Penetration Testing
大约 5 分钟
Penetration Testing
渗透测试
Overview of Security Assessments
- Vulnerability「漏洞」 Assessments, Penetration Testing, Security Audits
- High-level Concept/Architecture
- Blackbox: (can only do) Crawling, Fuzzing, Output Evaluating
- Whitebox: Source Code, Server Setting, etc. available for test/analysis
- “Greybox,” and Blackbox vs. Whitebox
- On actual usage, i.e., the tool -> Automated tools, but use them with human knowledge
SMTP Smuggling (2023)
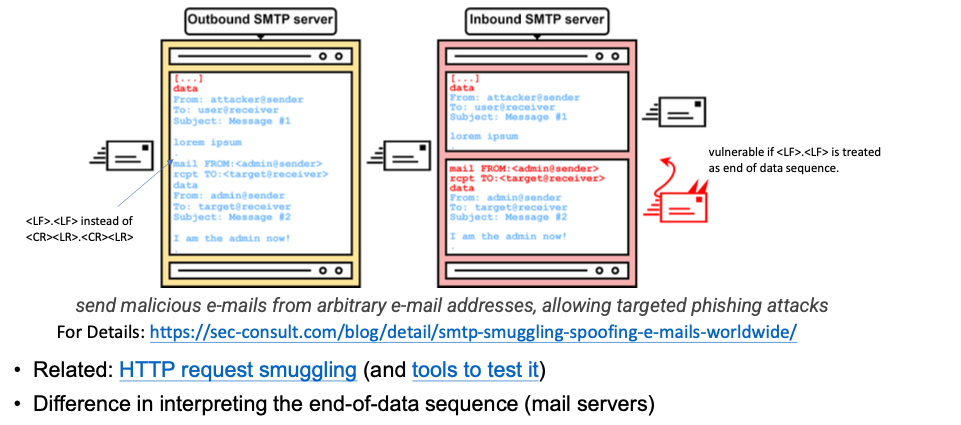
Difference in interpreting the end-of-data sequence (mail servers)
Different Kinds of Security Assessments
- Vulnerability Assessments
- Penetration Testing
- Security Audits
Vulnerability Assessments
- Scan a network for known security weaknesses -》 To test system and network devices for exposure to common attacks
- Evaluate the system security against known vulnerabilities
Limitations
- Only can guarantee the system security state at a certain point in time
- Has to be performed regularly
- especially when some major software updates or security attacks reported
- The outcome quality highly depends on the quality of the tools used
Penetration Testing (PT)
- Penetration Testing (PT)
- Malicious attack try to steal information or damage the target system
- Simulated attack
- “Simulated attack” try to have some better understanding of the system
- Many tools and methods
- Finding known and possibly unknown vulnerabilities
Security Audit
Auditing is on a broad scope, not just confined「confined」 to the code
- Infrastructure, Network
- Software, Hardware
- Policy, Procedure, Administrations, etc.
Not to focus on some specific technical problems
Evaluate the security level of the whole (collection of) system, an organization, or an ecosystem / some bigger context
Laws and Regulatory requirement:
- Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard (PCI DSS) compliance -> Protect the clients' private financial data
- HIPAA (Health Insurance Portability & Accountability Act)
- e.g., the data privacy of electronic medical records (EMR)
- EMR are made accessible to some healthcare personnel, but not others
- It is beyond the security of some code, or the use of encryption, etc.
- GDPR compliance (processing of personal data), …
Brief Summary of the Differences
- Vulnerability Assessments
- Check if a system has certain vulnerabilities + risk assessment
- The system may still suffer from unknown vulnerabilities
- Penetration Testing
- Check if a system is secure when under attacks (by professionals)
- Try to discover “unknown” vulnerabilities, e.g., not in the checklist
- But, of course, passing the PT does not mean there are no unknown bugs
- Security Audits
- Check if a system follows certain regulations
- Auditing can only reduce the risk, but no guarantees about security
Adversary Model
「对手模型」
Know your enemies (or some assumptions about them)
What do we know before testing?
- External testing: Based on all information that can be acquired publicly
- Internal testing: Tests will be performed from some internal network points
- Blackbox: “Zero-knowledge” testing
- “Greybox”: Partial-knowledge testing
- Whitebox: Complete-knowledge testing
Who do the testing?
Do-it-Yourself「DIY 自己动手进行测试。」
- Not recommended
- Limitations: Experiences, Effectiveness「有效性」, Cost, etc.
Outsourcing (hiring a tiger team)
- Recommended
- Need well-defined and reach some agreement
- Assumptions, resources, scope, testing locations/points, etc.
- Will not leak testing results to any third-party
- Still need the capability to understand the contract terms
How to do the testing?
- Manual testing, eg. Capture the Flag
- Automated testing: Cyber Grant Challenge
- A mixed approach for most of the time