Combinational Logic 4
Combinational Logic 4
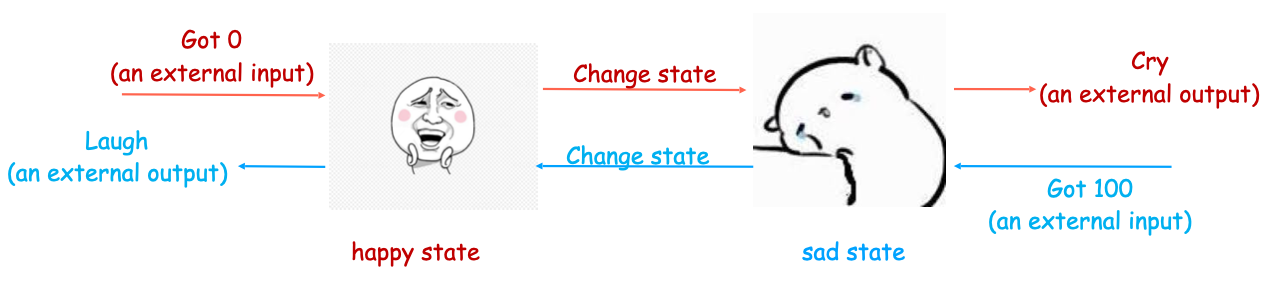
Finite State Machine (FSM)
Example:3-bit Synchronous Counter
- The counter will count through 000, 001, … , 111, then get back to 000
- Each count (e.g., 001) is a state of the counter (machine)
- The number of possible states is finite
This 3-bit Synchronous Counter is an example of Finite State Machine
Concept
FSM is an abstract model to describe real-world systems
- It uses states to represent the situations that the system is in
- It specifies「指定」 how the states of the system would change based on the external input, and how the system would produce external output accordingly 「它指定了系统状态如何根据外部输入进行更改,以及系统如何相应地产生外部输出」
- The 3-bit Synchronous Counter is a special case – it does not have external input and output「3位同步计数器是一种特殊情况–它没有外部输入和输出」
- However, the 3-bit Synchronous Counter did「确实」 demonstrate「演示」 an essential「重要」 part of FSM – the memory component to store the state「但是,3位同步计数器确实演示了FSM的重要部分–存储状态的内存组件」
Formal Model of FSM
FSM = (States, Inputs, Outputs, State Transition Function)
FSM = ( S, I, O, π)
- S: the finite set of states
- I: the finite set of inputs
- O: the finite set of outputs
- π: state transition function: define the relations among input, output, current state, next state「π:状态转换函数:定义输入,输出,当前状态,下一状态之间的关系」
Two important relations for FSM
- Next state = external input + current state (i.e., the next state depends on the current state and the external input)
- External output = external input + current state (note: not exactly as this; detailed later)
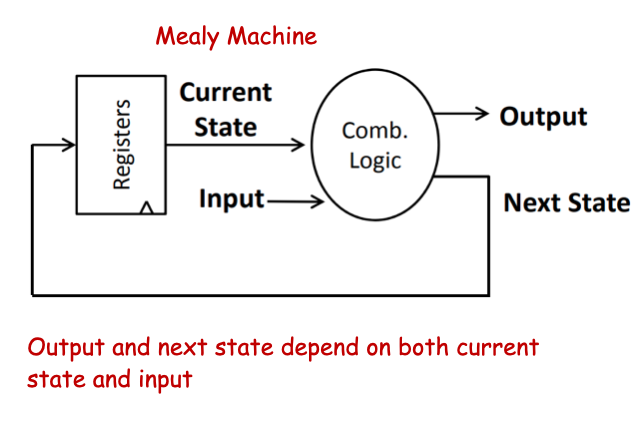
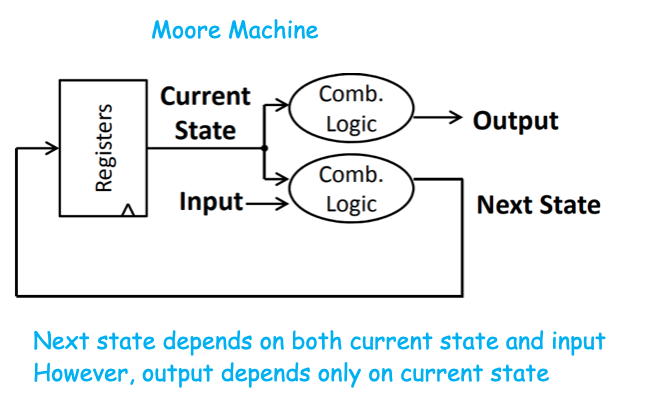
There are Two Sub-Models: Mealy Machine vs. Moore Machine
Mealy Machine
注:即输出结合input后再输出
Moore Machine
注:即结合input前输出
- combinational logic: relates the current state, external input and output, next state
- registers——memory compoennt: store the state of the machine
Represent
How to Represent FSM?There are two basic approaches
Key: represent the relations among current state, input and next state, output & Know how to transform between state diagram and state table
- State diagram
- State table
State Diagram
- Circles: represent states
- Labelled with「使用...标记」 S_k to denote「表示」 the state (or a binary encoding)「标记为S _ k表示状态(或二进制编码)」
- Directed arcs「有向弧」: represent the transitions between states
- Labelled with input/output for that state transition「标记有该状态转换的输入/输出」
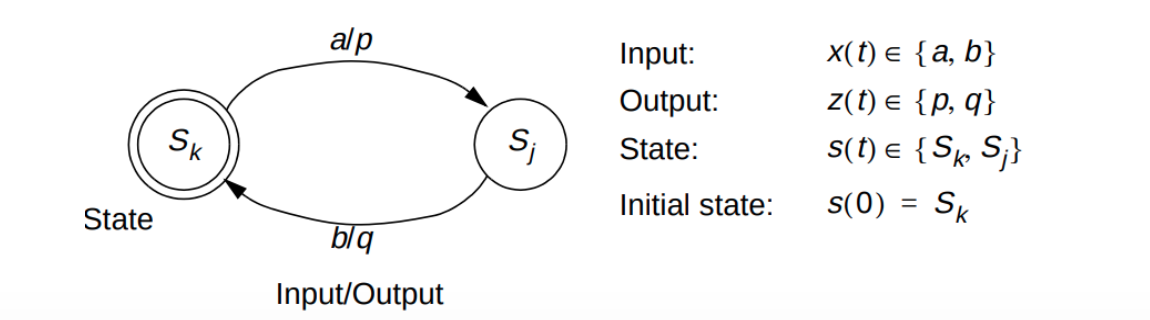
Two circles: initial states
Example: the current state is S_k, given an external input a, the state will transit to the next state S_j, and the external output is p
Encoding of states: we ususally use binary numbers to encode the states; for example, if there are four states: S_0 (00), S_1 (01), S_2(10), and S_3(11).
注:上图表示:在Sk状态,如果输入a,则会输出p,状态变成Sj。b/q同理。
Mealy machine and Moore machine can be labelled differently using State Diagram
- Mealy machine: label directed arcs with input/output for that state transition
- Moore machine: since output depends only on state, we can label directed arcs with input for that state transition, and label state circles with S_k/output
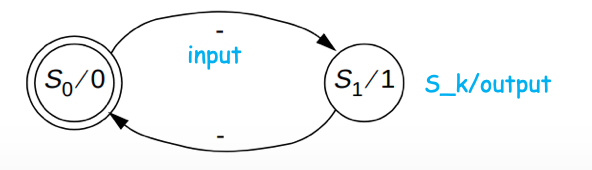
restrictions
Some restrictions on state diagram
- Time is discretized「离散化」: use clock signal to control the timming of the transitioning of states (synchronous!) -- we usually use time t and t+1 to denote the timing for the current state and next state「时间离散化:使用时钟信号控制状态转换的时间(同步!)-我们通常使用时间t和t + 1表示当前状态和下一个状态的时序」
- FSM can only be in one state at a time -- therefore, only in one state (or one circle) at a time「FSM一次只能处于一种状态-因此,一次只能处于一种状态(或一个圆圈)」
State diagram is a clear visualization of FSM; but it is not that convinient for computation – we use an alternative, which is state table
State Table
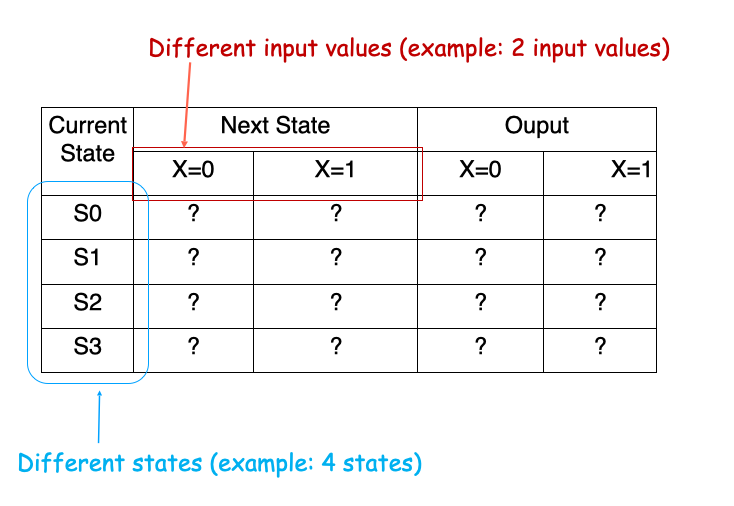
Example
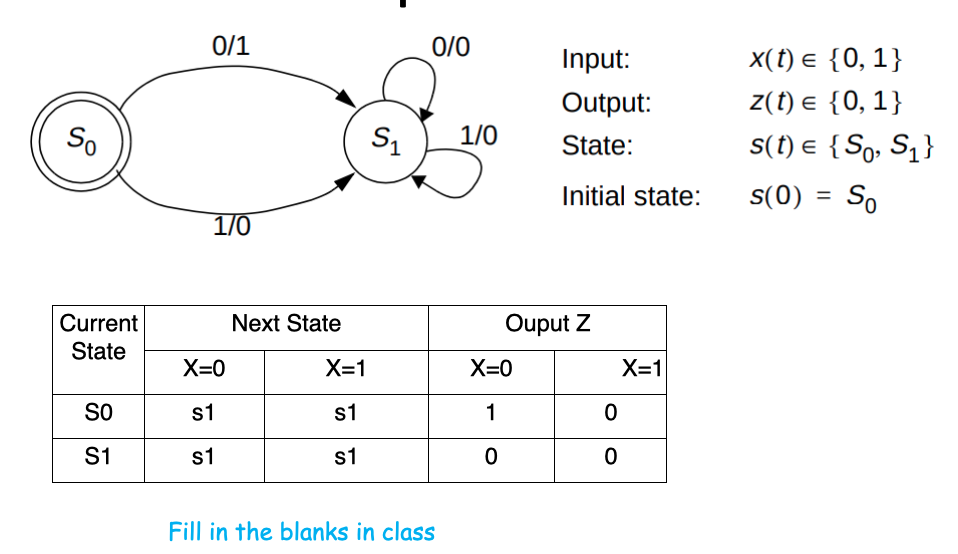
We know these tools to describe it, but what's the analytical task?
Analytical Task
The Essential Analytical Task for FSM is
- Given state diagram/state table, derive the functions that specify the relations among next state, output, current state, and input「给定状态图/状态表,导出指定下一个状态,输出,当前状态和输入之间的关系的函数」
- Next state = f (current state, input)
- Output = g (current state, input)
- The design of sequential circuits relies on the above two functions
Example: Pattern Detector
Design a machine that will detect a specific「特定的」 bit pattern「设计一台将检测特定位模式的机器」
- It receives bit stream
- It has one output Z: if the bit pattern appears in the bit stream, the output Z = 1; otherwise, Z = 0「它具有一个输出Z:如果位模式出现在位流中,则输出Z = 1;否则,输出Z = 1。否则,Z = 0」

Modelling the Problem
Modelling the Problem using FSM
We use the following states to model the possible situations that the machine is in (detect pattern 1101)
- S0: the initial state
- S1: the first desired symbol (1) is detected
- S2: the desired sub-pattern 11 is detected
- S3: the desired sub-pattern 110 is detected
Intuition: we want to record the situations that will lead to the target pattern 1101
States and States Transitions
States and States Transitions (pattern 1101)
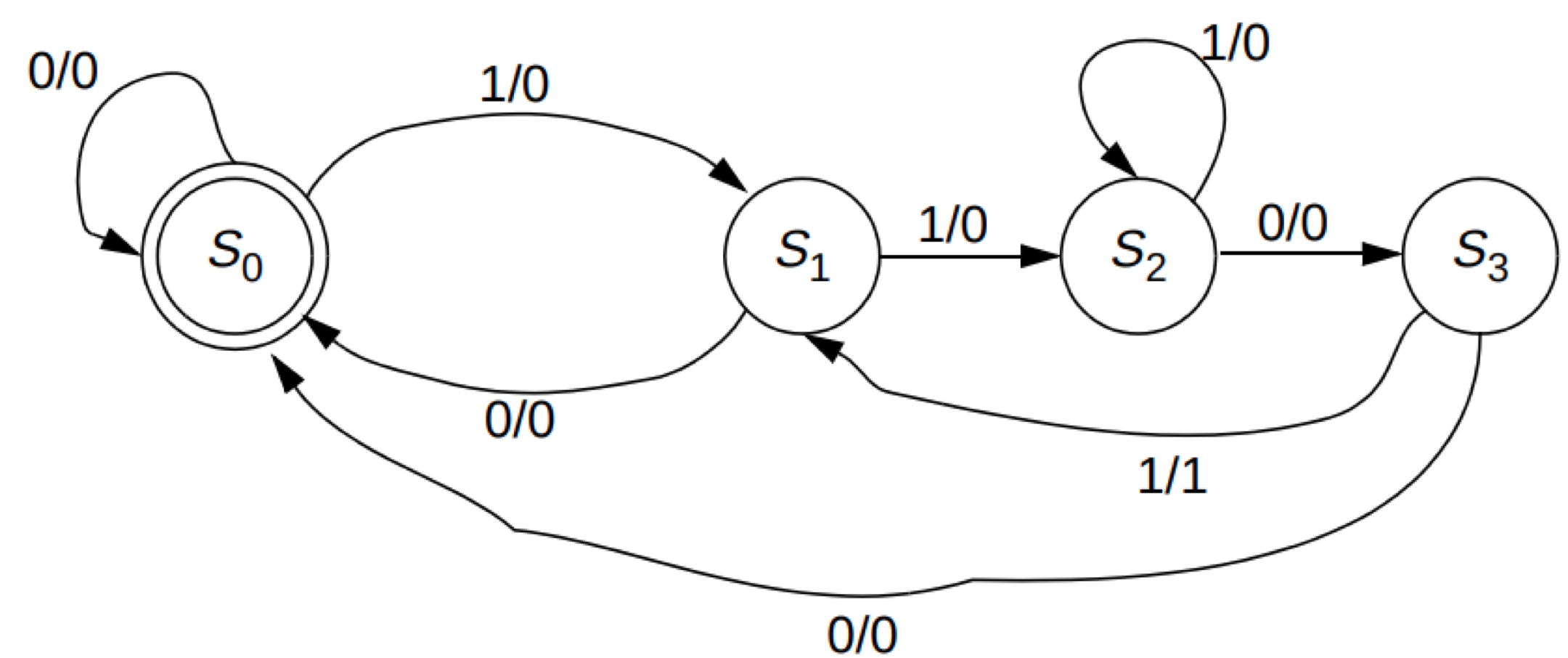
Worth to note:
(1) the transitions from S0 to S1 to S2 to S3 (when desired bit is received)「(1)从S0到S1到S2到S3的转换(接收到所需位时)」
(2) For most of the cases when undesired bit is received, it goes back to S0 (restart the detection again)「(2)在大多数情况下,当收到不希望的位时,它会返回到S0(再次重新开始检测)」
(3) Some special cases: S2 goes back to S2 (11 when received 1); S3 goes to S1 (110 when received 1)「(3)一些特殊情况:S2返回到S2(收到1时为11); S3转到S1(收到1时为110)」
This process needs case-by-case careful design
From State Diagram to Functions
Approach: use Truth Table and Karnaugh Map
- Encode the states, input, and output
- S0 (00), S1(01), S2(10), S3(11)
- Construct the state diagram (it is actually a truth table)
Now you can use K-map
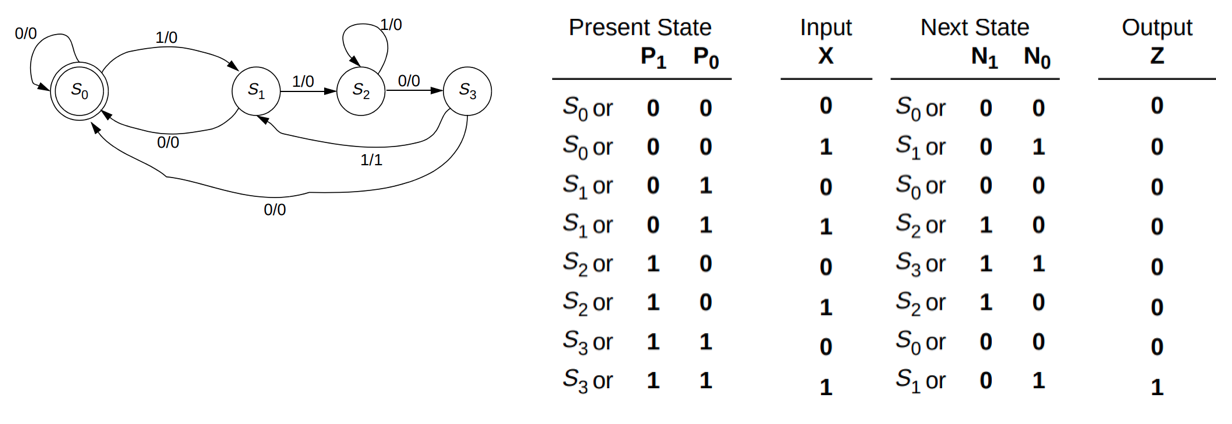
In the State Diagram (truth table):
(1) we use two bits P1,P0 to denote the current state; use N1, N0 for the next state
(2) (P1,P0,X) are the variables, N1, N0, Z are the function values
(3) Given a combination of (P1,P0,X), we need to find the value for N1, N0, Z from the state diagram
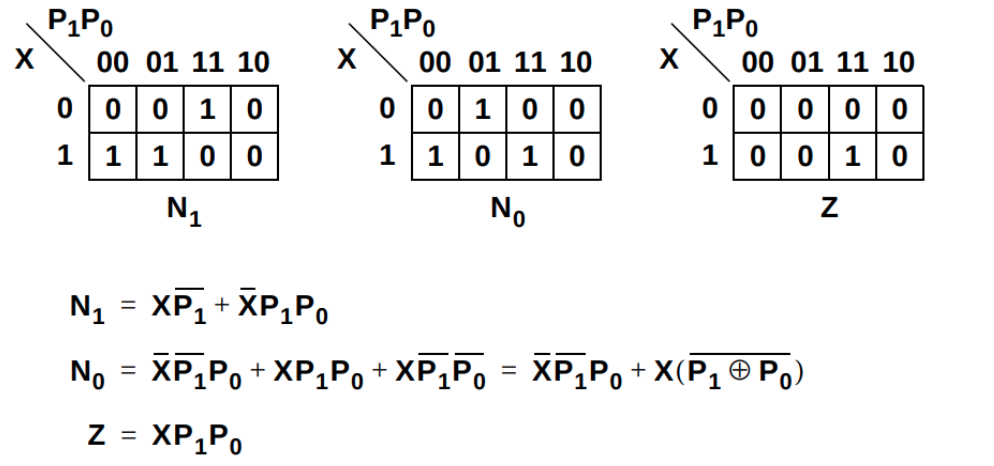
The two important relations:
- Next state = current state + input
- Output = current state + input
We can then contruct the circuits using memory components and combinational logic
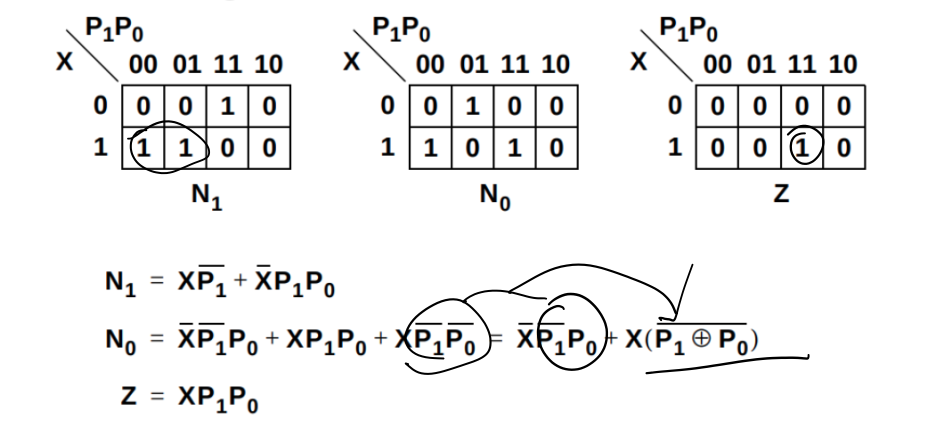
Design of sequential circuits
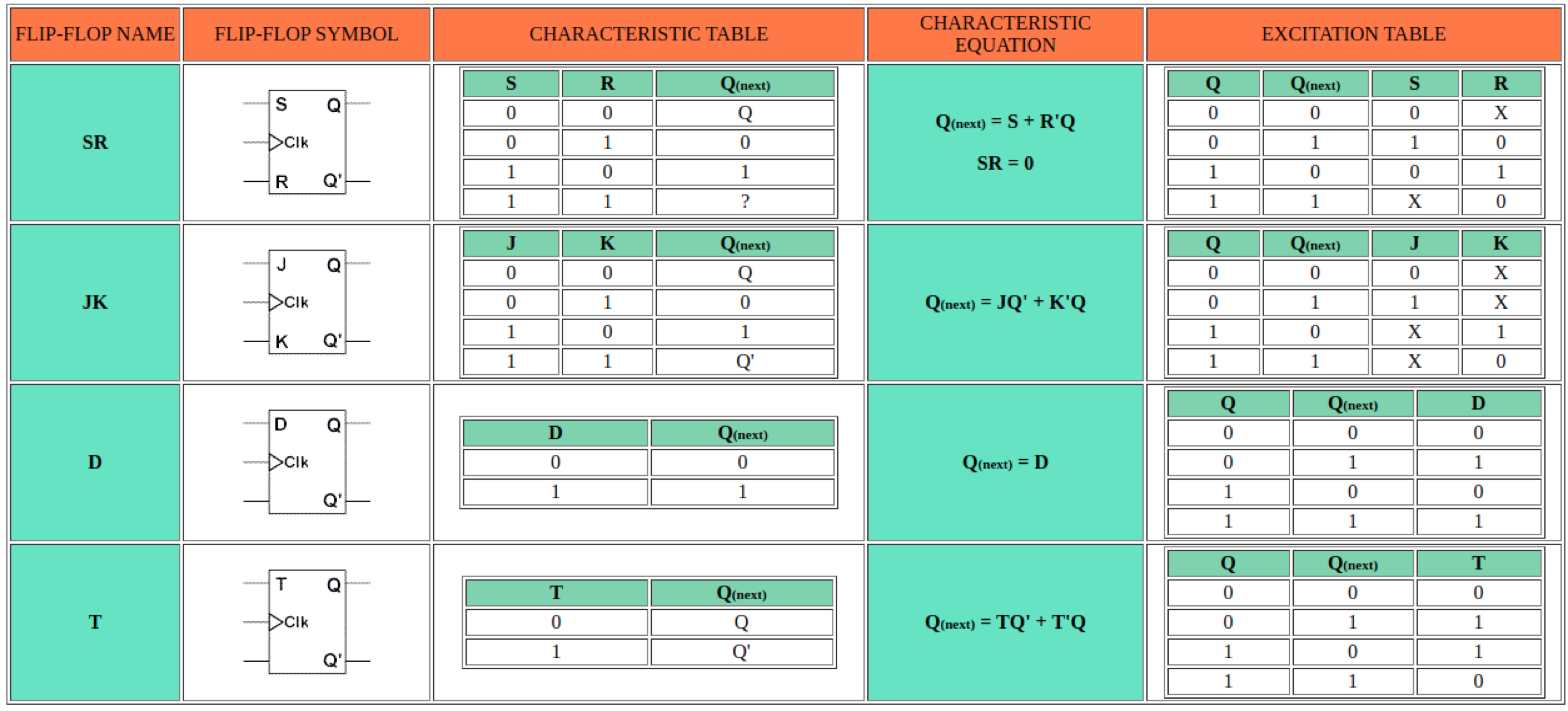
A Recap of Terminologies on Flip-Flops
「Flip-Flops 术语的回顾」
- Symbol (diagram)
- Charactristic table/characteristic equation
- Excitation table
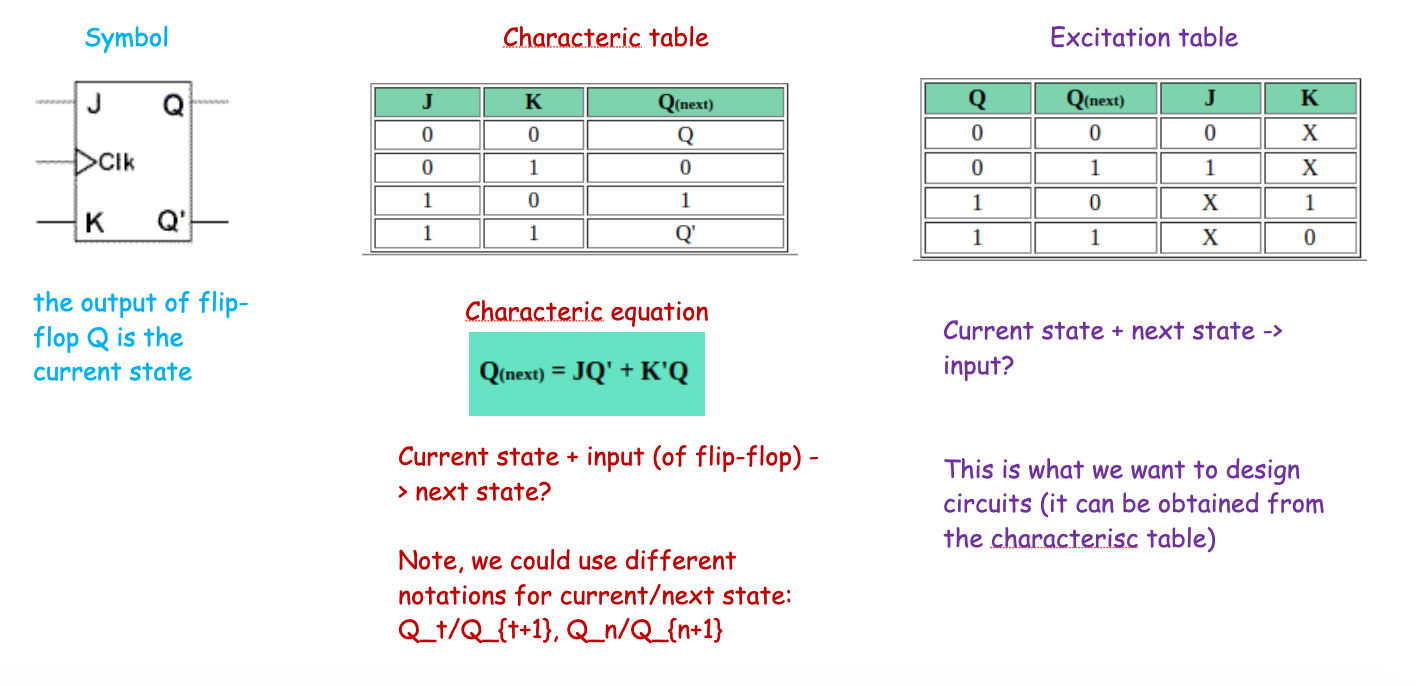
Common Flip-Flop Types
Think
For a real-world problem, we know how to get the relations (functions) among input, current state and next state, output「对于一个现实世界的问题,我们知道如何获得输入,当前状态和下一状态,输出之间的关系(函数)」
For implementation using Flip-Flops, we need the input/output of that type of flip-flops「对于使用触发器的实现,我们需要该类型触发器的输入/输出」
What are the relations between current state/next state and input/output of flip-flops?「触发器的当前状态/下一个状态与输入/输出之间有什么关系?」
Back to the Previous Problem
We are given the state diagram of FSM. We can drive the functions:
- Next state = f (external input, current state)
- External output = g (external input, current state)
Note: f, g can be relialized using combinational logic
However, we need to implement f and g using Flip-Flops. What's the next state? What's the input to the flip-flops?
For D Flip-flop, it is easy
- Characteristic equation: Q_{next} = D
- Next state = f (external input, current state)
- D = f (external input, current state)
Generally, for other flip-flops
- We will use the excitation table of that flip-flop to derive the excitation table of the circuit
- Excitation table: what inputs of the flip-flop are required to transit from one state to the next state「从一个状态转换到下一个状态需要触发器的哪些输入」
- This excitation table of the circuit is also a truth table: the inputs of the flip-flop are the fucntion values and others are variables
Example
Design a sequential circuit whose state diagram is shown as follows, using J-K Flip-Flops「使用J-K触发器设计时序电路,其状态图如下所示」
Encoding:
- Use the outputs of two J-K Flip-Flops Q0, Q1 to denote the four states
- Use X to denote the external input
- There is no external output for this FSM
批注:用x为输入,x作为下一个的输入,随着输入的变化, Q0, Q1发生变化。无输出。即 x_next = f(x), 或者 input = f(x) 这时我们用找出影响x的基本要素。
目的:构建 input = f(x) 函数
1.先画出 总部件 的 Symbol (diagram)
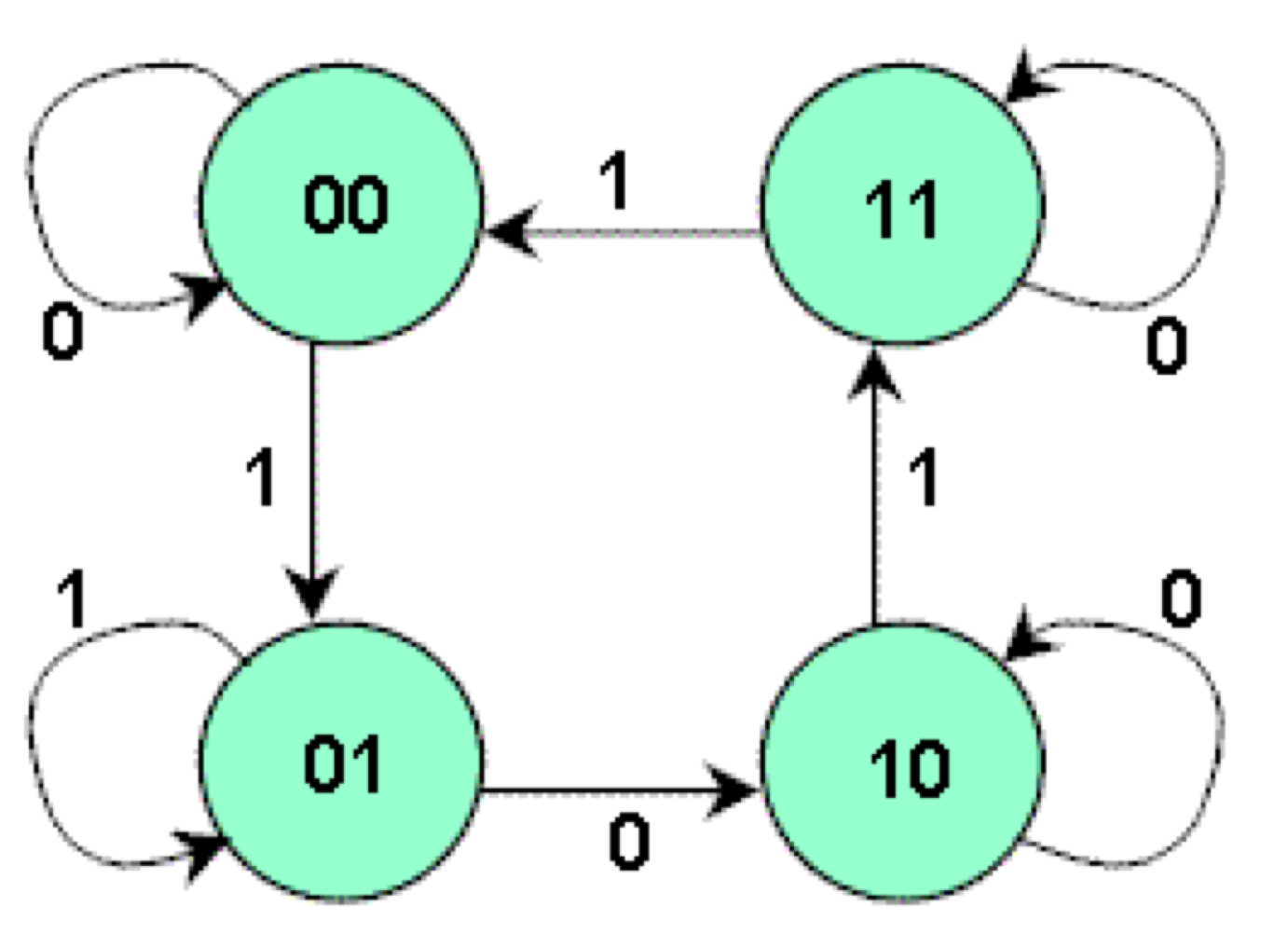
- 画出 元部件的 Exitation table
分析:Q0, Q1的变化是由 Q0、Q1的当前状态 和 J0,K0,J1,K1 决定的
- 根据 总部件 的 Symbol (diagram) 画出 总部件 的 state table
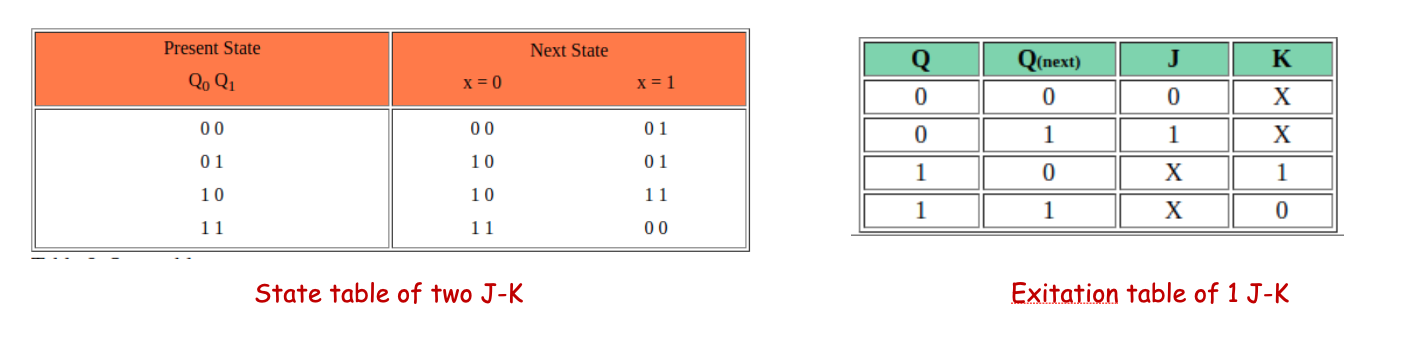
- 根据 总部件 的 state table 画出 总部件 的 Excitation table
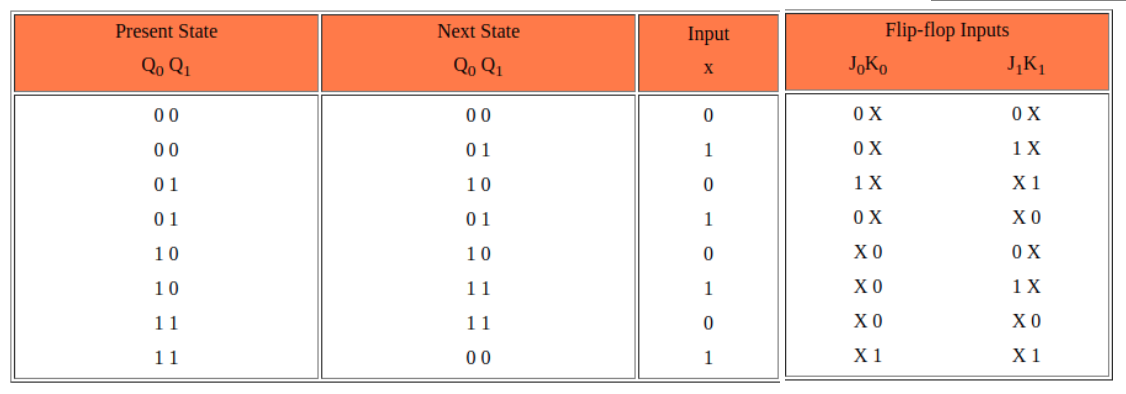
For example: the first row, look at Q0, 0 -> 0, the required inputs are J0 = 0, K0 =X
This is a truth table with Q0 Q1 as variables and J0, K0, J1, K1 as function values (it contains don't care conditions「它包含 无关条件 」)
**这时,我们要用 Q0,Q1,x **去表示 next ,即 next = f(Q0,Q1,x )
- 将 元部件 的 输入(J0,K0,J1,K1) 和 总部件的输入x 进行对应,使用多种化简方法,比如k-map
k-map的两个维度分别是两组变量。
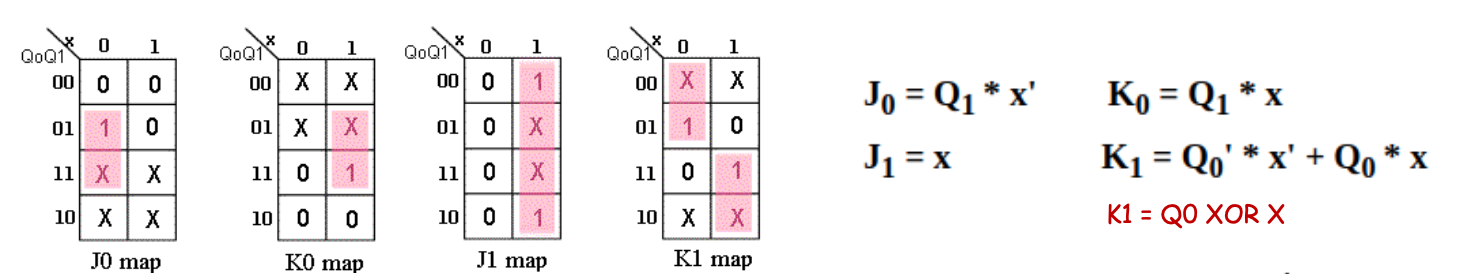
- 画出电路
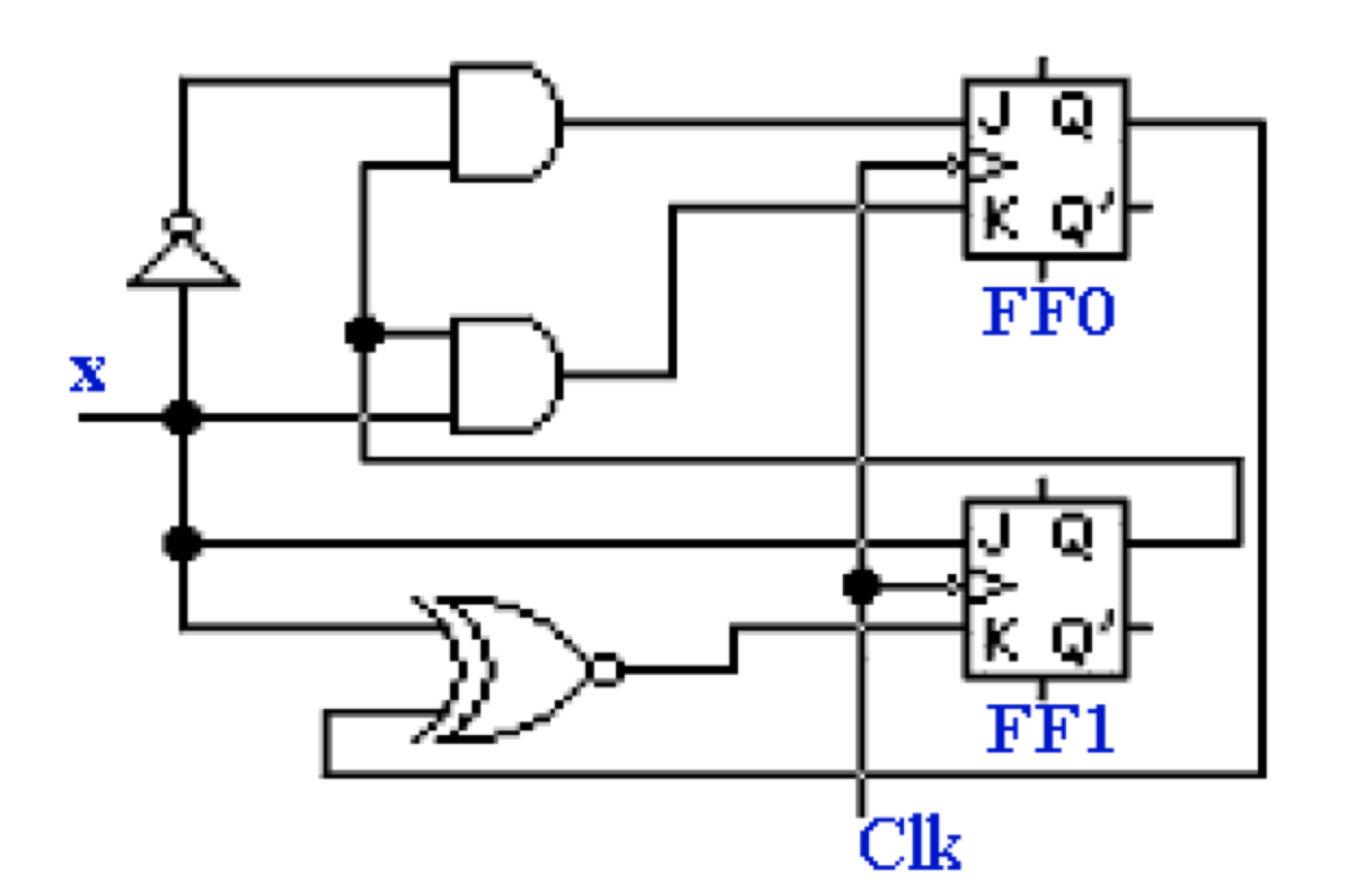
Summary
Critical steps of designing sequential circuits
FSM model (this is the hardest part): define the states and state transitions「FSM模型(这是最难的部分):定义状态和状态转换」
The rest is routine「例行的」:
- State table + excitation table of flip-flops -> excitation table of the circuit
- Use K-map to derive the SOP form of two functions:
- Input of Flip-flips = current state (output of flip-flops) + external input
- External output = current state (output of flip-flops) + external input
批注
- 对于 Next ,我们要找的函数是 Next = f(变量);
- Next 能够被 拆解成 有很多个 基本元件的Next,这里需要多个函数:比如外界输入的x,和 当前状态值
- 一般题目会给出 基本元件。
- 对于 Output, 我们要找的函数是 output = g(变量);