Operating System
大约 6 分钟
Operating System
本章OS,主要围绕着Unix和Linux展开。
OS and Computer System
A computer system contains four components.
- Hardware
- Provide basic computing resources.
- CPU, memory, I/O devices.
- Operating system
- Control and coordinate use of hardware among variousapplications and users.
- Windows 11, OS X, Unix, Linux.
- Application programs
- Define the ways that system resources are used to solve usercomputing problems.
- Word processors, compilers, web browsers, database systems,video games.
- Users
OS is the manager of the computer system.
OS goals:
- 执行用户程序,解决用户的问题。
- 让计算机系统使用起来更方便。
- 以有效的方式使用计算机硬件。
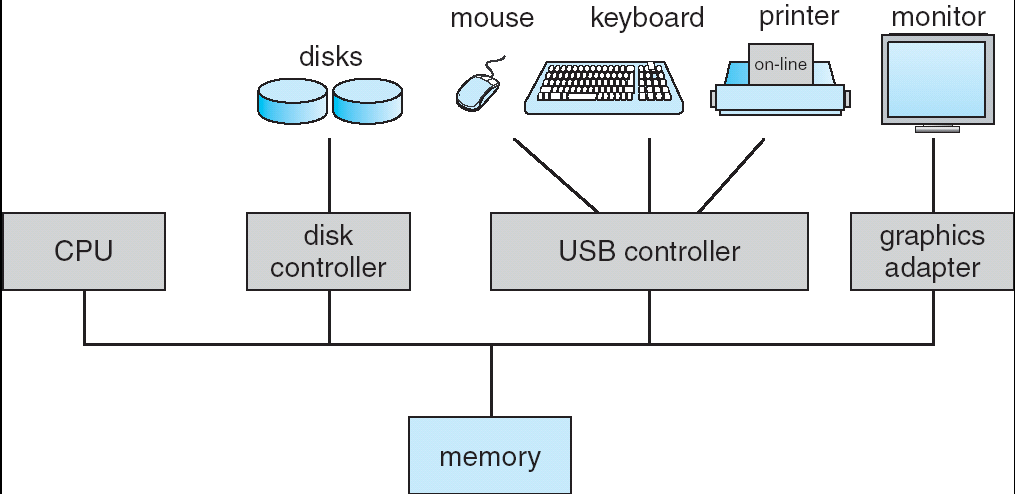
At the hardware level, one or more CPUs and devicecontrollers are connected through common bus to access shared memory.
Concurrent execution of CPU and devices arecompeting for access to memory (memory cycles).
Operating System
An operating system is
- A resource manager
- Manage the allocation of computer resources.
- 在相互冲突的请求之间做出决定,以实现资源的有效和公平使用。
- A control program
- 控制程序的执行以防止错误和不当使用计算机。
OS boundary
- Everything a vendor ships when you buy an OS.
- The one program that is running at all times on computer.
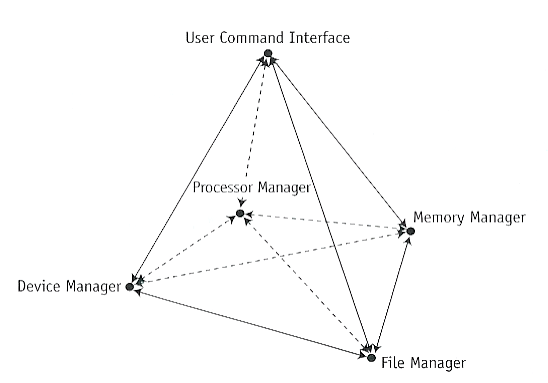
- OS must manage the use of resources by users.
- Processor or CPU, memory, file, device are all resources.
- The presence of a user in the OS could be represented by a task or a process.
- A process is a program in execution.
- Program is a passive entity. You write a program to beexecuted.
- Process is an active entity. You run a program to create aprocess.
- A process needs resources like CPU, memory, files toperform its functions.
- A process executes its program instructions sequentially, one at a time, until completion.
- A typical computer system has many processes running concurrently.
- OS is responsible for several process management activities.
- Data should be in memory when a process is executing.
- Instructions of the program for a process should be in memory for execution.
- OS must keep track of the usage of memory.
- Files are often collected and managed under a file system.
- OS should hide variations and details of hardware devices from the user.
- Two major types of interfaces
- Batch interface: commands are stored in a file (script file or*.bat file) before hand.
- Interactive interface: commands are issued on the fly byusers. There are two types of interactive interfaces:
- Command line interface (CLI)
- Graphical user interface (GUI)
- Network manager
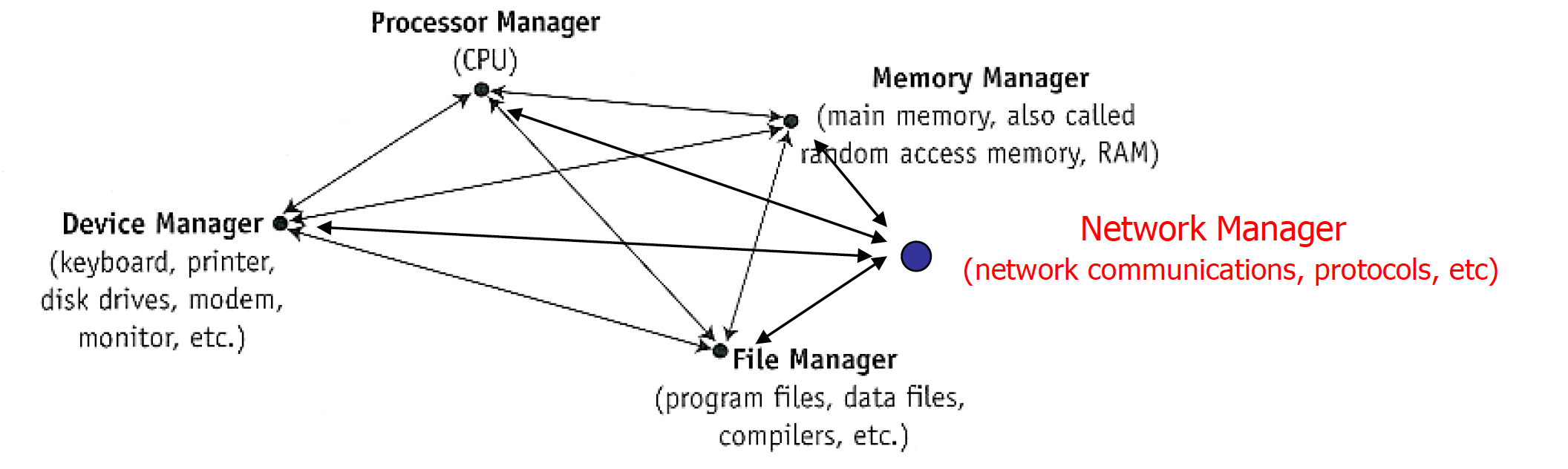
Protection and Security
- Protection
- A mechanism for controlling access of processes or users toresources defined by the system.
- Provide ways for users to specify the control and to enforceit.
- Security
- The defense of the computer system against internal andexternal attacks.
- Types of attacks: worms, viruses, denial-of-service, identitytheft, theft of service.
- OS can only protect against some of the attacks. Othersshould be managed by human.
Operating System Services
Let us summarize the functions or services provided by an operating system to help users.
- User command interface
- Program execution
- I/O operations
- File-system manipulation
- Communications
- Error detection
Operating system also provides these functions to improve system efficiency.
- Resource allocation
- Accounting
- Protection and security