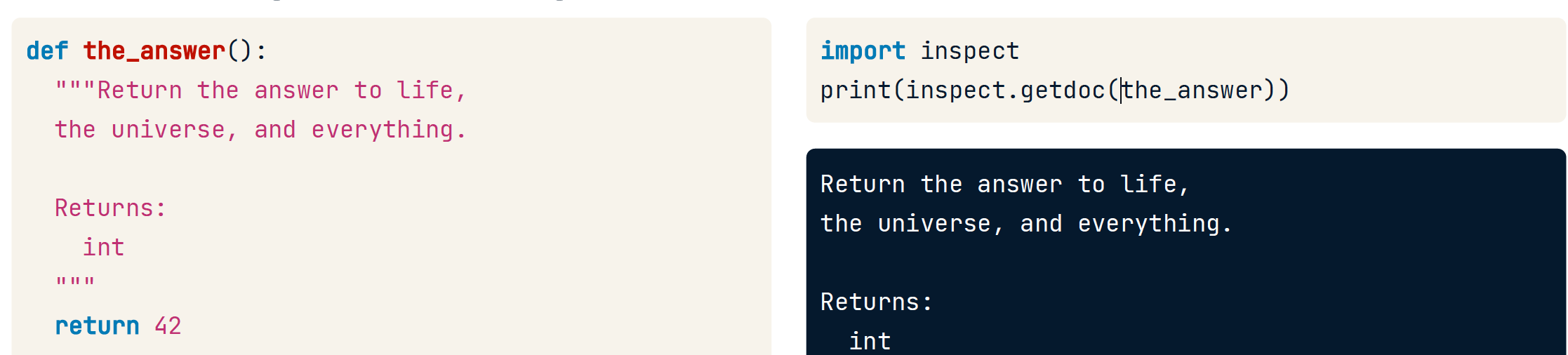
# Get the "count_letter" docstring by using an attribute of the function
docstring = count_letter.__doc__
border = '#' * 28
print('{}\n{}\n{}'.format(border, docstring, border))
<script.py> output:
############################
Count the number of times `letter` appears in `content`.
Args:
content (str): The string to search.
letter (str): The letter to search for.
Returns:
int
Raises:
ValueError: If `letter` is not a one-character string.
############################
inspect.getdoc()获取
Pass by assignment
和Java 的 Pass by reference相似。只不过需要注意不能更改的变量有什么。


context managers
作用
- 设置一个上下文
- 运行你的代码
- 删除上下文
open()
open() does three things:
- Sets up a context by opening a file
- Lets you run any code you want on that file
- Removes the context by closing the file
Using a context manager
with <context-manager>(<args>) as <variable-name>:
# Run your code here
# This code is running "inside the context"
# This code runs after the context is removed
举例
with open('my_file.txt')as my_file: text = my_file.read() length = len(text)
print('The file is {} characters long'.format(length))
define a context manager
Two ways:
- Class-based
- Function-based
此处关注基于函数的
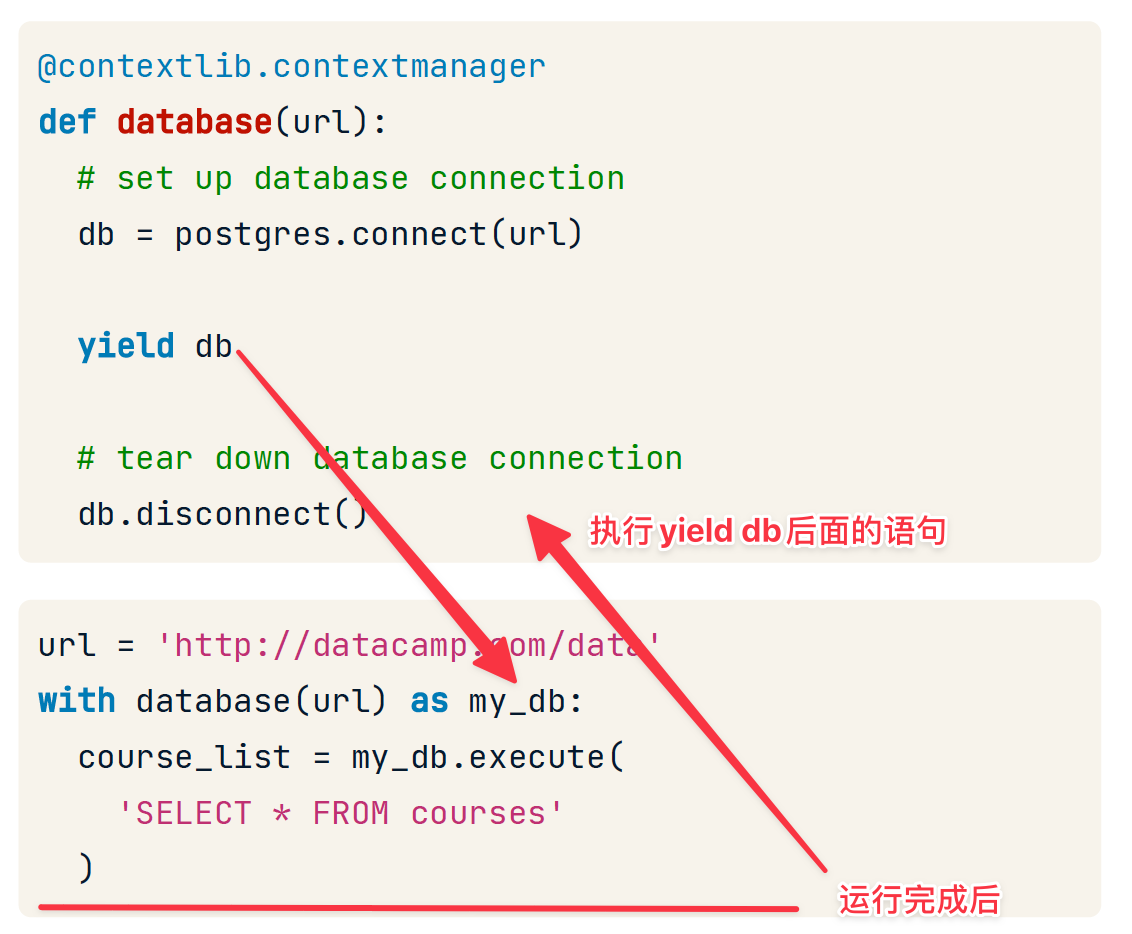

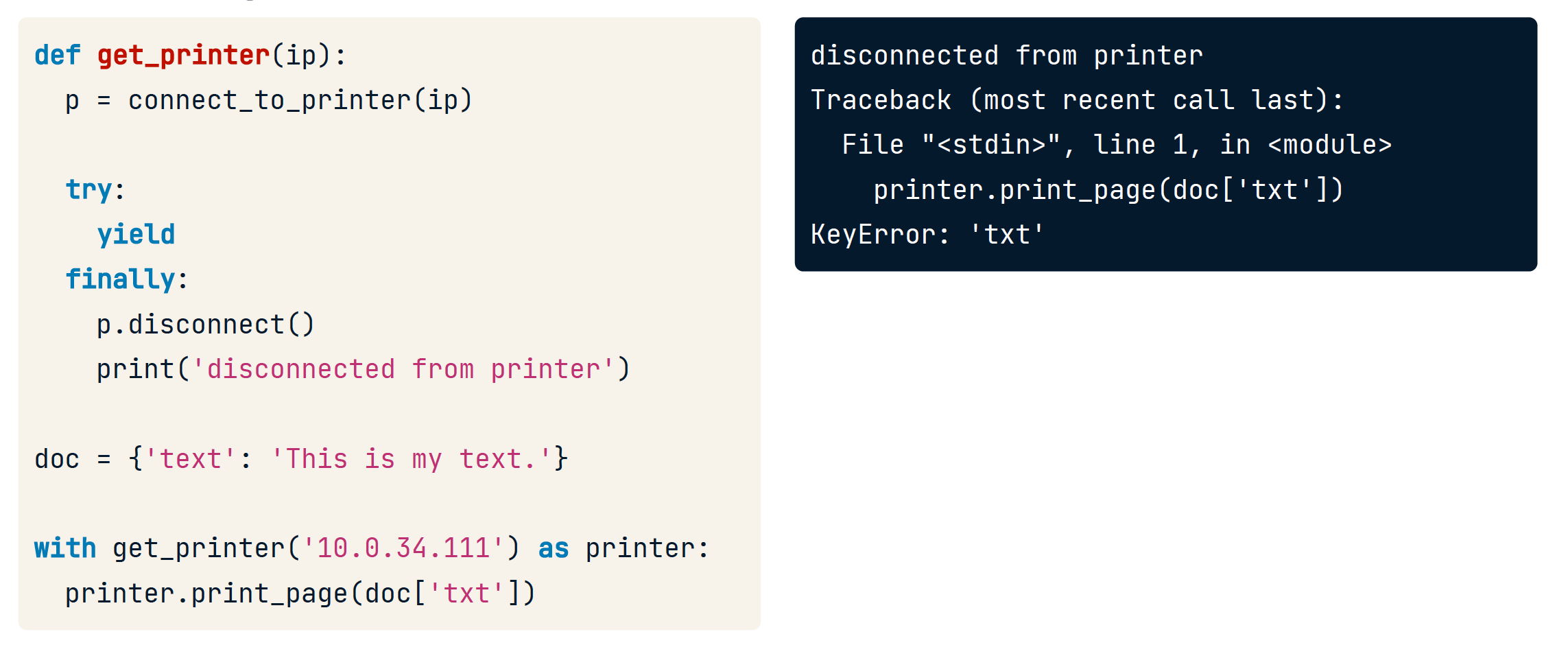
应当添加try-catch 保证最终一定关闭资源
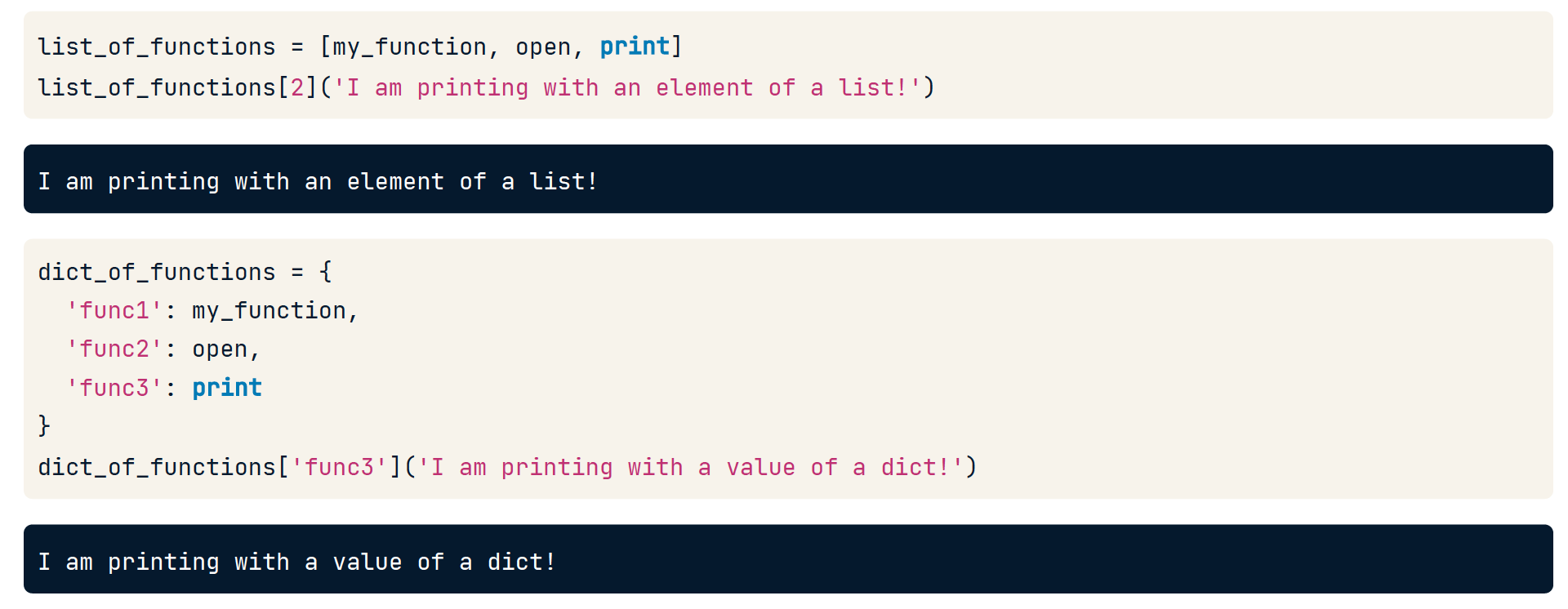
Functions as objects
Python 思想:一切都是 object
调用和赋值

Functions as variables
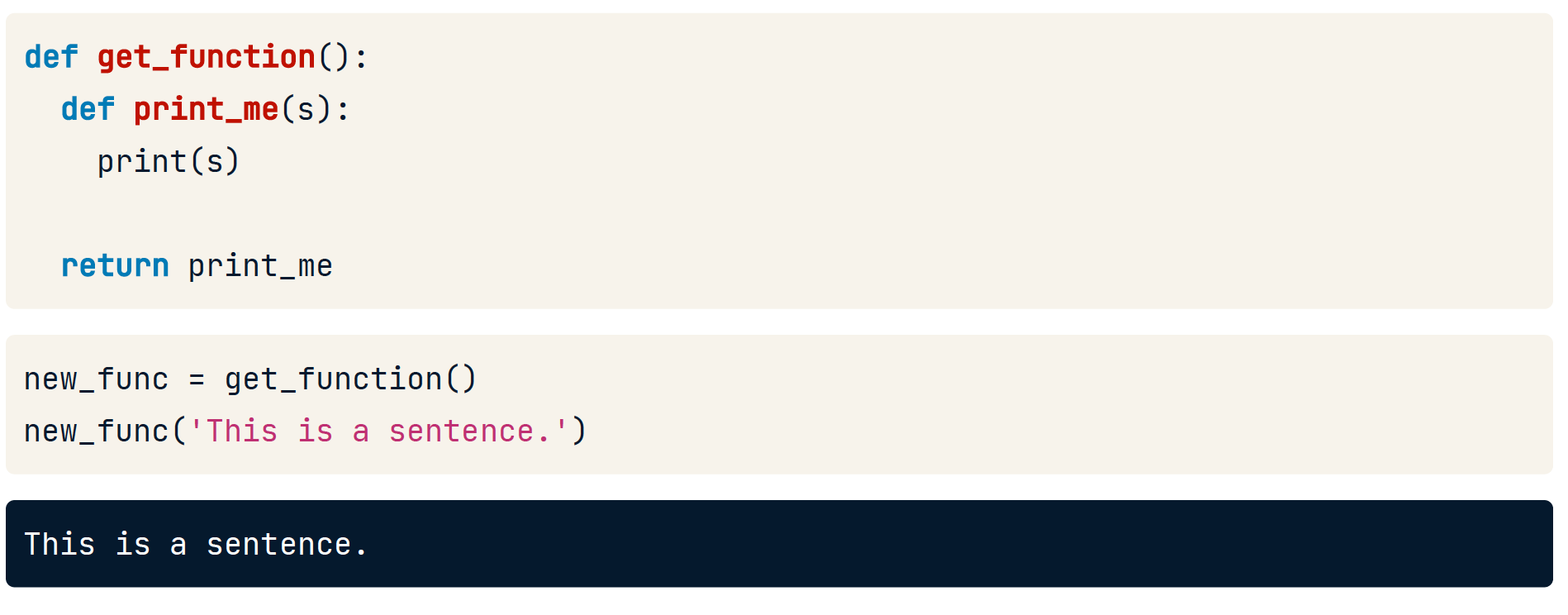
子函数
def foo():
x = [3, 6, 9]
def bar(y):
print(y)
for value in x:
bar(x)
同样的,子函数对象也可以作返回值
Scope
不妨先做个对比
| Language | 全局变量 | 局部变量 | 全局变量在函数内 |
|---|---|---|---|
| C/C++ | 有(函数外声明) | 有(函数/{}内声明) | 可读 可写 |
| Python3 | 有(函数外声明) (global函数内声明) | 有(函数内声明) | 可读, 不可写 加global后可写 |
| Java | 无(只有类变量,被成员共享访问) | 有(函数/{}内声明) | 类变量可读可写 除非用关键字控制 |
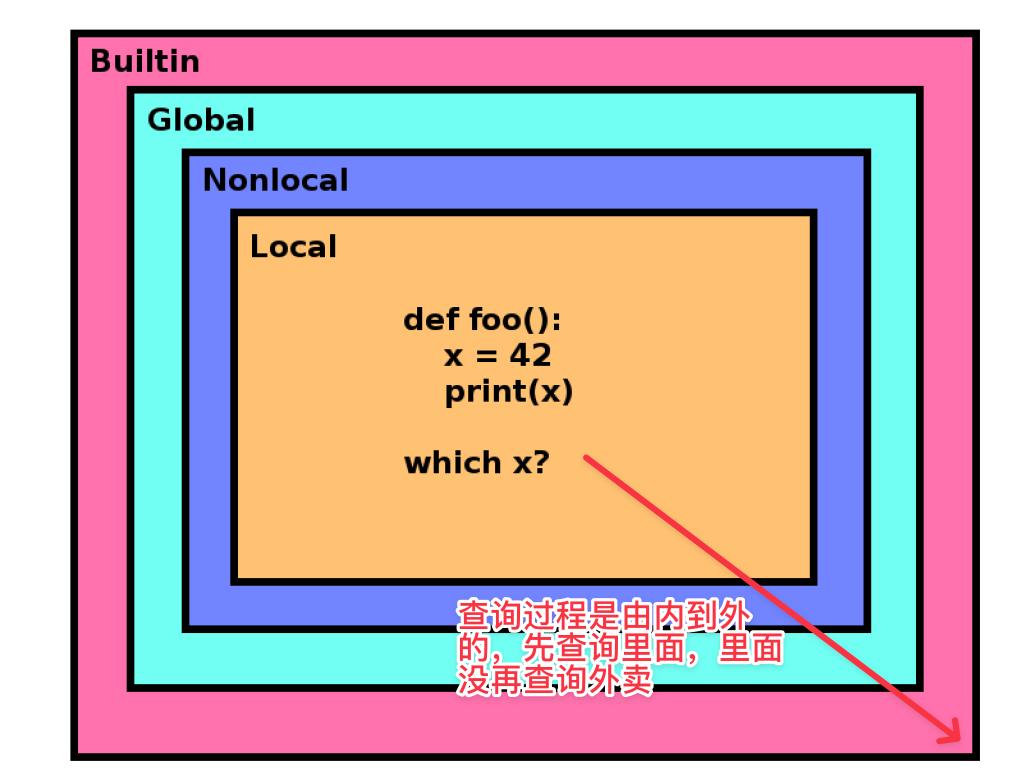
Python 变量作用域
全局变量在函数内可读不可写
x = 7
y = 200
def foo():
x = 42 #创建x为局部变量,忽略全局变量x
print(x)
print(y)
foo()
42
200
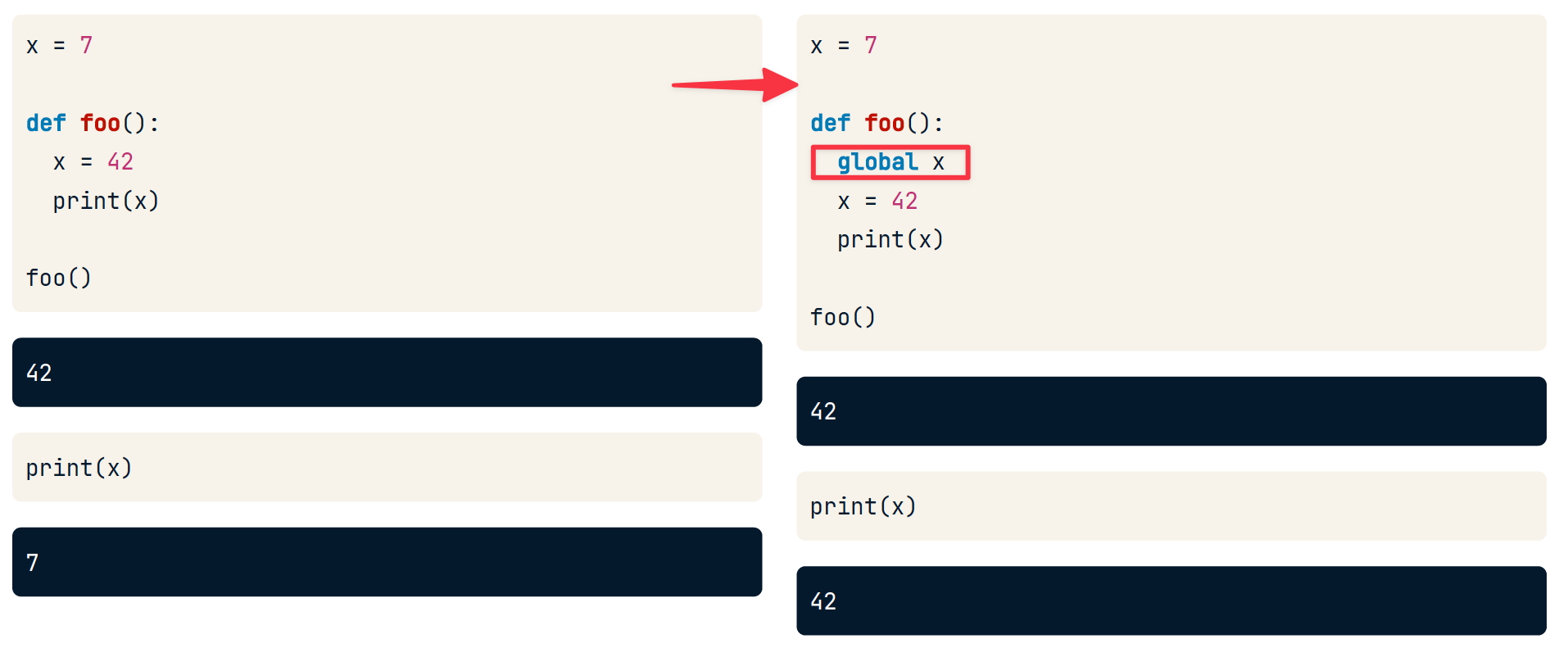
global 关键字
global 关键字在函数内修饰变量,有两个作用
- 在函数内声明一个新的全局变量,并且使该变量在函数内可读可写
- 若修饰的变量已经在全局定义,则使该变量在函数内可读可写
nonlocal 关键字
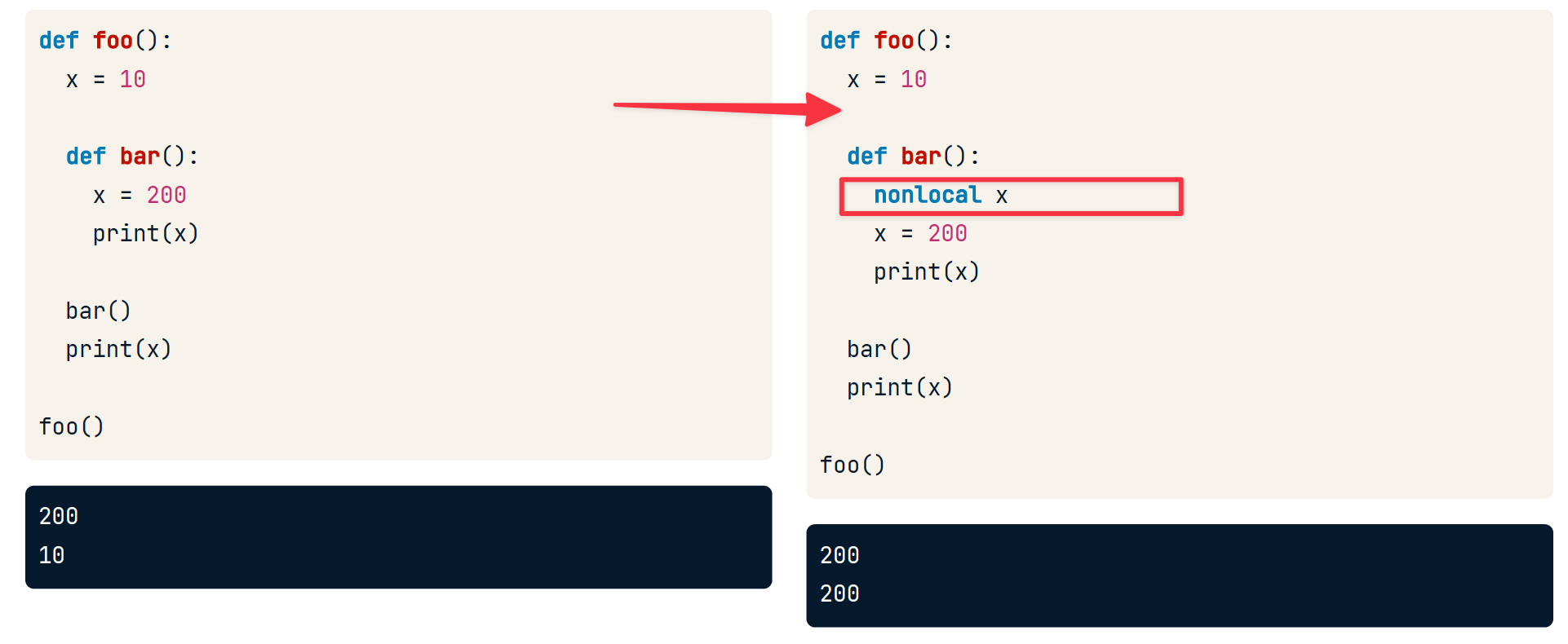
前面介绍了函数中可以创建子函数,然而子函数只能读取父函数的变量,并不能写。
nonlocal 关键字作用类似于global,是
在函数内声明一个新的变量,并且使该变量在其子函数内可读可写
Closures
作用是 Attaching nonlocal variables to nested functions
思考子函数 离开了父函数 被传递给一个新的引用后,子函数 需要的读的父函数变量怎么获取?
答案就是 传递时,会将函数需要的 父函数变量 复制一份,放到 返回的子函数的__closure__里面。
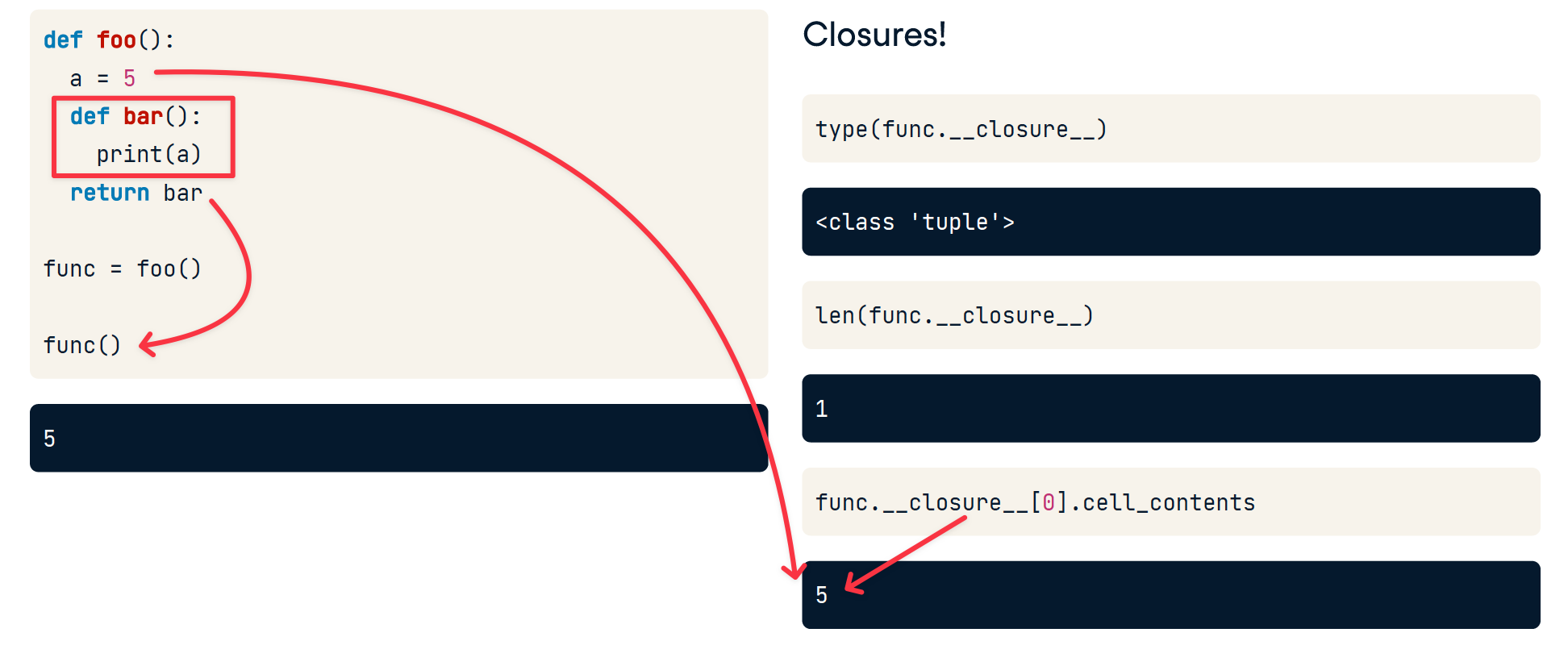
这里有一点需要注意的是每一次将返回一个新的子函数object,而不是共享一个子函数object
因此__closure__元组中的元素复制后就不会改变了。
删除变量不影响:
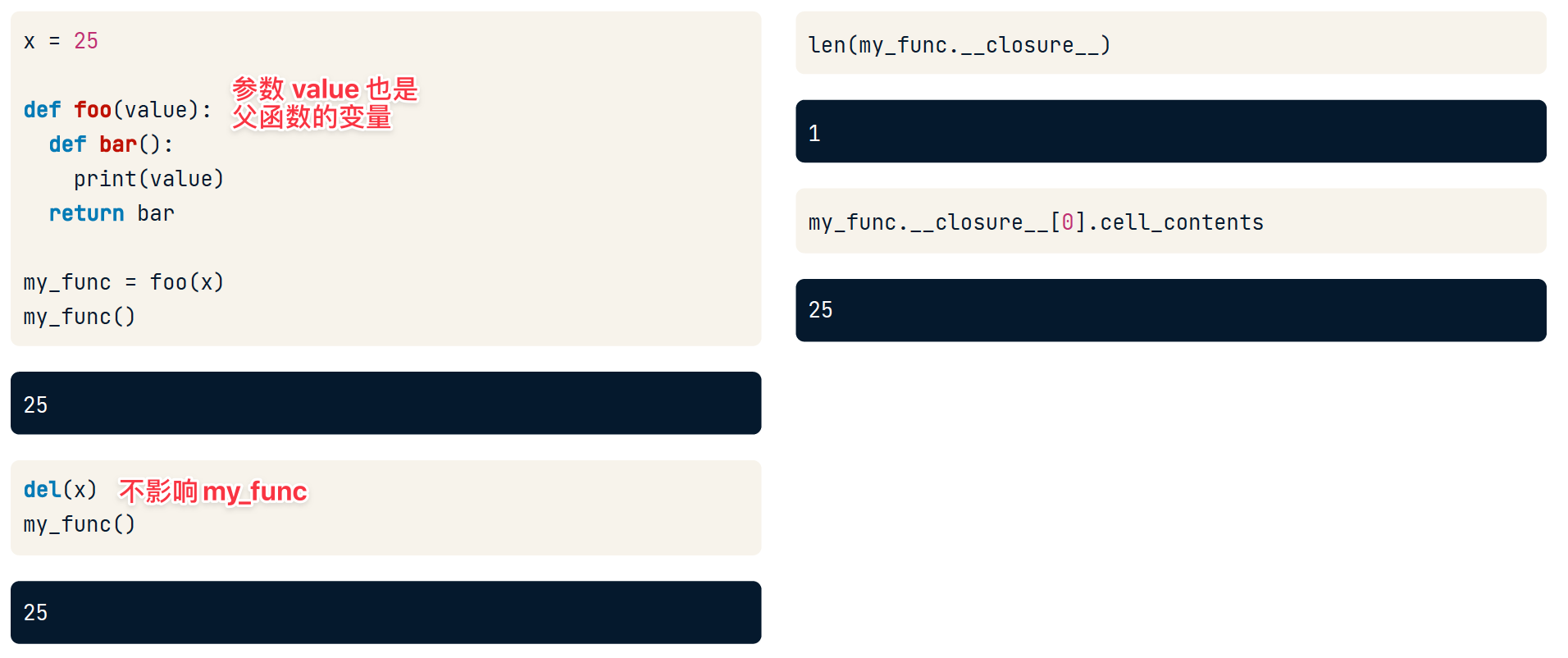
修改变量不影响:

Decorators
首先明确一点,Java注解(Annotation) 和 Python的装饰器(Decorators)不是一个东西。Java也有Decorators。
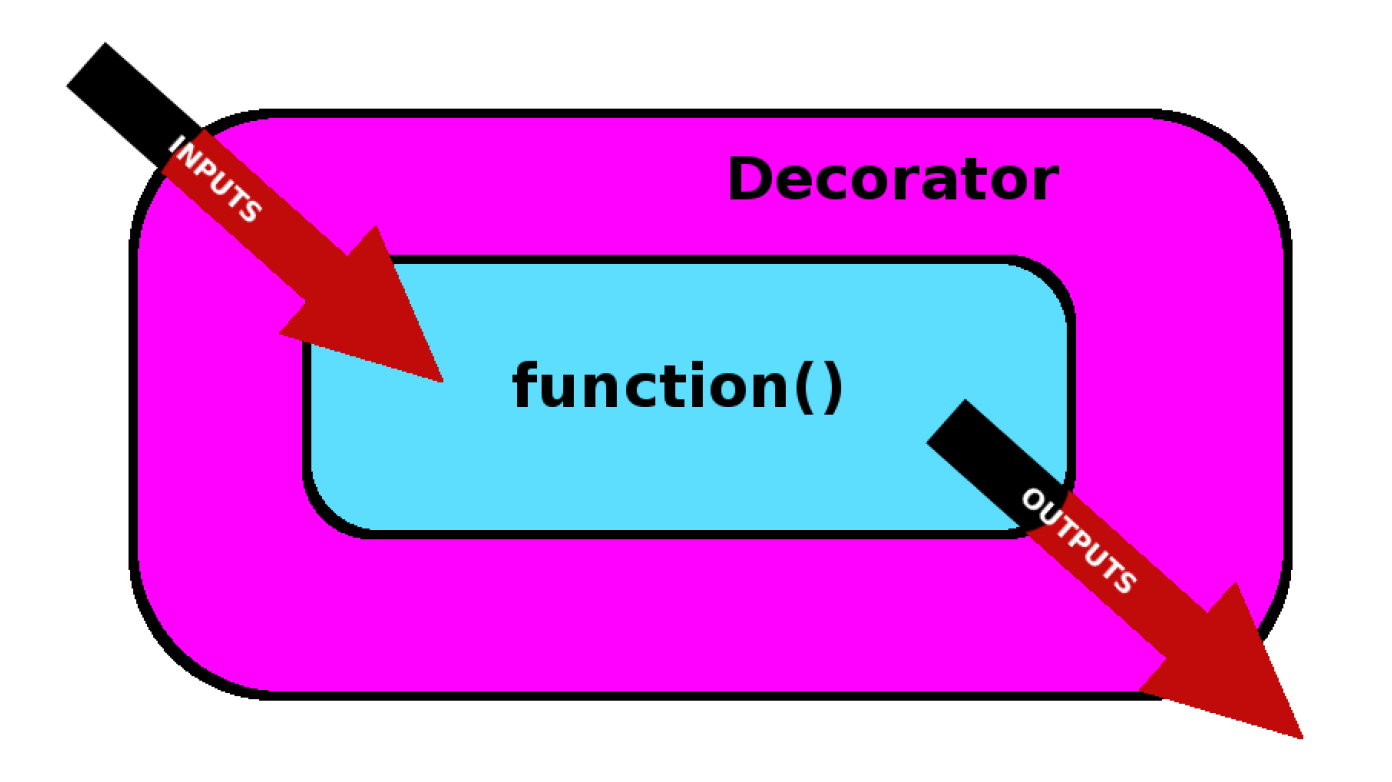
Decorators 的功能总的来说就是劫持函数并修改其功能,实质是用一个新的函数把旧的函数进行一些修改后包装起来。
- 修改输入
- 修改输出
- 改变函数本身的行为
使用修饰器
@double_args
def multiply(a, b):
return a * b
multiply(1, 5)
20
创建修饰器
修饰器本身就是一个函数,以目标函数为参数,修改目标函数,之后把修改好的目标函数传传递给原引用。
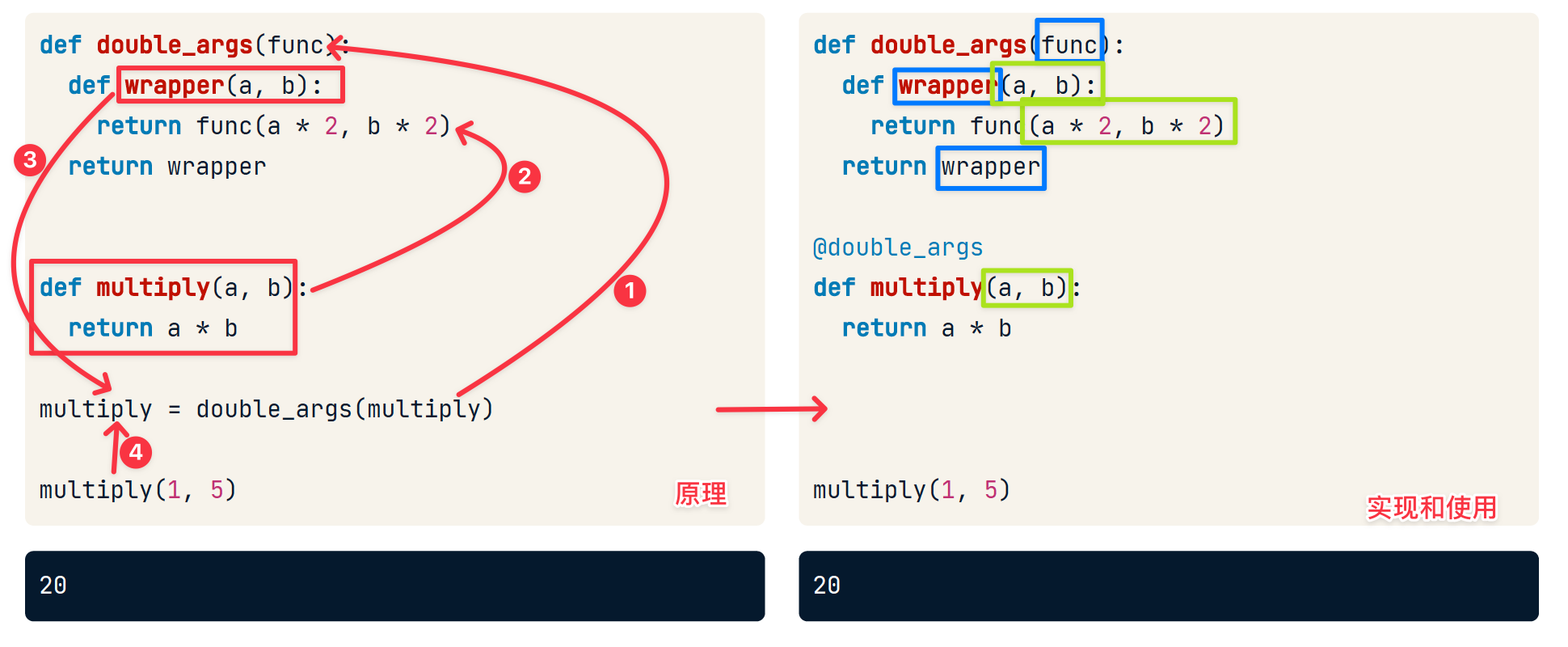
在创建修饰器的时候,需要注意的是应把修饰器函数的
- 接受唯一参数,即函数object
- 返回唯一参数,即函数object
- 返回的函数object的 参数个数以及类型顺序 应当和旧函数的 参数个数以及类型顺序 相同。
示例1
def print_before_and_after(func):
def wrapper(*args):
print('Before {}'.format(func.__name__))
# Call the function being decorated with *args
func(*args)
print('After {}'.format(func.__name__))
# Return the nested function
return wrapper
@print_before_and_after
def multiply(a, b):
print(a * b)
multiply(5, 10)
Before multiply
50
After multiply
示例2
def counter(func):
def wrapper(*args, **kwargs):
wrapper.count += 1
# Call the function being decorated and return the result
return func(*args, **kwargs)
wrapper.count = 0
# Return the new decorated function
return wrapper
# Decorate foo() with the counter() decorator
@counter
def foo():
print('calling foo()')
foo()
foo()
print('foo() was called {} times.'.format(foo.count))
calling foo()
calling foo()
foo() was called 2 times.
functools.wraps
由于被修饰后,原有的metadata将被包装而无法访问。
__name__:函数的名称__defaults__:函数的默认参数__doc__:函数的注释
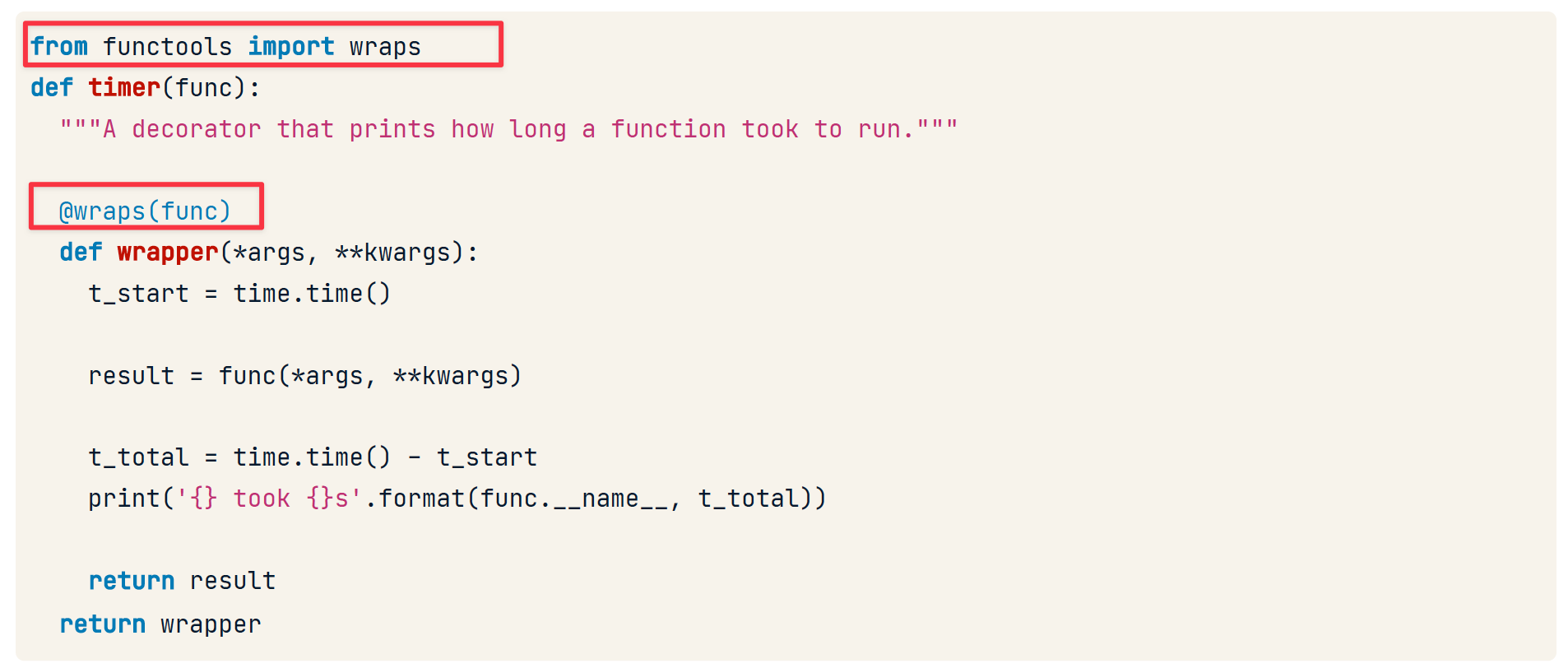
给子函数wrapper添加修饰器即可解决这个问题。这样新函数的所有metadata将会赋值包装前函数的元数据。
此外,加上这个修饰器后支持访问包装前的函数。使用 __wrapped__

Decorators Application
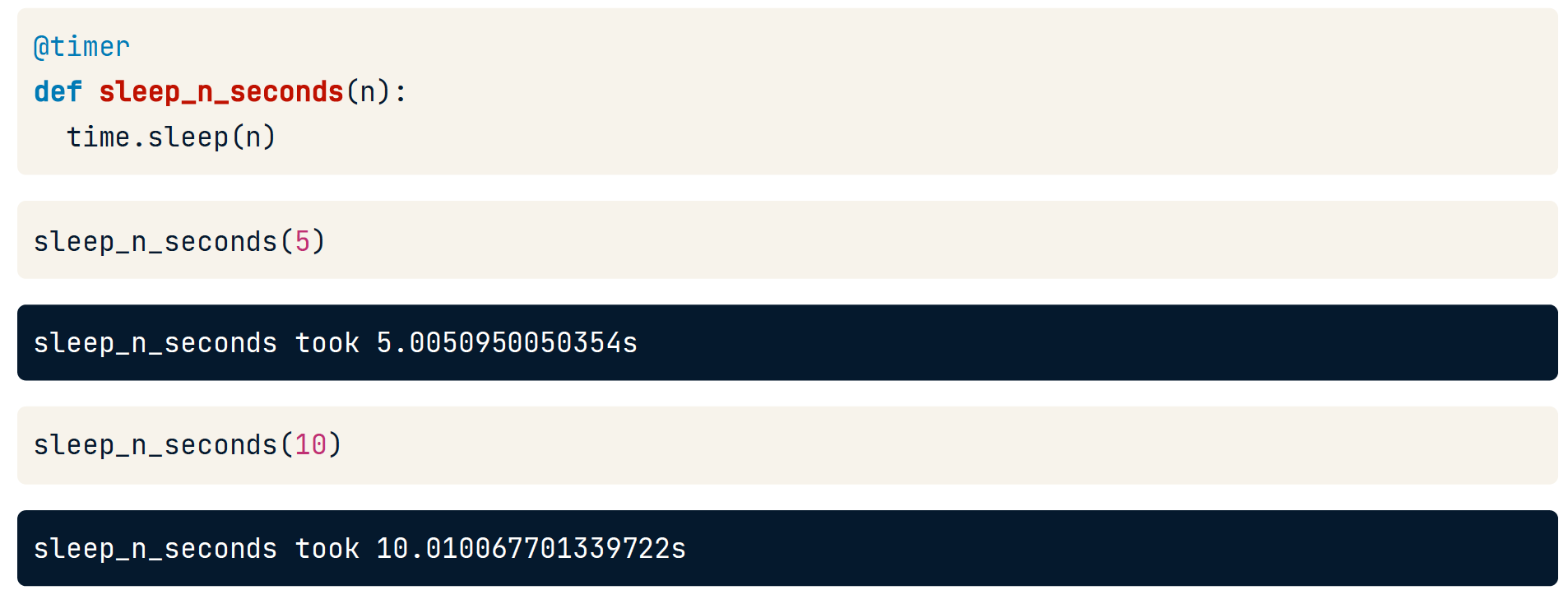
@timer
import time
def timer(func):
"""A decorator that prints how long a function took to run."""
# Define the wrapper function to return.
def wrapper(*args, **kwargs):
# When wrapper() is called, get the current time.
t_start = time.time()
# Call the decorated function and store the result.
result = func(*args, **kwargs)
# Get the total time it took to run, and print it.
t_total = time.time() - t_start
print('{} took {}s'.format(func.__name__, t_total))
return result
return wrapper
@memoize
def memoize(func):
"""Store the results of the decorated function for fast lookup
"""
# Store results in a dict that maps arguments to results
cache = {}
# Define the wrapper function to return.
def wrapper(*args, **kwargs):
# If these arguments haven't been seen before,
if (args, kwargs) not in cache:
# Call func() and store the result.
cache[(args, kwargs)] = func(*args, **kwargs)
# 注意如果cache中存在,则直接跳过了中间步骤而直接return
return cache[(args, kwargs)]
return wrapper

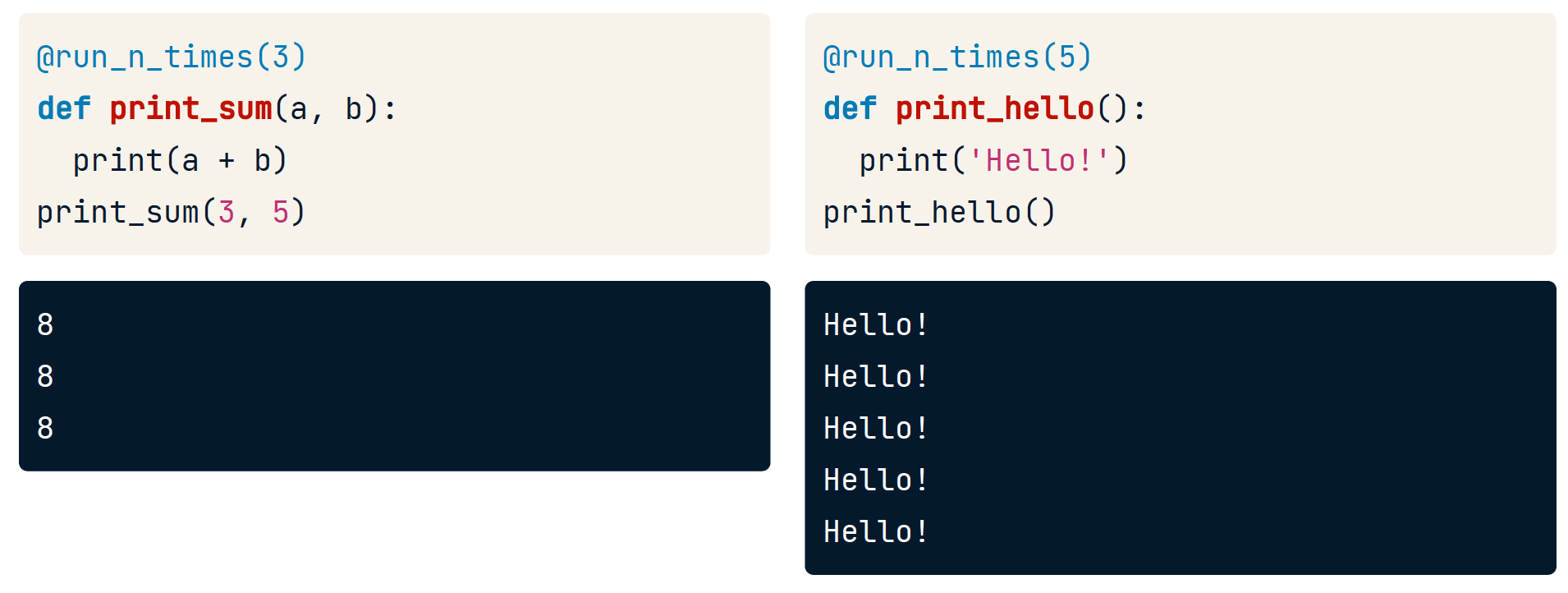
Decorators with args
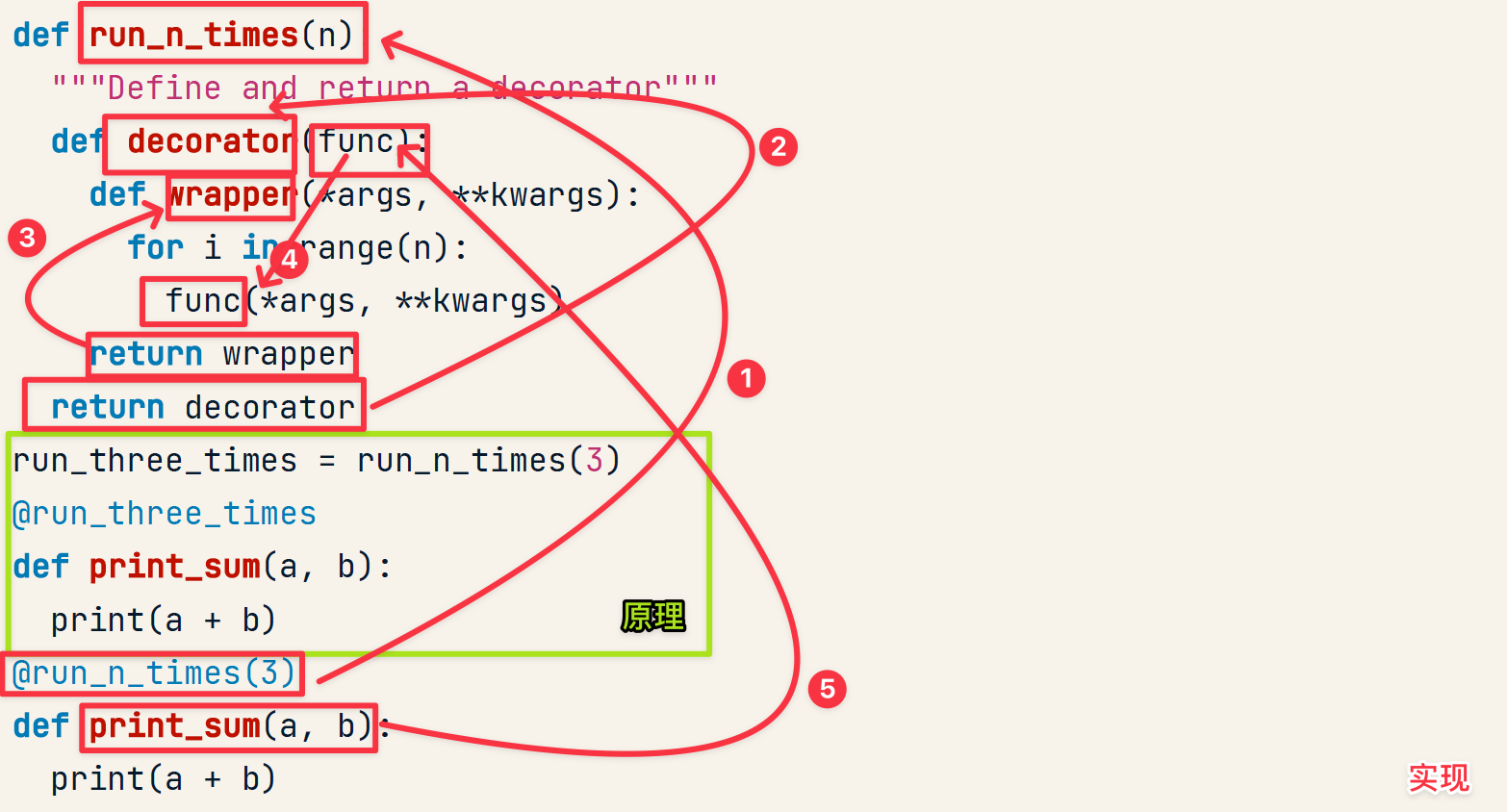
run_n_times()
实现
不妨当做对旧的函数进行两次包装...
@timeout()
def timeout(n_seconds):
def decorator(func):
@wraps(func)
def wrapper(*args, **kwargs):
# Set an alarm for n seconds
signal.alarm(n_seconds)
try:
# Call the decorated func
return func(*args, **kwargs)
finally:
# Cancel alarm
signal.alarm(0)
return wrapper
return decorator

@tag(*tags)
给某物打标签意味着你给该物打了一个或多个字符串,作为标签。例如,我们经常给电子邮件或照片打上标签,这样我们以后就可以搜索它们了。你决定写一个装饰器,让你用一个任意的标签列表来标记你的函数。你可以将这些标签用于许多事情。
def tag(*tags):
# Define a new decorator, named "decorator", to return
def decorator(func):
# Ensure the decorated function keeps its metadata
@wraps(func)
def wrapper(*args, **kwargs):
# Call the function being decorated and return the result
return func(*args, **kwargs)
wrapper.tags = tags
return wrapper
# Return the new decorator
return decorator
@tag('test', 'this is a tag')
def foo():
pass
print(foo.tags)
('test', 'this is a tag')
@returns()
def returns(return_type):
# Complete the returns() decorator
def decorator(func):
def wrapper(*args, **kwargs):
result = func(*args, **kwargs)
assert type(result) == return_type
return result
return wrapper
return decorator
@returns(dict)
def foo(value):
return value
try:
print(foo([1,2,3]))
except AssertionError:
print('foo() did not return a dict!')
foo() did not return a dict!