Interrupts and System Calls
Interrupts and System Calls
Introduction
Operating system is the manager of a computer system.
Remember that OS is itself a program and that a process is a program in execution.
When there are multiple processes executing, how can the OS control and manage them?
- The OS relies on a special alarm system, called the interrupt processing mechanism.
- When an interrupt occurs, there is a chance for OS to grasp the CPU and make decision and arrangement to control the system.
I/O Processing
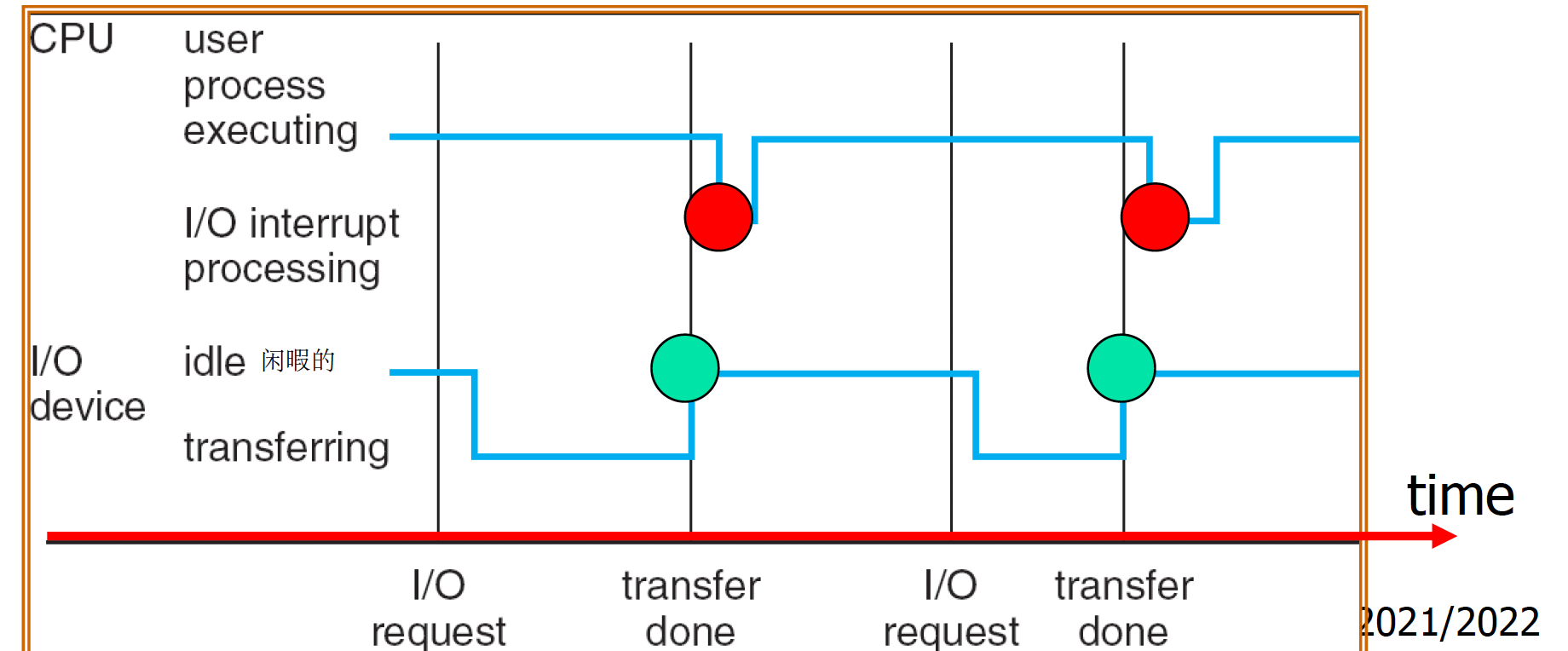
One can perform I/O when CPU is doing useful work.
When I/O is completed, OS needs to put aside its current work and looks at I/O device for next I/O. 「当I/O完成后,操作系统需要将其当前的工作放在一边,并查看I/O设备的下一个I/O。」
- The event that I/O is completed causes an interrupt.
- The suspension (interruption) of current work to handle the event is called interrupt processing.
Two methods for I/O processing
Synchronous
Asynchronous
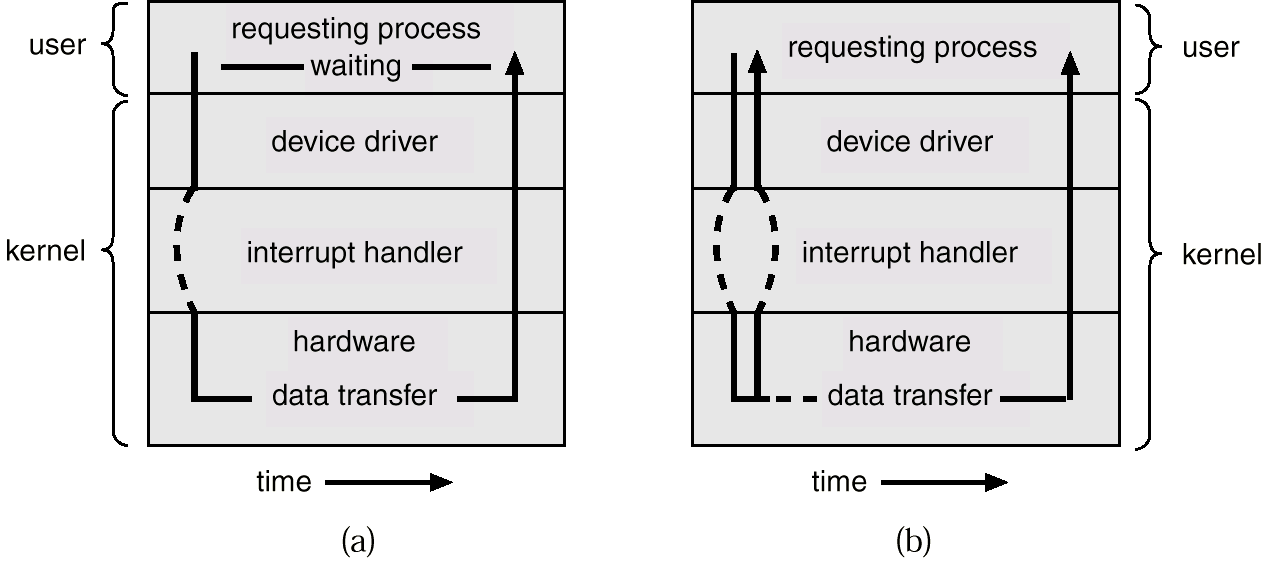
Synchronous I/O
- I/O开始后,用户程序将等待,直到I/O完成。
- 程序等待并不做任何事情,直到收到I/O完成中断。
- 每次最多只有一个I/O请求未完成,没有同时的I/O处理。
Asynchronous I/O
- 在I/O开始后,用户程序继续执行,不需要等待I/O完成。
- 当I/O完成后,程序将收到一个中断。
- 可能有几个I/O请求一起工作
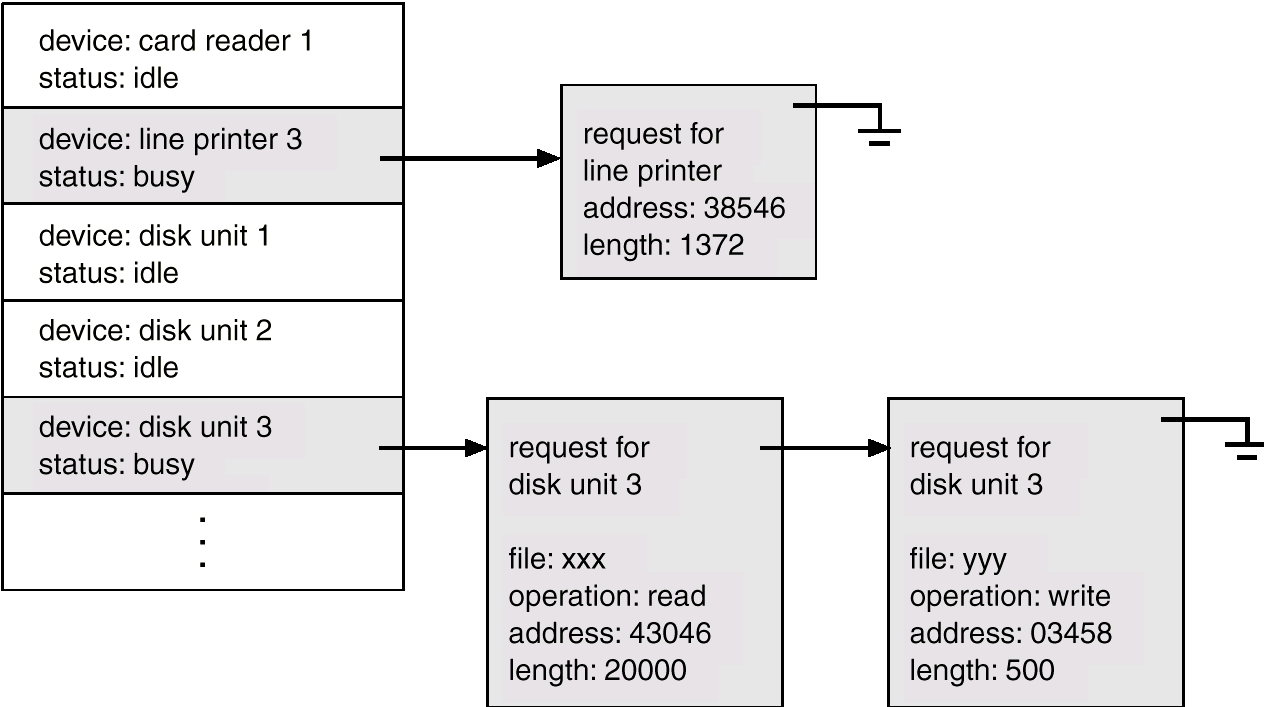
- 使用一个设备状态表(device-status table )来存储每个I/O设备的状态,包括其类型和状态。
Device-Status Table
Interrupt
Interrupt Processing
An interrupt is a signal to the CPU to tell it about the occurrence of a major event. 「中断是给CPU的一个信号,告诉它一个重大事件的发生。」
- An error in calculation (illegal instruction, division by zero).
- Completion of an I/O.
- Hardware alarm.
- User-generated event (often called a trap or signal).
「Interrupt is the mechanism the OS uses so that it could turn attention to other activities and to manage resources, because interrupt will seize the CPU. 」中断是操作系统使用的机制,以便它可以将注意力转向其他活动并管理资源,因为中断会抢占CPU。
Two types of interrupts:
- Maskable interrupt: interrupt that may be ignored or handled later. A lower priority interrupt is maskable.
- Non-maskable interrupt: interrupt that cannot be ignored. The CPU must handle this interrupt immediately.
- A non-maskable interrupt may be “over”-interrupted by another non-maskable higher priority one.
Depending on the cause of interrupts, we could classify them into 3 categories:
- Program interrupt
- Caused by conditions within CPU that requires attention, e.g. illegal instruction, overflow, division by zero, memory access violation, special instruction.
- Sometimes also called traps (or signals in Unix/Linux).
- I/O interrupt
- Caused by I/O related events, e.g. I/O completion or device errors.
- Timer interrupt
- Caused by the hardware timer of the system to handle time-related activities.
中断意味着紧急情况。在一个(不可屏蔽的)中断发生后,CPU将搁置它正在执行的程序,保存程序计数器和寄存器的值(在堆栈上)。它以中断号为索引,查找中断表,寻找执行的程序。这个程序被称为中断处理程序,或中断服务程序(ISR)。这个程序被称为中断处理程序或中断服务例程(ISR),它在响应中断时被执行,以服务于中断。
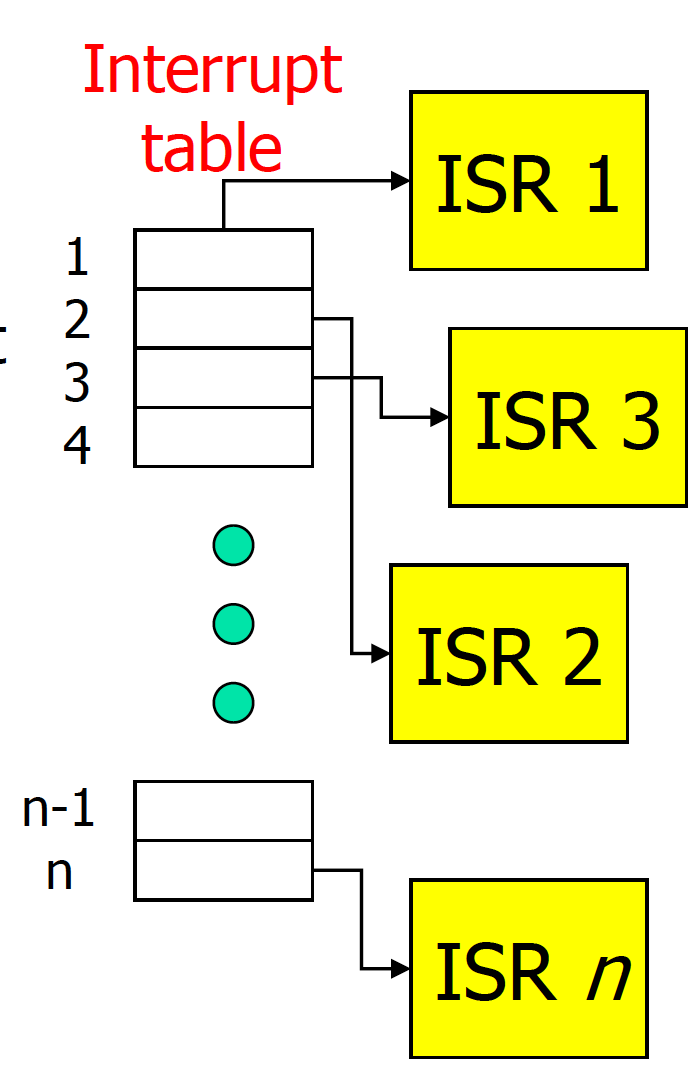
Interrupt Handling
- 有可能当一个中断被服务时,另一个中断可能会到来。
- 如果进入的新中断Y的优先级较低,它将等待直到第一个中断X完成。
- 如果新中断Y的优先级较高,它将从当前的中断处理程序X中夺取CPU。
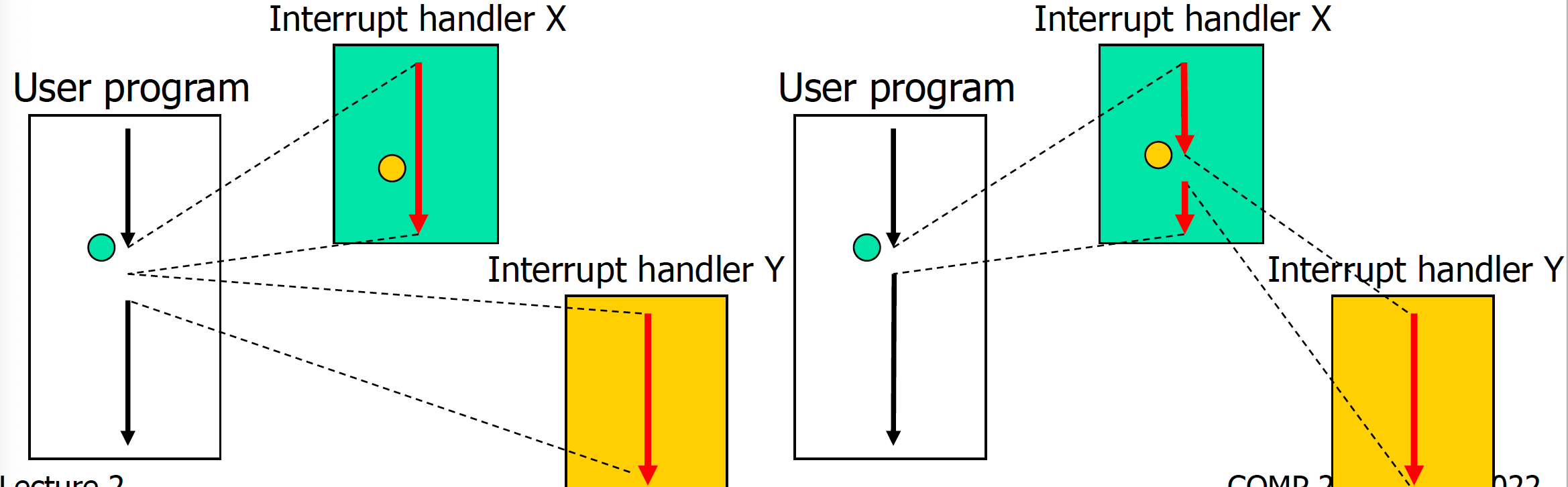
Operating System Operation
Almost all OS are interrupt-driven.
Without interrupt, there is no way the OS can get back the CPU from a program falling into infinite loop.
在PC上,你可以用<Ctrl><Alt><Del>中断一个程序,并在任务管理器下杀死该任务,但为什么呢?在<Ctrl><Alt><Del>时,会有一个硬件中断产生。无限循环中的程序将被中断。CPU被交给中断处理程序(任务管理器)。因此,你可以杀死这个任务。
在Unix中,你可以用<Ctrl><C>来中断一个程序,会有一个信号(user trap)被发送到程序中。如果程序中没有针对该信号的中断处理程序(称为信号处理程序),程序将被终止。这就是所谓的signal processing ( in system programming )。
中断允许操作系统在必要时获得系统的控制(有一个特殊事件)。
Basic interrupts are driven by hardware (often I/O devices or special interrupt pin) to the microprocessor.
Trap
A trap is a software-generated interrupt caused either by an error or a user request.
- 软件错误或软件请求产生异常或陷阱,例如除以0,请求操作系统服务。
- 一个系统可能想通过做一些事情来回应除以0的错误(例如Java异常)。
The timer mechanism
- 防止无限循环和进程占用资源的一个简单方法。
- 设置中断,在特定的时间段(报警)后发生。
- Operating system decrements counter upon timer interrupt.
- 当计数器达到零时,就会发生一些错误。
- 杀死进程或夺回资源(如解锁文件)。
- 有时,这被称为看门狗定时器(watchdog timer )。
- 由timer interrupt mechanism 提供。
In Unix, a special timer interrupt handler, called the clock routine, plays a central role in process scheduling and resource management. It is triggered by the hardware clock every 1/60 second in the original Unix design.「它由原始UNIX设计中的每1/60秒触发硬件时钟。」
User and Kernel Mode
由于中断处理很重要,在编写中断处理程序时必须特别小心。允许或禁用中断是非常重要的。回顾一下,中断是操作系统在必要时收回CPU的机制。如果用户程序可以禁用中断,操作系统就没有办法收回CPU并做一些补救措施。其结果是系统挂起(例如,Windows蓝屏)。
因此,硬件应该提供帮助,防止普通用户执行与中断有关的特殊命令。就计算机结构而言,这些命令被称为特权命令,包括I/O命令。常见的解决方案是在CPU硬件中提供双操作模式(dual operation mode )。
如果一个用户进程在用户模式下执行,它如何做需要执行特权指令的I/O呢?通过系统调用实现。系统调用是操作系统的一个入口端口。系统调用实际上是一个trap,它从用户模式变为内核模式,执行特权I/O指令,从系统调用返回,并恢复到用户模式,继续执行。
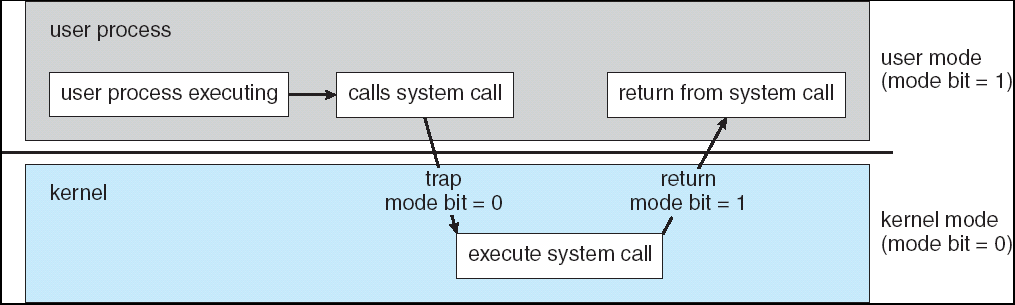
System Calls
A system call is a programming interface to the services provided by the OS.
The nature of a system call is similar to a procedure call (a very special procedure call).
- Often written in a high-level language like C/C++.
- User programs could not execute privileged instructions, except through the OS.
- System call provides the interface to execute these system functions by user programs.
- To facilitate programmers, a high-level Application Program Interface (API) is often provided (e.g. Java API).
- An API hides the details about system calls from programmers
Example system call sequence to copy the contents of a file to another file.

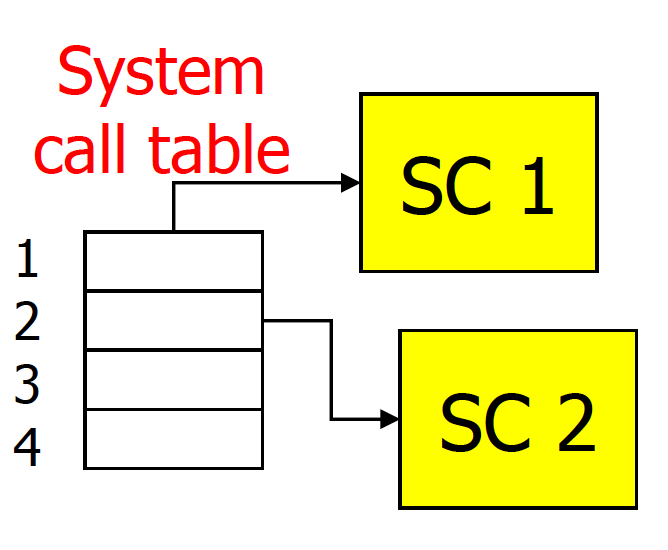
Inside the OS, a number would beassociated with each system call.
- System-call interface maintains a table indexed according to these numbers.
- Such a table looks like a table ofinterrupt handlers.
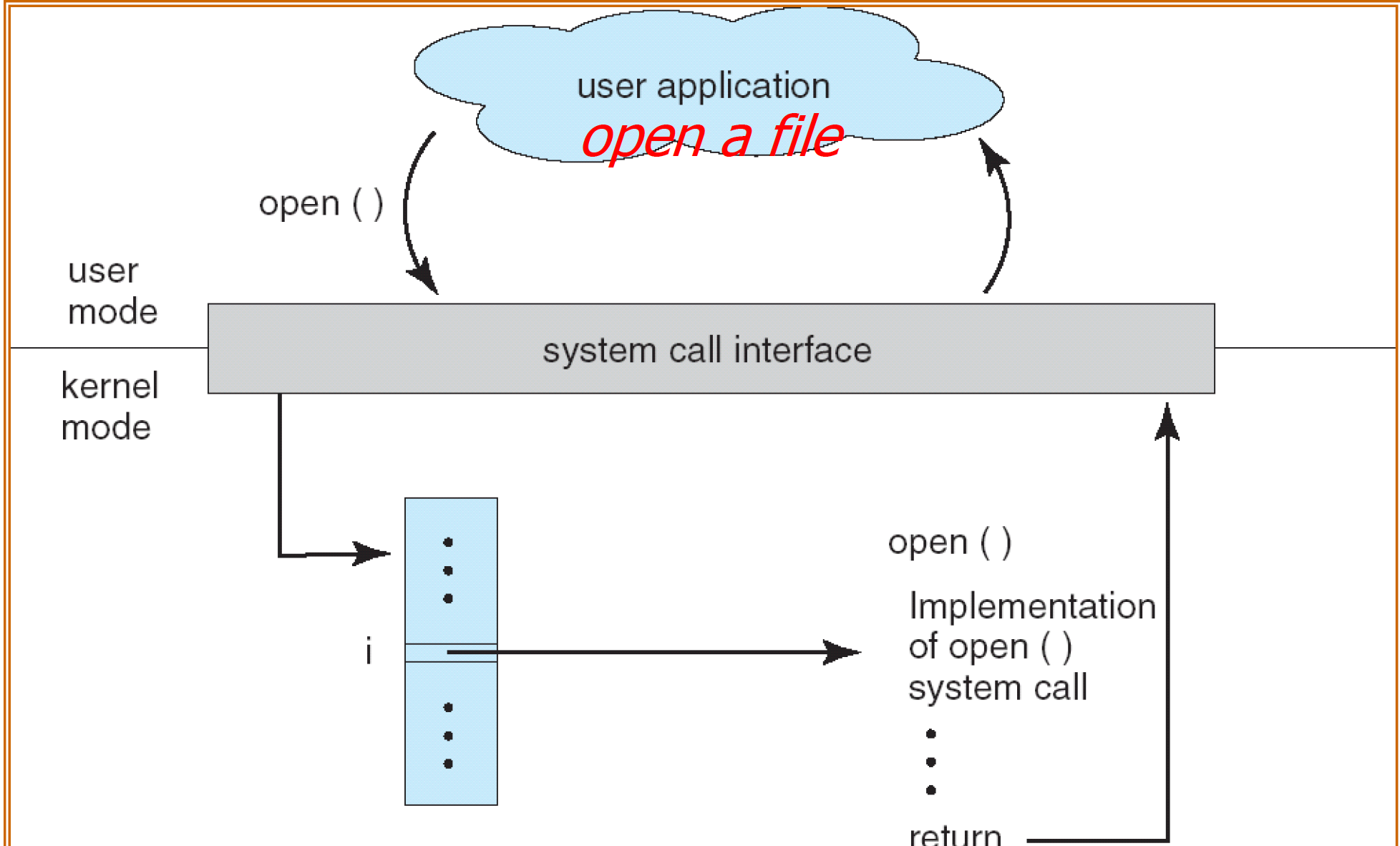
When the user process executesthe system call, the system call interface generates a software trap.
The CPU switches to kernel mode and the system callroutine is executed (like interrupt).
Status of the system call is returned to the caller,together with any return values.
The caller needs to know nothing about how thesystem call is implemented.
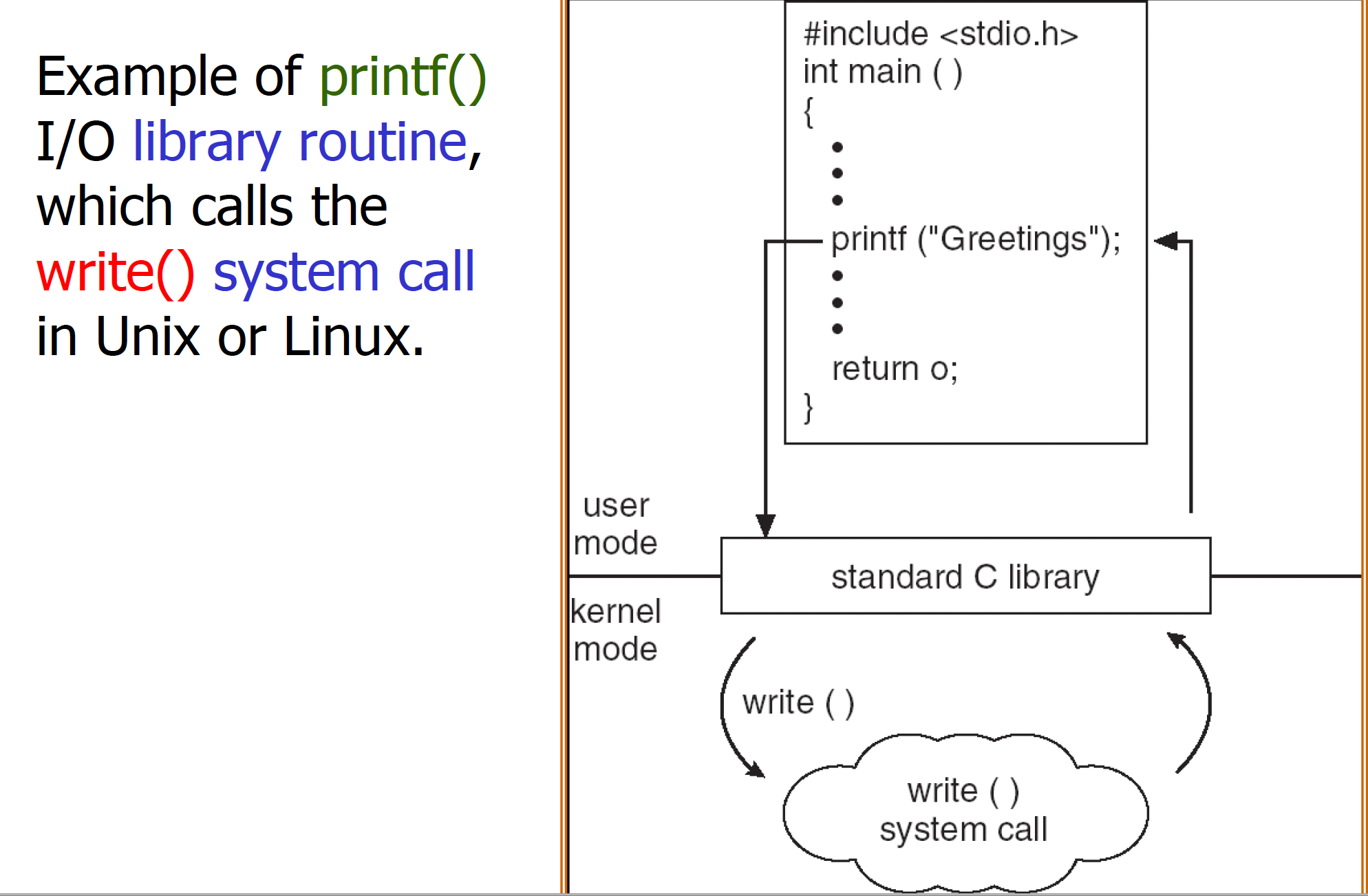
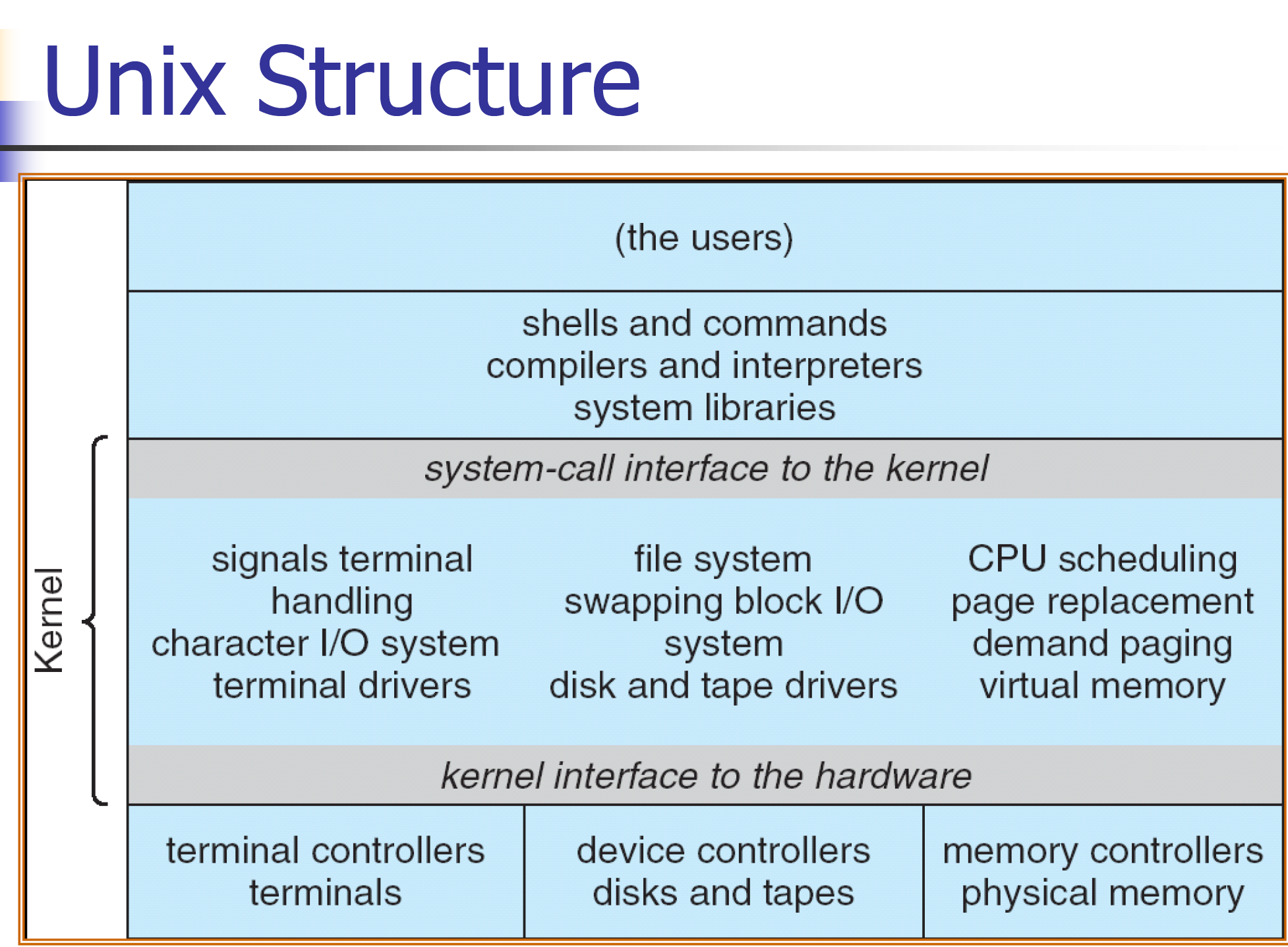
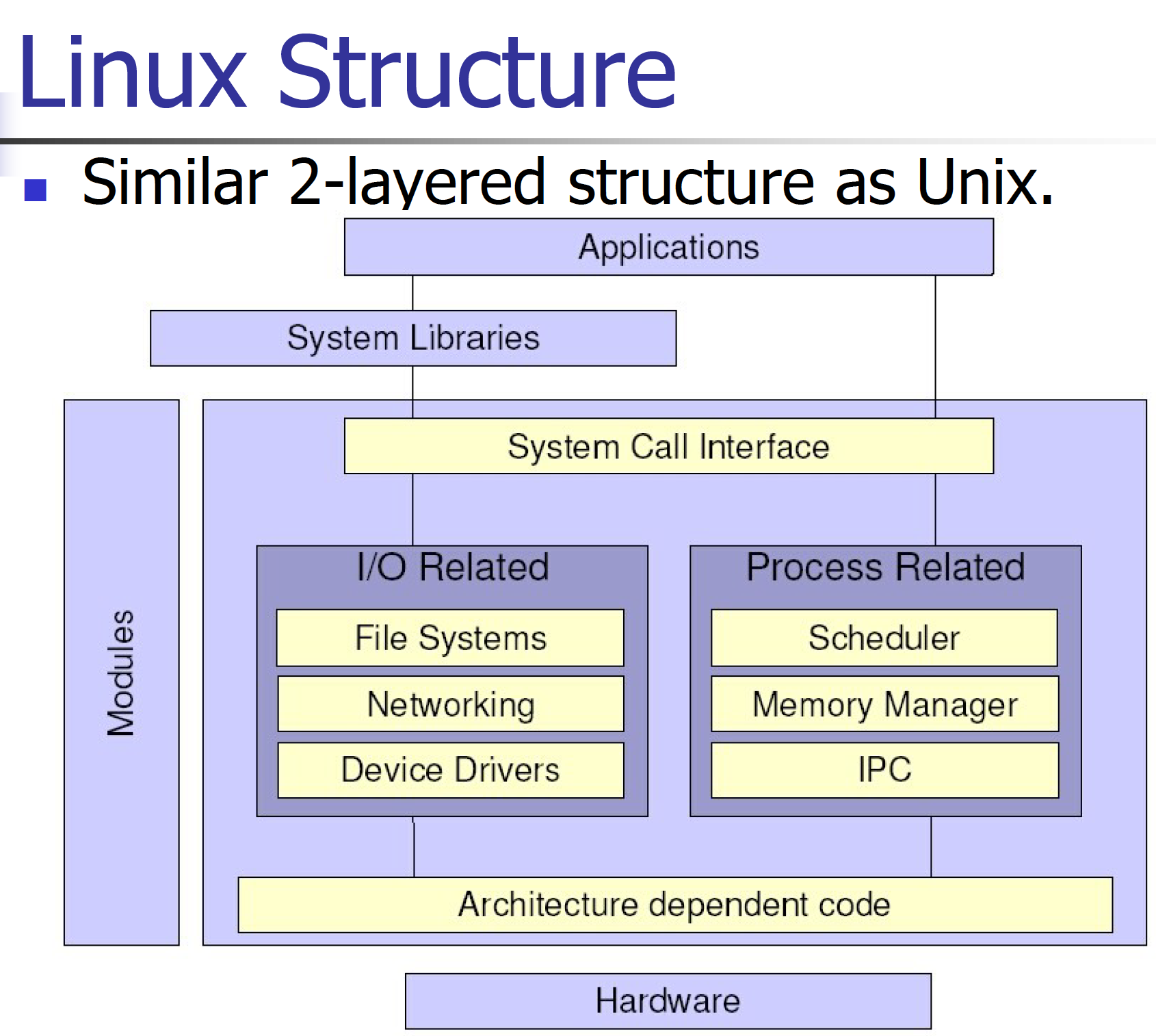
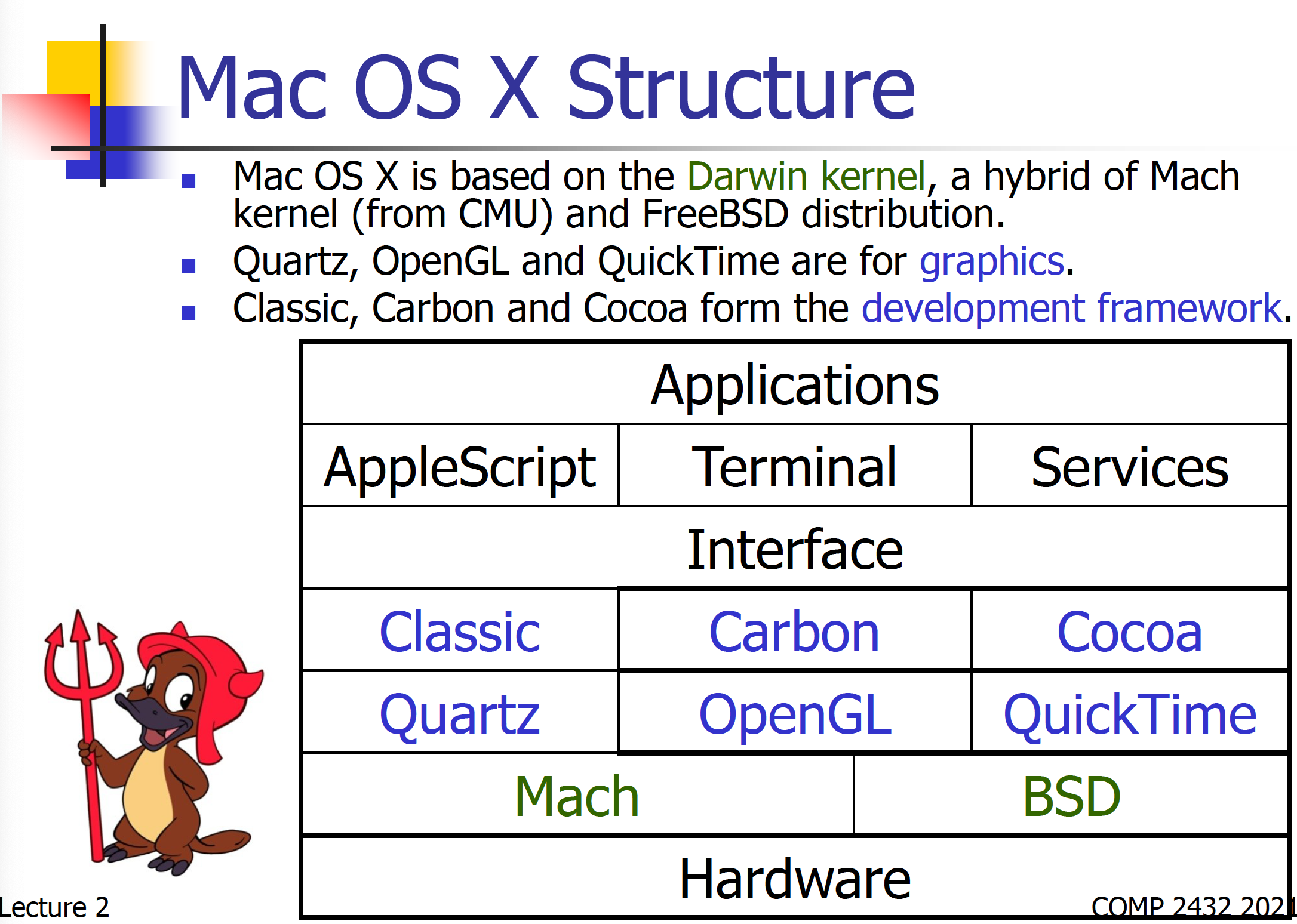
Operating System Structure