Deadlock
Deadlock
用一个看起来类似的案例来比较 Deadlock。两个人正向对方走去,几乎相撞。两人都看到他们要撞上对方,都试图通过转向道路的一边来避免。会发生什么呢?他们俩会再次相撞。所以他们又做了一个动作来避免。在一个不幸运的情况下,当两个人总是做错动作时,他们最终会花时间去尝试其他的路线,但不成功。我们称这种情况为 Deadlock。
死锁是一组阻塞进程,每个过程都包含资源并等待在集合中获取由另一个进程所持持有的资源。
如果它正在等待当前由另一个进程持有的资源,则会阻止进程。 我们称之为这个资源僵局,这也是本文讨论的重点。
Example
Consider two processes P1 and P2 communicating via pipes.
- P1: read(fd2to1[0], b1, 80); write(fd1to2[1], b1, strlen(b1));
- P2: read(fd1to2[0], b2, 80); write(fd2to1[1], b2, strlen(b2));
Both processes will wait to read from the pipe before each goes ahead to write into the pipe.
Resource Model
资源是能够被使用的对象
- 一个进程通过打开文件并获得 opening the file 且 gets the file pointer or file descriptor. 来使用一个文件
- 一个进程通过
malloc()获得一个内存块 - 一个进程通过系统调用设备驱动程序来使用I/O设备。
Steps to use a resource
- Request for the resource (acquire or open).
- Wait until the resource is allocated or granted.
- Wait until the resource is allocated or granted.
- Release the resource (return or close).
资源只能由一个进程使用,在它向资源管理器发出请求之后,管理器批准其用量(grant the resource)。
Resources can be grouped into types
- There are m types of resources: R1, R2, . . ., Rm.
- Each resource type Ri has Wi copies (or Wi instances).
For example, there may be 10 shared buffers, 80 physical memory frames, and 4 worker threads in the thread pool.
Deadlock Characterization
- Mutual exclusion (相互排斥)
- Only one process at a time can use a resource.
- Hold and wait
- 持有至少一个资源的过程正在等待获取由其他进程所持持的额外资源。
- No preemption (无法抢占)
- 在该过程完成任务之后,只能通过持有该过程的流程自愿释放资源。
- Circular wait(循环等待)
Resource Allocation Graph
A resource allocation graph has a set of vertices V and a set of edges E. 「资源分配图具有一组顶点V和一组边缘。」
There are two types of vertices V:
P = {P1, P2, …, Pn}is the set of all processes.R = {R1, R2, …, Rm}is the set of all resource types.Pi -> Rjmeans that Pi is requesting for resource Rj.Rj -> Pimeans that Rj is allocated/assigned to Pi, which holds the resource.
Quick rules of thumb
- 如果图表不包含循环,那么绝对没有死锁。
- 如果每个资源类型只有一个实例,那么循环意味着存在死锁。
- 如果每个资源类型有几个实例,那么循环只意味着有可能出现死锁。
Algorithm
在分配资源之前,操作系统检查分配是否会导致循环。如果产生了循环,就不要分配资源。只有在将请求边转换为分配边不会导致资源分配图的循环时,才能批准对资源的请求。
Deadlock Handling
- Ostrich approach: Ignore the deadlock problem and pretend that deadlocks never occur in the system.
- Deadlock prevention: Ensure that the system will never enter a deadlock state.
- Deadlock avoidance: Allocate the resources very carefully so that system will not enter a deadlock state.
- Deadlock detection: Allow the system to enter a deadlock state, detect it and then recover from it.
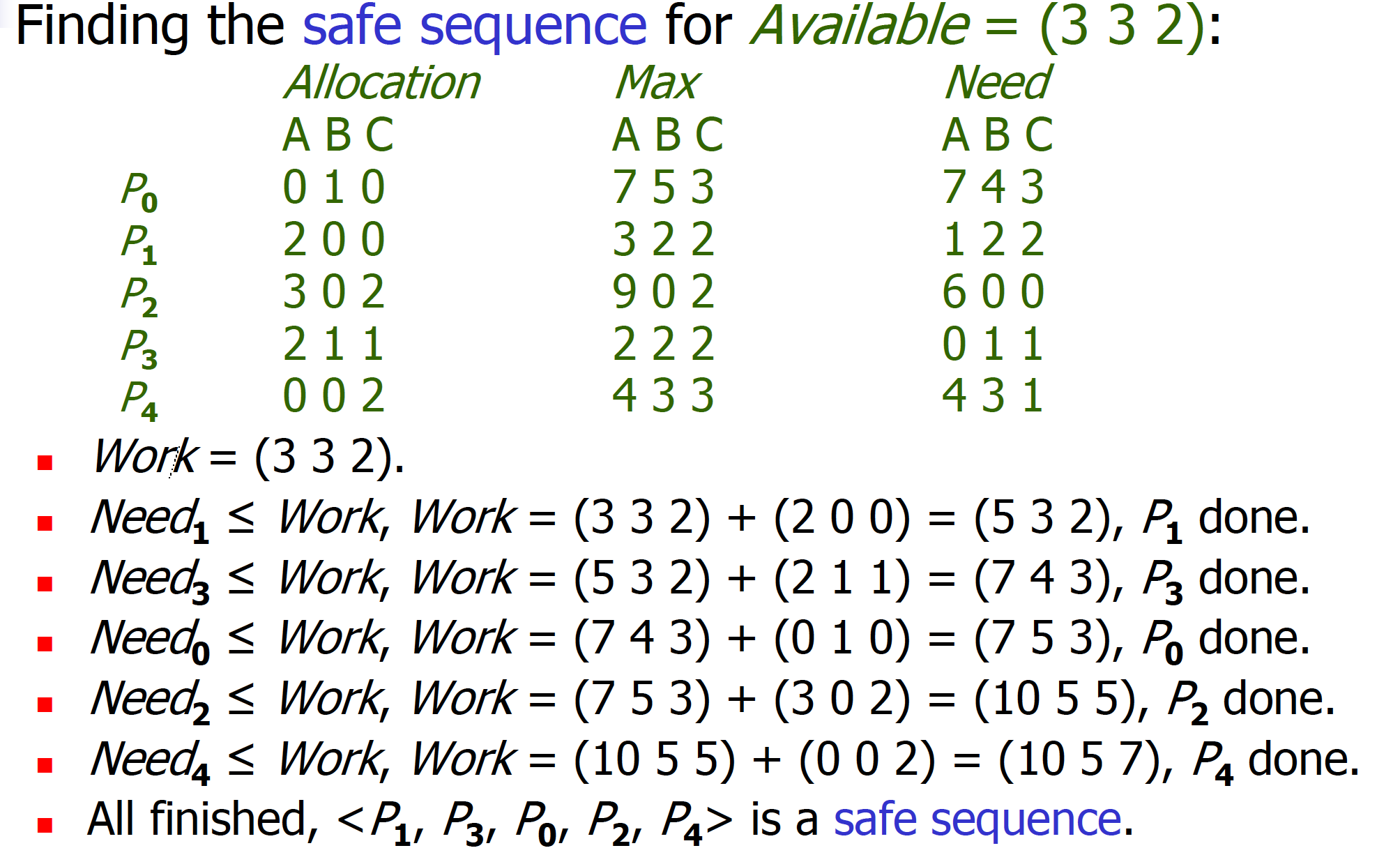
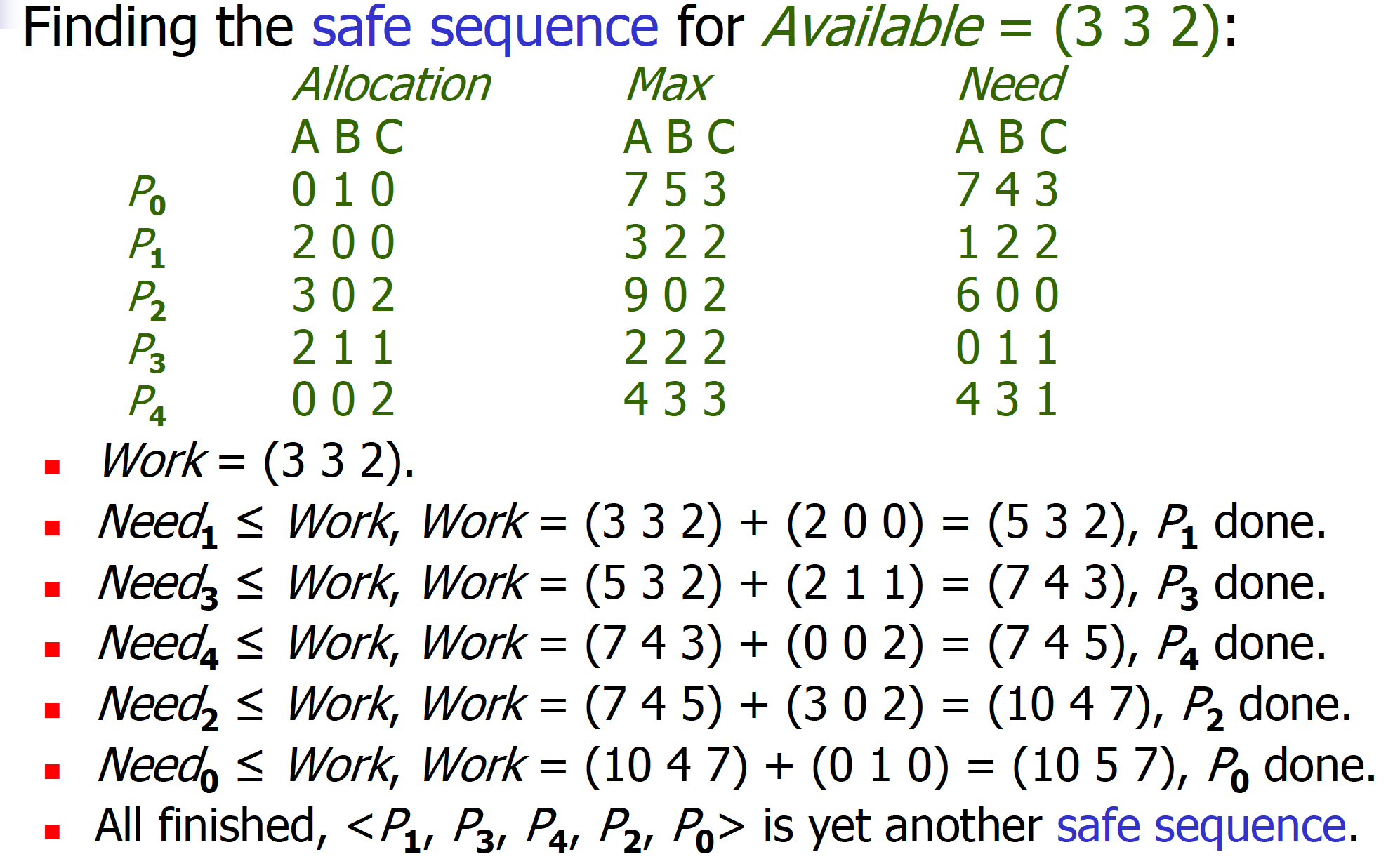
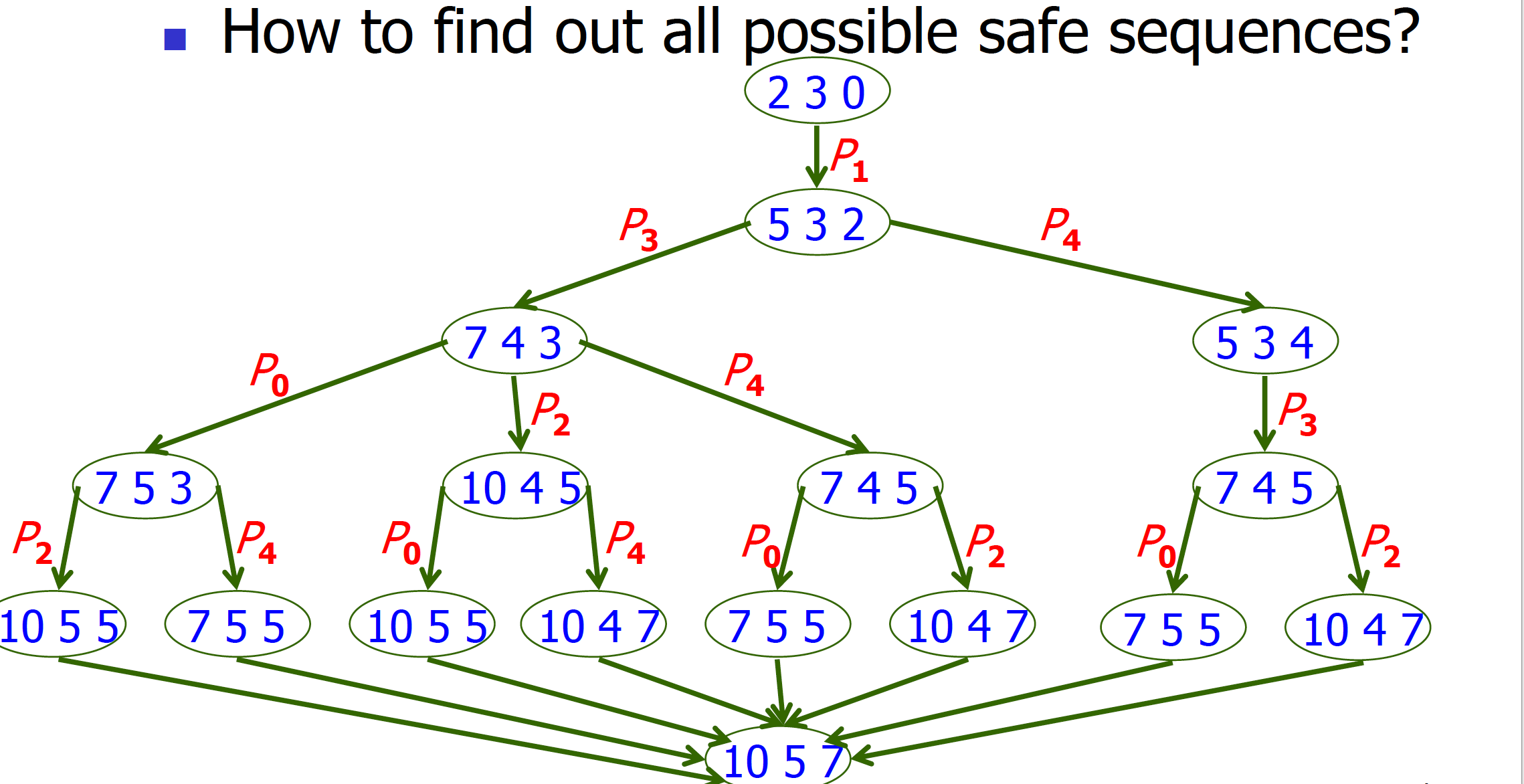
Banker’s Algorithm is an algorithm for multiple instances of resource types.