Combinational Logic 2
Combinational Logic 2
logica gates
logica gates 「逻辑门」
Basic Logic Gates
- Each gate is defined in three ways: graphical symbol, algebraic notation, and truth table「图形符号,代数符号和真值表」
- Each gate has two inputs (NOT has only one) and one single output; it can be easily extended to multiple inputs.「每个门有两个输入(不只有一个)和一个单输出。它可以轻松扩展到多个输入。」
- note the different shapes, the “little bubble” for NOT gate「注意不同的形状,“非门”的“小气泡”」
- XOR is also very useful「异或 也 非常有用」
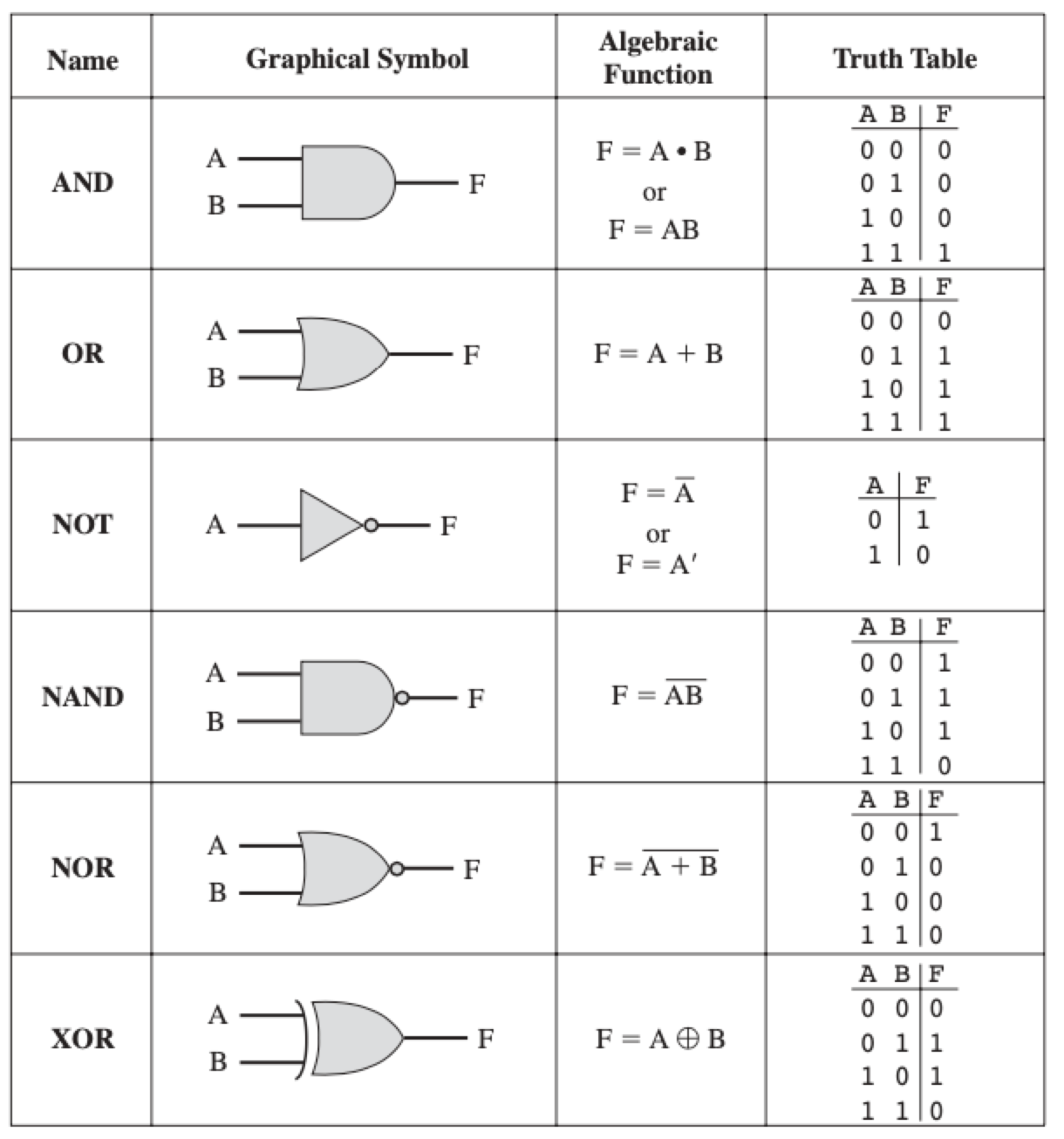
记忆:直的是且,弯的是或;XOR要A与B的信号不同时才行;
A gate is the fundamental building block of all digital logic circuits
- itself is a electronic circuit, producing an output signal that is a simple Boolean operation on its input signals「它本身是一个电子电路,产生一个输出信号,该输出信号对其输入信号进行简单的布尔运算」
- Gate delay: when one input value changes, the correct output signal appears almost instantaneously, delayed only by the propagation time of signals through the gate「门延迟:当一个输入值改变时,正确的输出信号几乎立即出现,仅延迟发生在通过门的传播时间」
Circuit
Interconnections of Gates — Circuit
Example: use NAND gate to implement NOT, AND, and OR
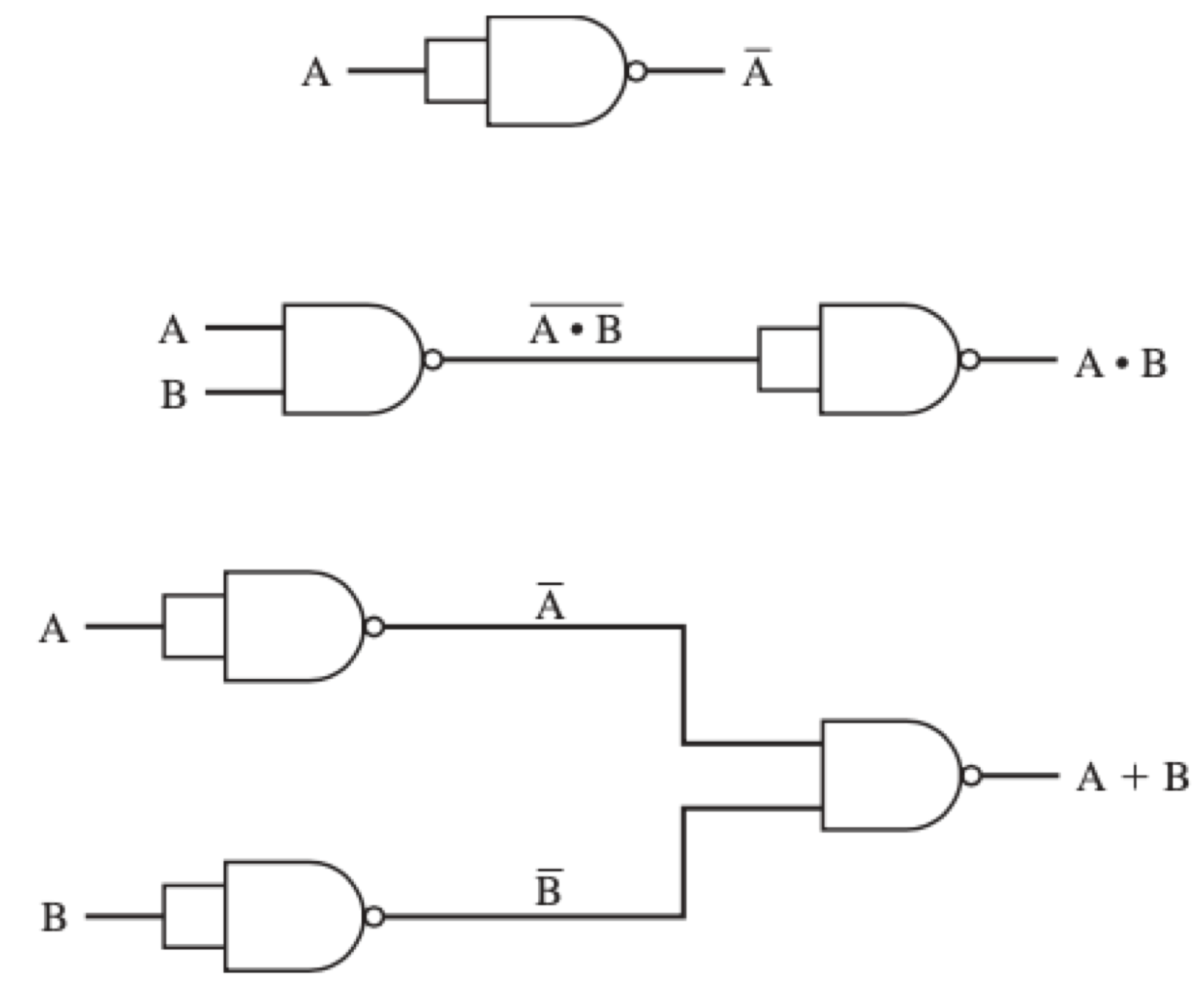
Representations
A circuit is a “larger gate”: multiple inputs and a single output
- switching function (logical expression) Z = f(A, B, C,…)
- circuit (graphical/symbolic representation)
- truth table
know how to translate among these three representations — useful for implementation
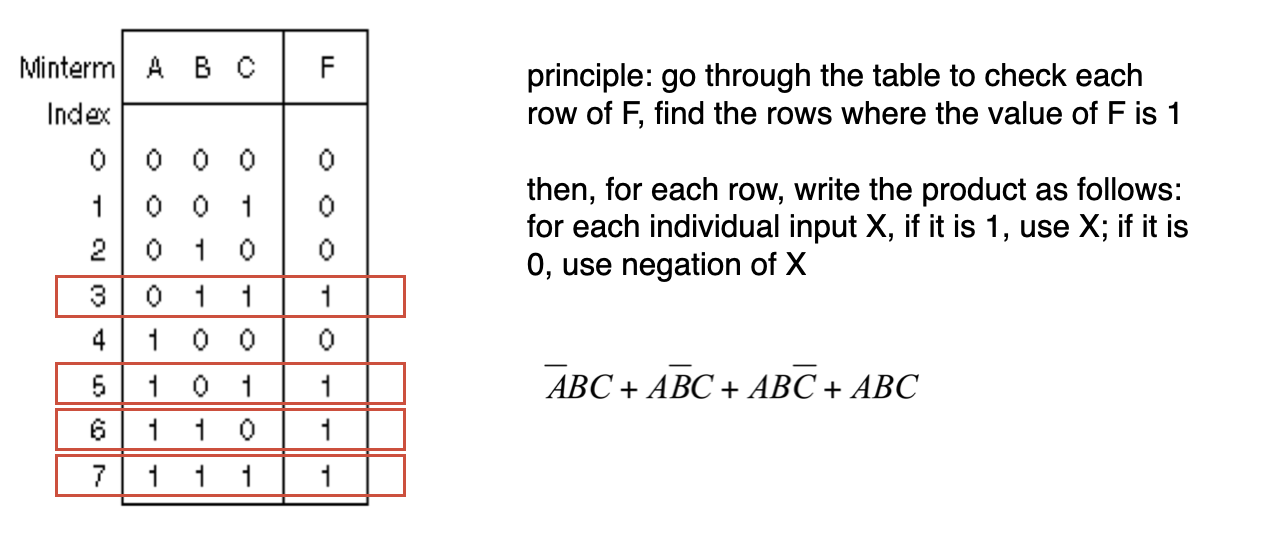
Example
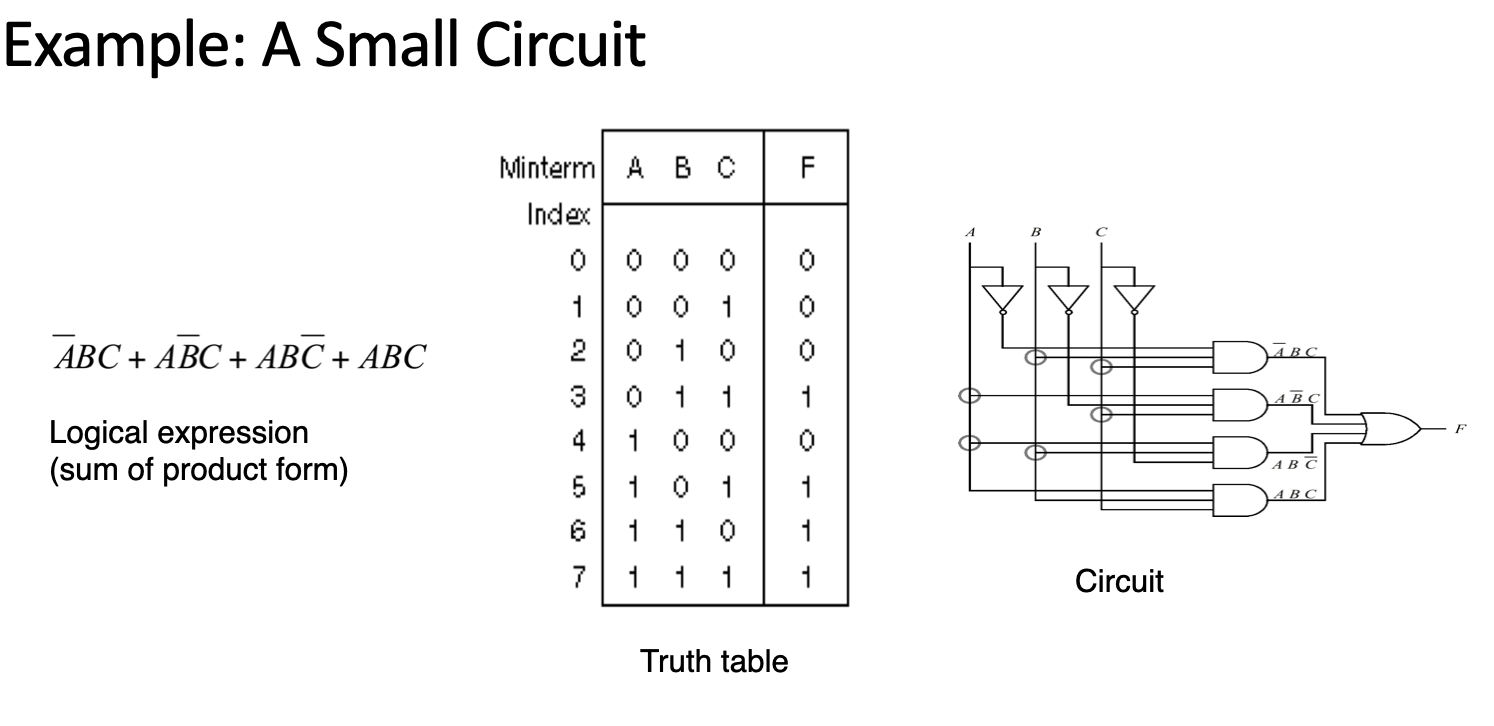
注:由表转SOP识式子,只需找到F为1的行。
Obtain the circuit
A very convenient way is to use “Sum of Product” (SOP) form of a logical expression**「SOP表示积的和」**
- it’s a sum of terms, where term is the product of inputs (or negation of inputs)「它是项的总和,其中项是输入的乘积(或输入的取反)」
- it’s easy to obtain the circuit from SOP
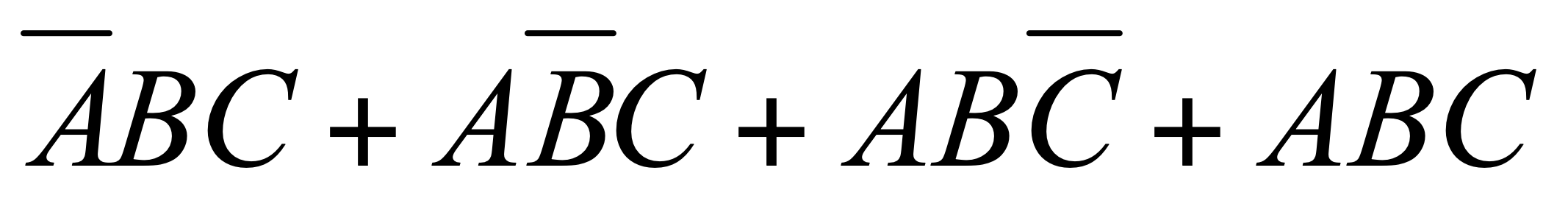
SOP to Circuit
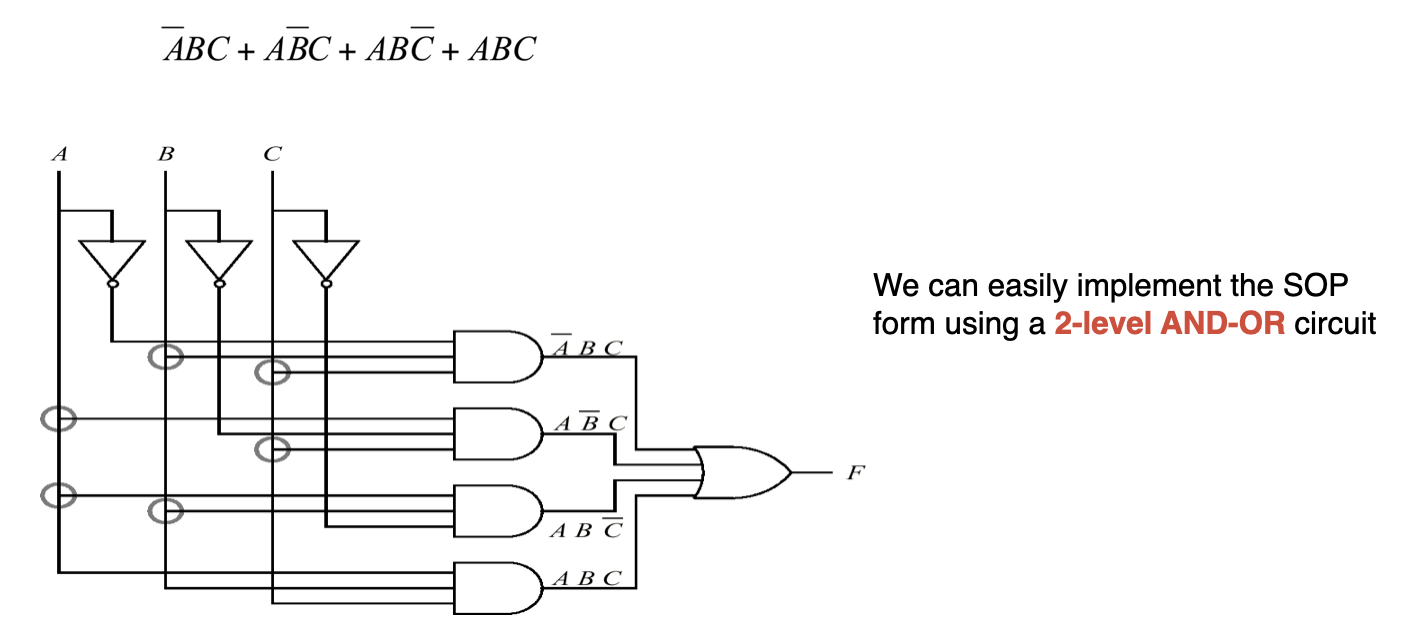
注:F前用或表示,前面在再用四个且表示;对于输入电路ABC,只需按照是否取反,接入即可。
POS to Circuit

Choose What?
- Intuition — for shorter expression「简短表达」
- less 1’s in F — use SOP
- less 0’s in F — use POS
- however, shorter expression is not the only consideration when designing circuits, also consider the types of gates available
Digital Components
Digital Components 「数字原件」
A digital component is a collection of gates that has a specific function
——think about function or method in high-level programming language
The design of digital circuits is often at the component level「组件级别」
- Digital component is also called Integrated Circuit「集成电路」/IC component「IC组件」
- important to know some commonly used「常用的」 digital component
Multiplexer (MUX)
N input to 1 output unit (N-to-1) MUX: choose one of the N inputs as the output depending on control signal「控制信号」 (also known as data selector「数据选择器」)「N个输入到1个输出单元(N-至-1)MUX:根据控制信号选择N个输入之一作为输出(也称为数据选择器)」

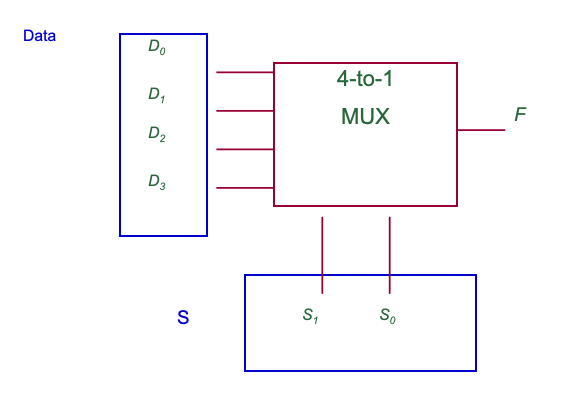
2^n number of input requires n number of selection controls
Note: the output value in the truth table is not 0/1, instead it is D「注意:真值表中的输出值不是0/1,而是D」
注:D是位组合
Implement
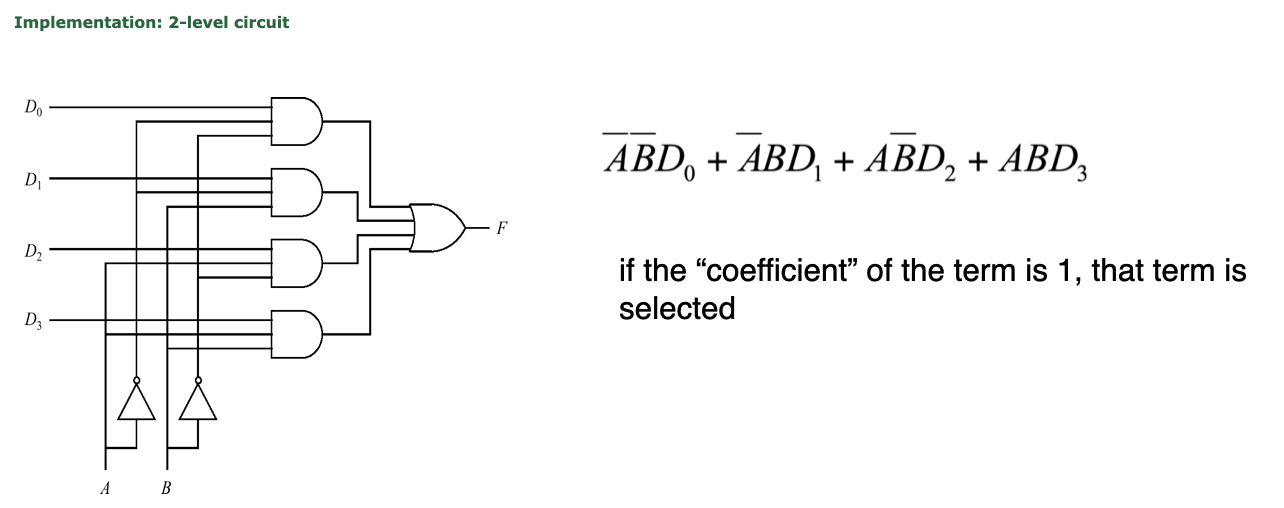
How can we implement this 4-to-1 MUX?
idea is similar to that of transforming a Truth table to SOP form
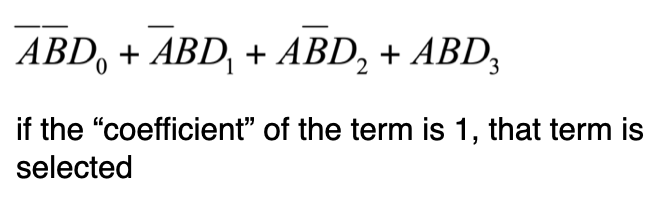
Applications
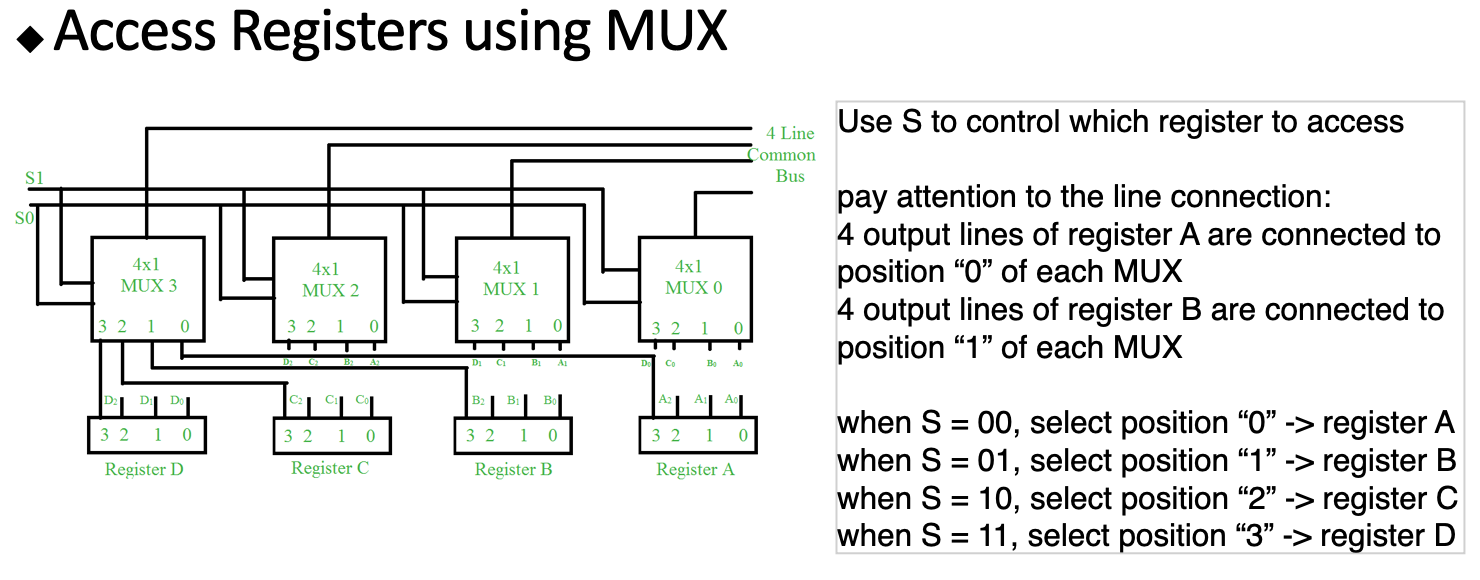
Main advantage:reduce the usage of wires — multiple input wires vs. control wires and one single output wire「减少电线的使用-多根输入线与控制线和一根单根输出线」
Example of application:remember Bus? (different data can travel over the same bus)
Demultiplexer (DEMUX)
- A Decoder with an Enabler「带启动器的解码器」
- less input (A,B); more output (F)
- an Enabler D
- when D = 0, all output = 0
- when D = 1, A,B control which output wire is “on”
Why it is called decoder: we use two bits A and B to encode four states (which output wire is on); this digital component will try to decode the input AB
when there is no Enabler D, DEMUX is a Decoder (n inputs, 2^n outputs)
「为何称为解码器:我们使用两位A和B来编码四个状态(输出线已打开);该数字组件将尝试解码输入AB
如果没有启动器D,则DEMUX是解码器(n个输入,2 ^ n个输出)」
注:结果是只有一F为1,其他均为0;
Application
- connect the source signal to multiple destinations, where each output wire is connected to one destination「将源信号连接到多个目的地,其中每条输出线都连接到一个目的地」
- the source signal (AB) decides which destination is “on”「源信号(AB)决定哪个目的地“打开”」
- Simple example: the output line can act as an Enabler for the destination machine「简单示例:输出行可以充当目标计算机的启动器」
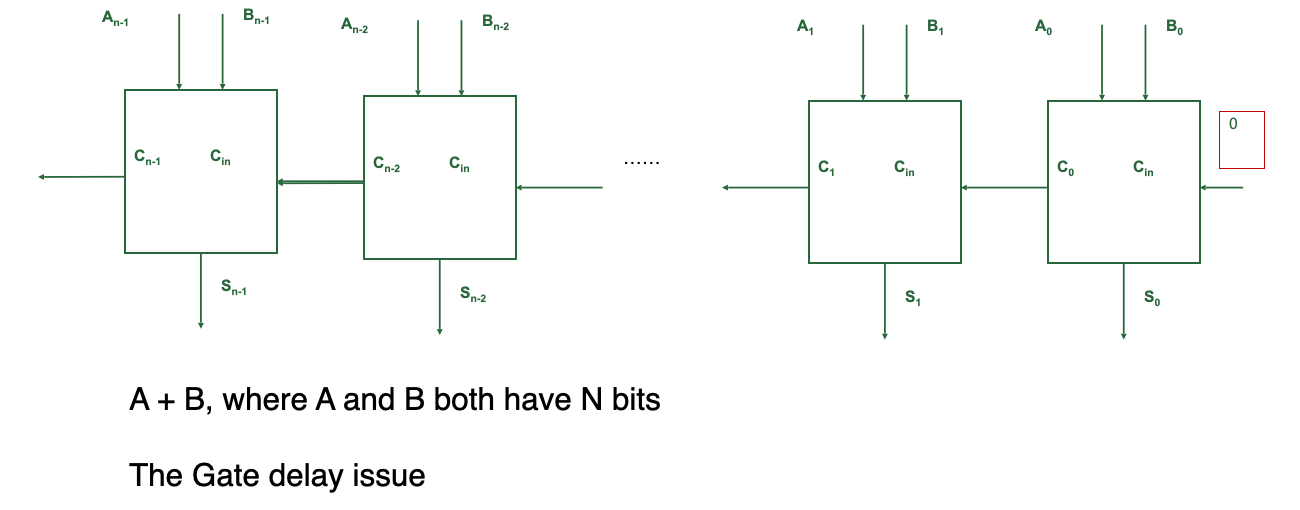
Binary Adder
One-bit Adder with Carry Input: the carry forward bit from the previous bit position「前一位的进位」
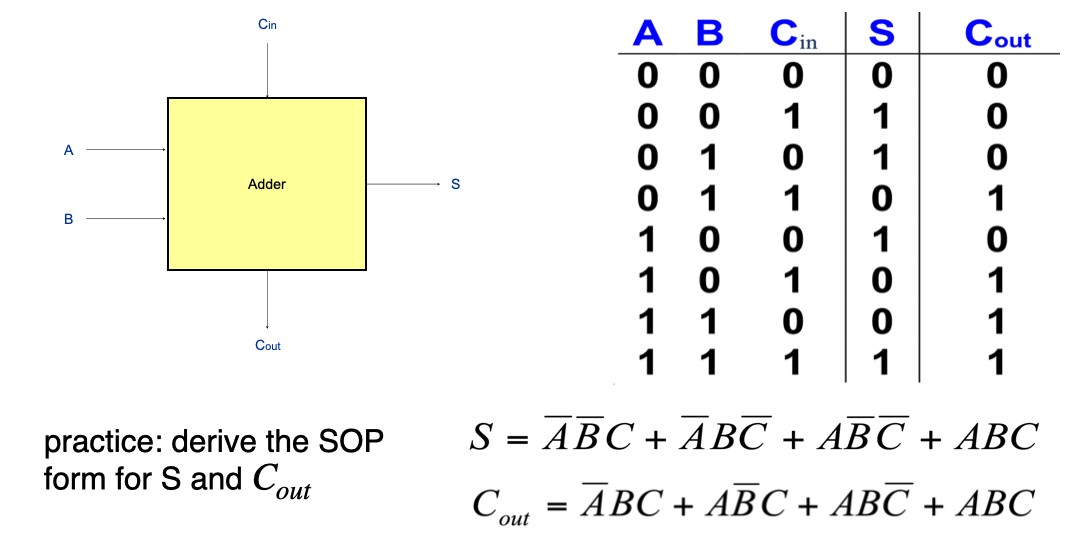
注:将A与B与C加和,结果的"十位" 放到 Cout,"个位"放到S;注意这里是二进制!