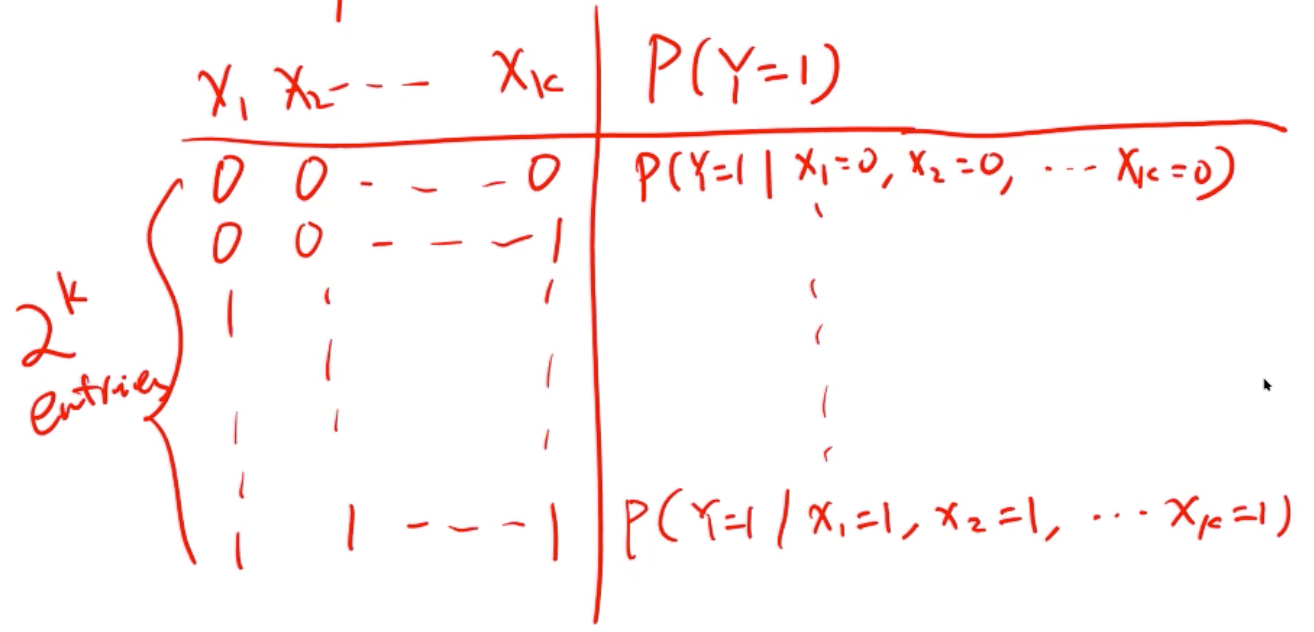Bayesian Network
Bayesian Networks
将多个因子联系起来。
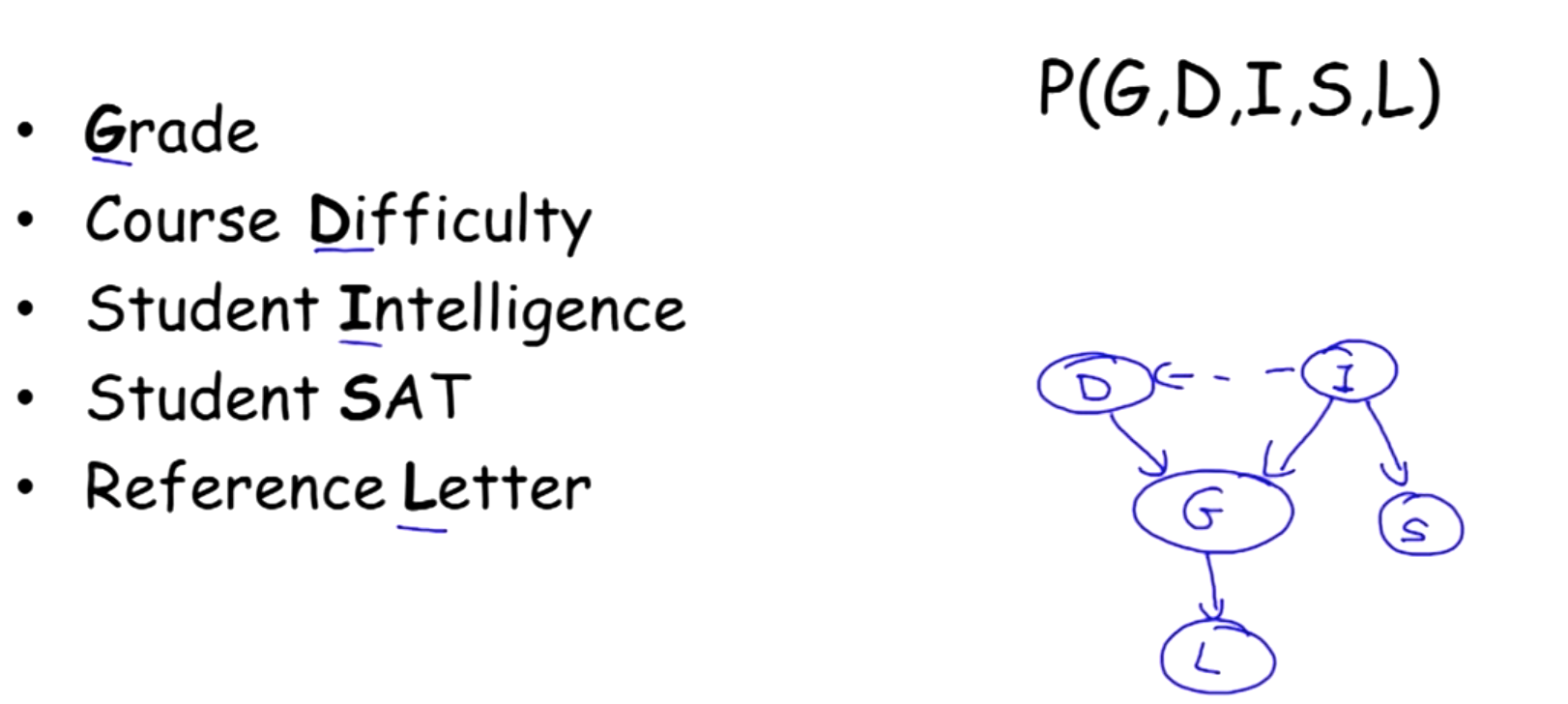
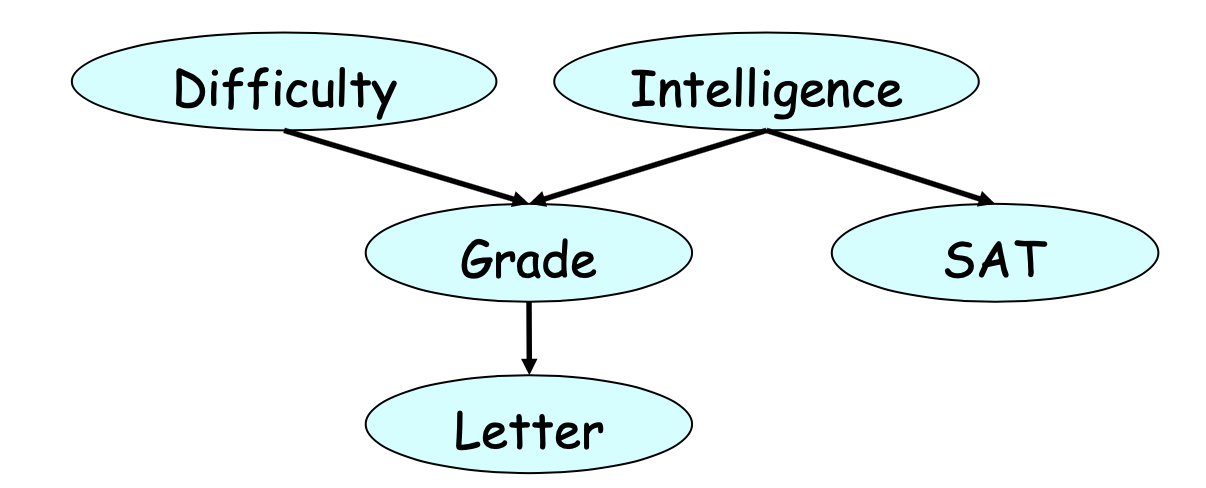
下图展示的就是一个参数化的贝叶斯网络。
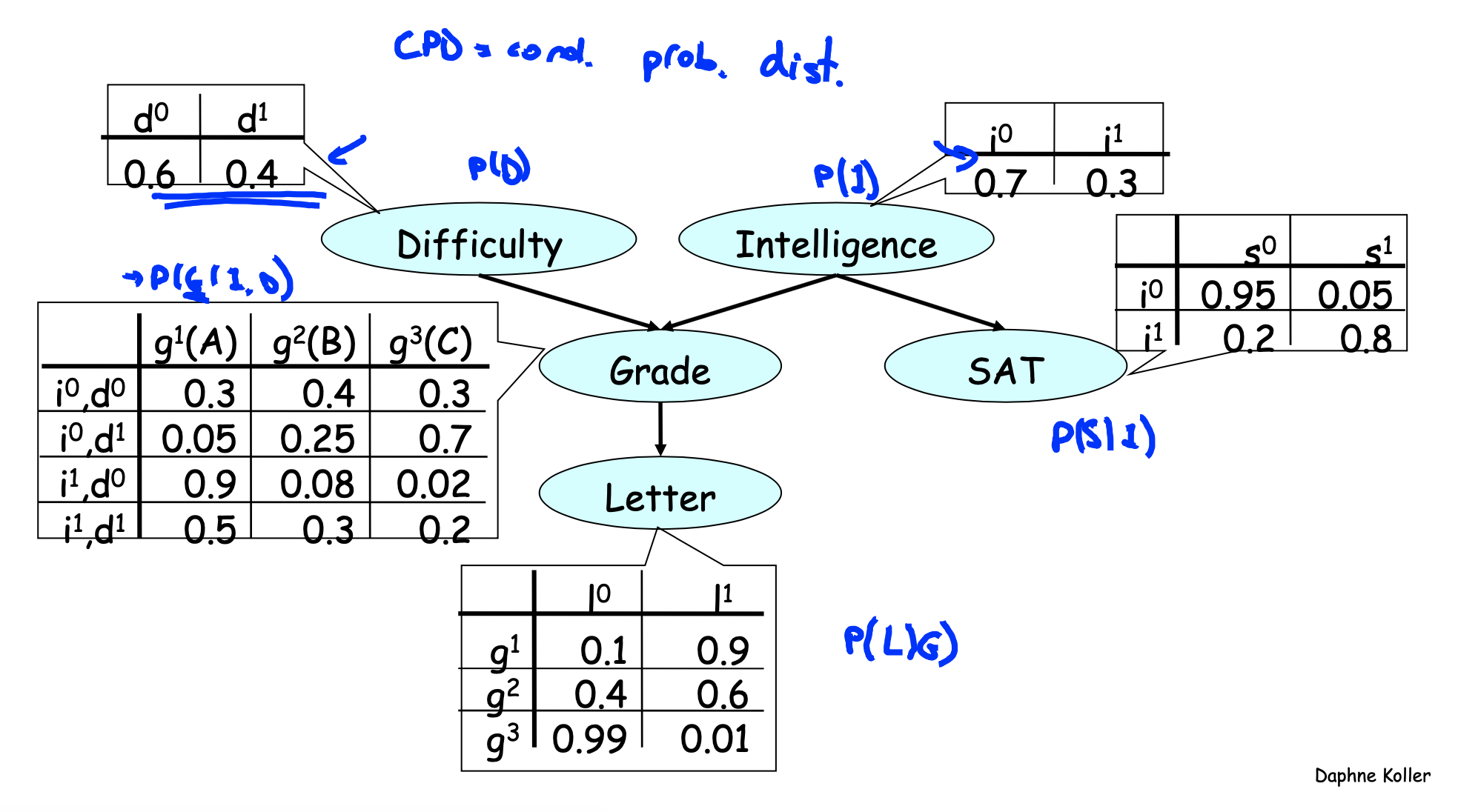 1672818055475.png
1672818055475.png后续将了解如何让从贝叶斯网络得到联合概率分布。
We can directly apply the chain rule for Bayesian networks here. This comes from the standard chain rule of probability, which states that
P(D,I,G,S,L)=P(D)P(I∣D)P(G∣D,I)P(S∣D,I,G)P(L∣D,I,G,S)
贝叶斯网络
A Bayesian network is:
- A directed acyclic graph「有向无环图」 (DAG)G whose nodes represent the random variables X1,....Xn
- For each node Xi, a CPD P(Xi∣ParG(Xi))
- The BN represents a joint distribution
Chain Rule
简单的说,就是把各个 CPD 乘起来。
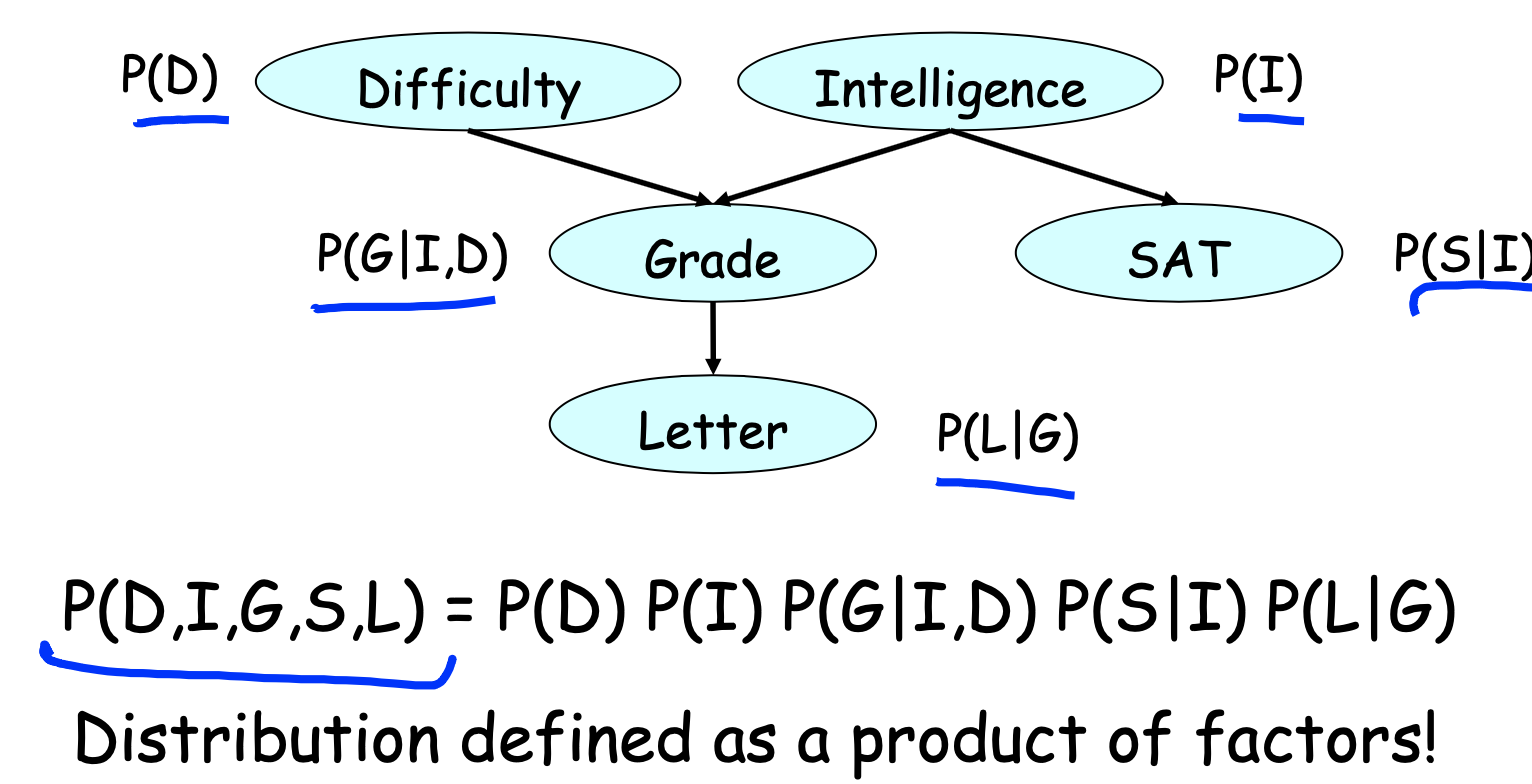
这种情况下,我们得到一个scope = 5 的因子。
建立贝叶斯网络
- 选择随机变量
- 选择顺序(最好是从根到子)
- 当有变量剩下的时候
- Add node 𝑋𝑖 to the BN
- Set parents of 𝑋𝑖 to the minimal subset such that 𝑋𝑖 is conditionally independent from non-parent nodes preceding i, given its parents.
- Define 𝑃 ( 𝑋𝑖|𝑝𝑎𝑟𝑒𝑛𝑡(𝑋𝑖) ) CPT
CPT是什么
全称 Conditional Probabilities Table
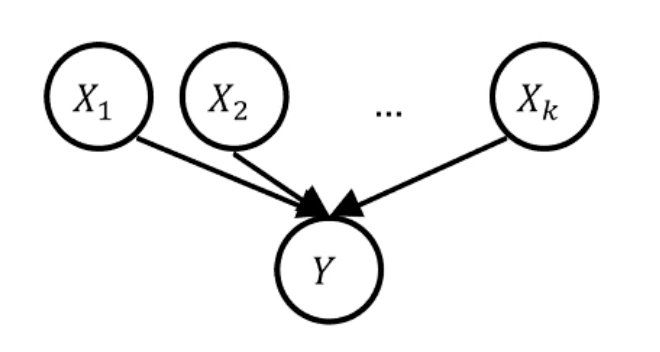
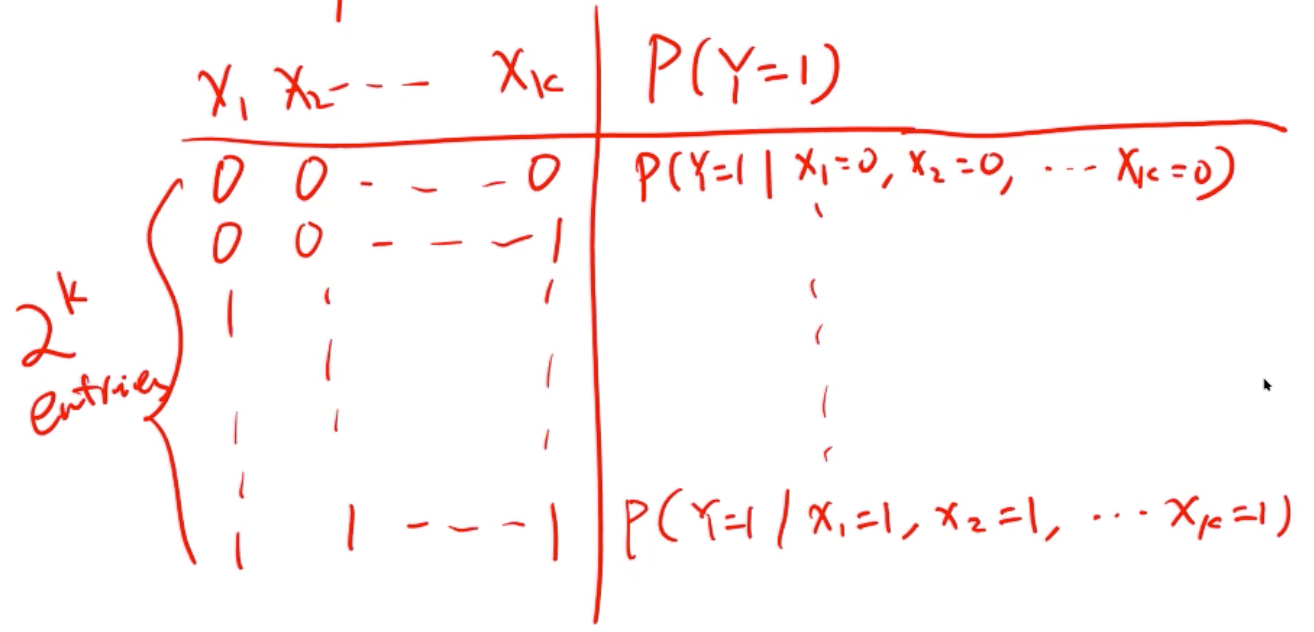
Noisy-or
基于 Y 的 Parent 预测 P(Y = 1 | Parent)

由 P(Y=0∣x……xk)=1−OR(x1…xk) 和 OR(x1⋯xk)={10 if any xi=1 otherwise ,可得
P(Y=0∣x1⋯xk)=i=1∏k(1−pi)xi
P(Y=1∣x1⋯xk)=1−i=1∏k(1−pi)xi
其中 xi = 0 或者 xi = 1
例题
Let P(Y=1∣X1=0,…,Xi=1,Xj=1,…,Xk=0)=31 and pi=51,what is pj ?
1−(1−51)(1−pj)=31
Active Trails
When can X influence y?

When can X influence Y Given evidence about Z?
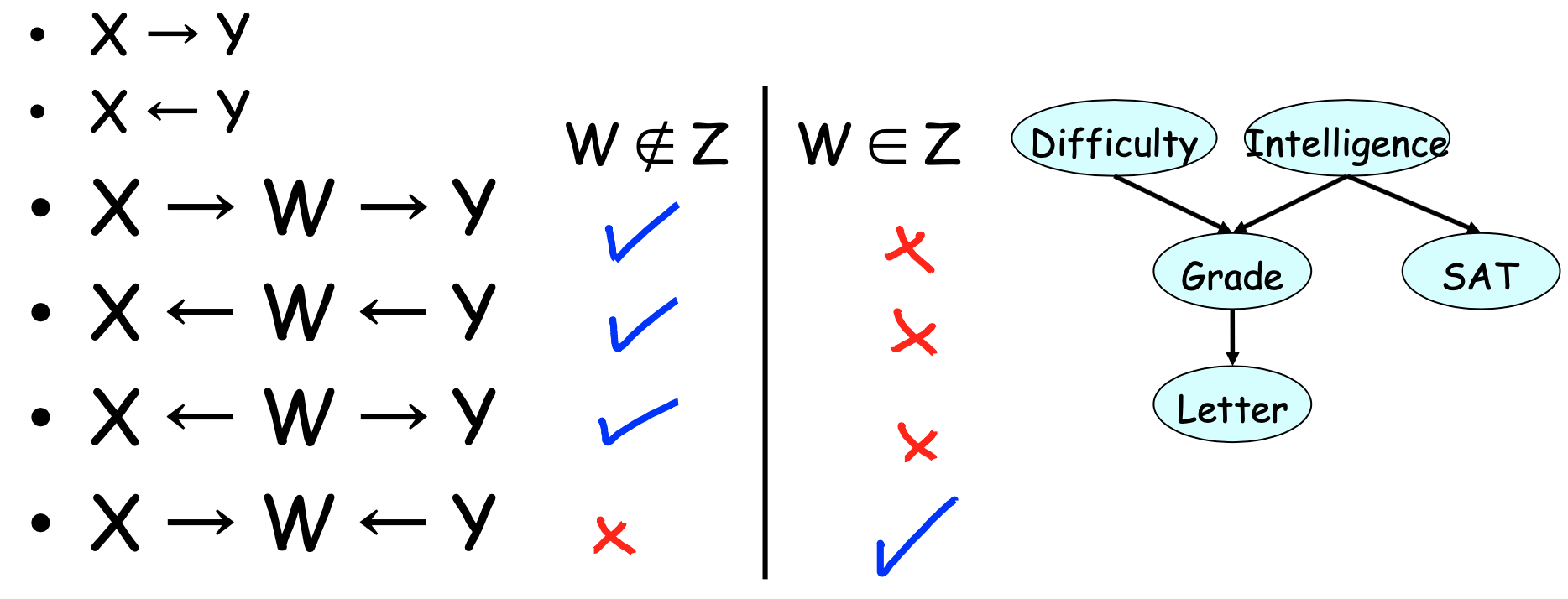

A trail X1 - ... - Xn is active given Z if:
- If or any v-structure Xi-1 → Xi ← Xi+1 we have that Xi or one of its descendants ∈Z
- no other Xi is in Z
条件独立
When is X conditionally independent of Y given E(evidence)?
- P(X,Y∣E)=P(X∣E)P(Y∣E)
- P(Y∣X,E)=P(Y∣E)
- P(X∣Y,E)=P(X∣E)
提示
Theorem: P(X,Y∣E)=P(X∣E)P(Y∣E) if and only if every UNDIRECTED path from a node in X to a node in Y is "d-separated" ("blocked") by E.