Virtual Memory
Virtual Memory
Introduce
Problem: if a program requires 1GB main memory, but we have only 1MB physical main memory, how can execute the program?「问题:如果一个程序需要1 GB的主内存,而我们只有1 MB的物理主内存,那么如何执行该程序?」
- 1K = 2^10 = 1024
- 1M = 2^20 = 1024 * K
- 1G = 2^30 = 1024 * M
- 1T = 2^40 = 1024 * G
Virtual memory, a technique that allows to fit the 1GB program into the 1MB physical main memory so that the program can execute
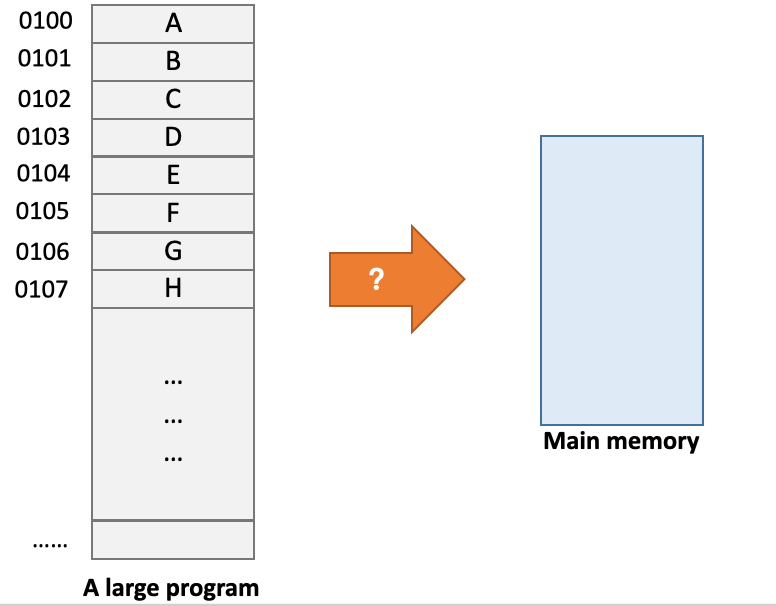
Program Image

The program image is too large to be fit into the main memory
Process
Executing a program
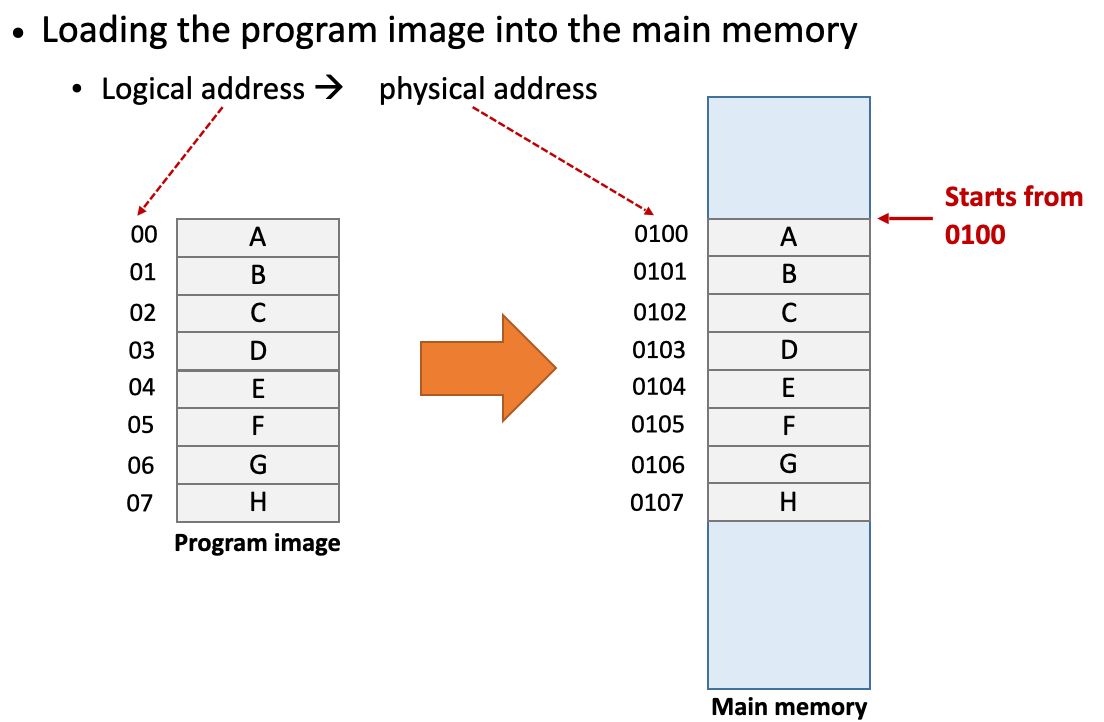
Memory access in program execution
During execution, the CPU frequently goes to main memory to fetch data (instructions, data)「在执行期间,CPU经常进入主存储器以获取数据(指令,数据)」
Paging
- Chunk the program image into virtual pages「将程序映像分块为虚拟页面」
- into physical pages, also called frames「将主内存分成物理页面,也称为框架」
- Each time, load a page into a specific frame of the main memory「每次将页面加载到主存储器的特定帧中」
Each time, load a page into a frame of the main memory
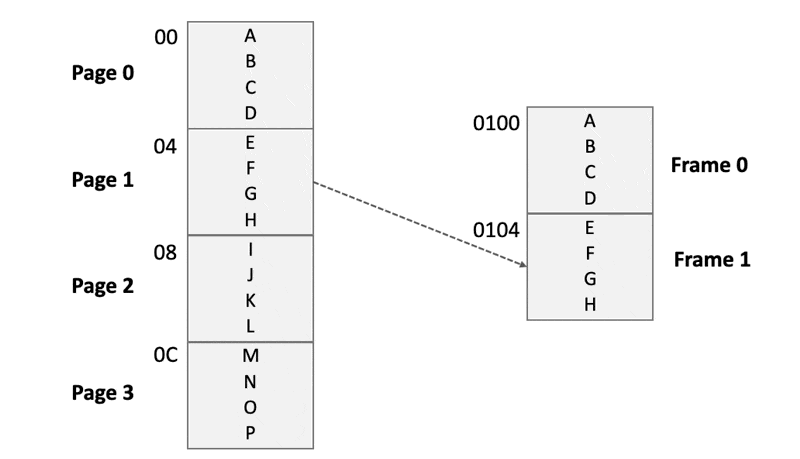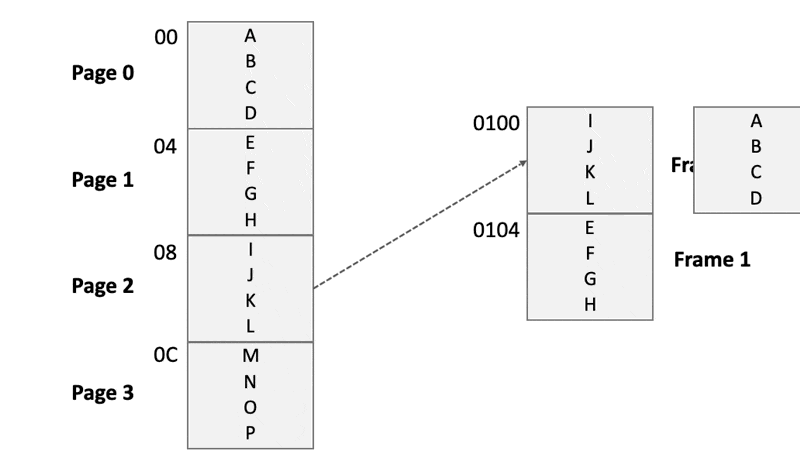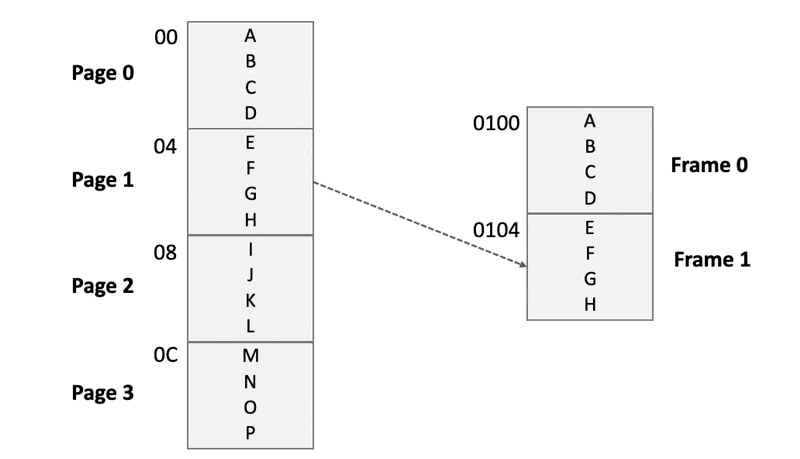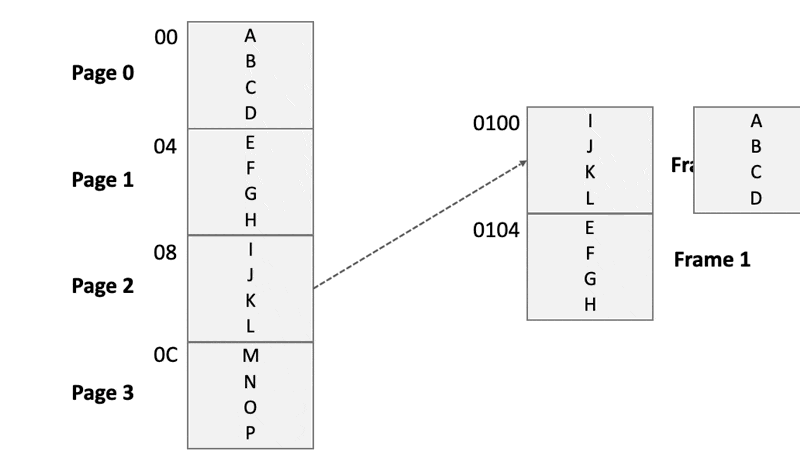
Page 2 will use the physical address that has been used by Page 0
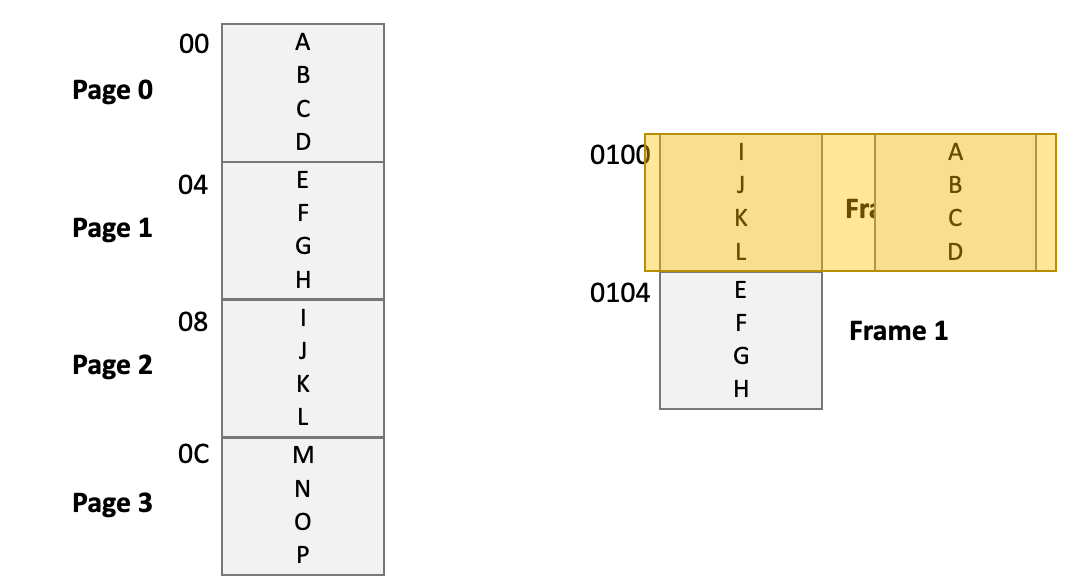
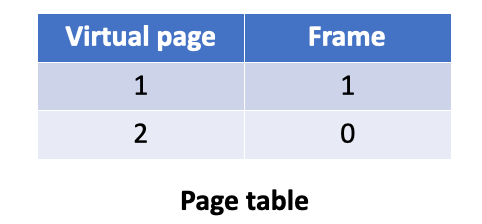
Issue 1: needs to remember which page is put into which frame
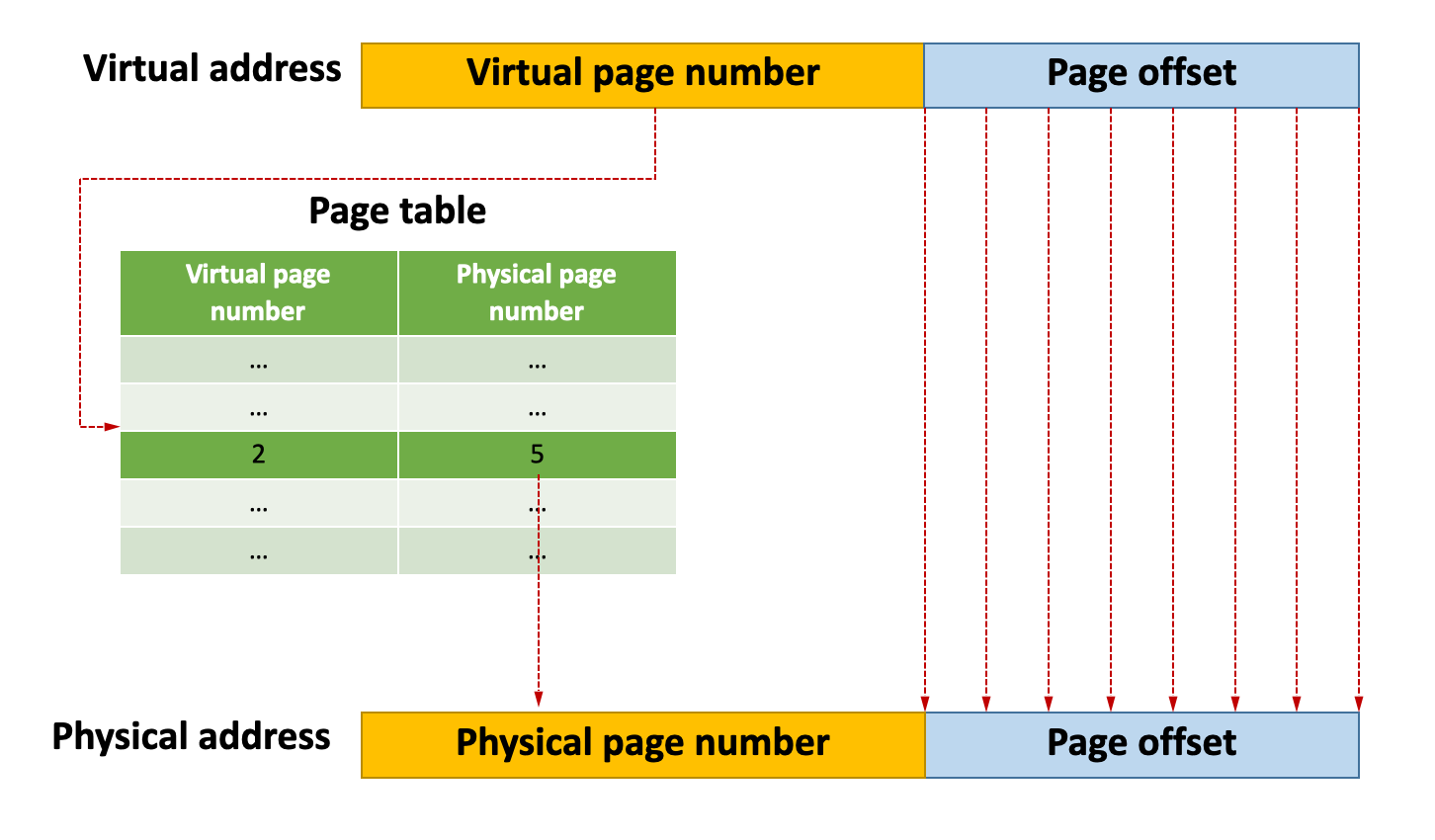
Page table: a mapping from virtual pages to frames
Issue 2: if the memory is full, and a new page will be loaded, which old page to replace?
- Similar to cache
- Many replacement policies, leveraging locality
Page table
页表的大小是 Number of page table entries「页表条目数」
一般的,一行有一个条目「entires」
体积大小
- Page entry size = virtual page bits + physical page bits
- Page table size = Number of page table entries * entries
General Address translation
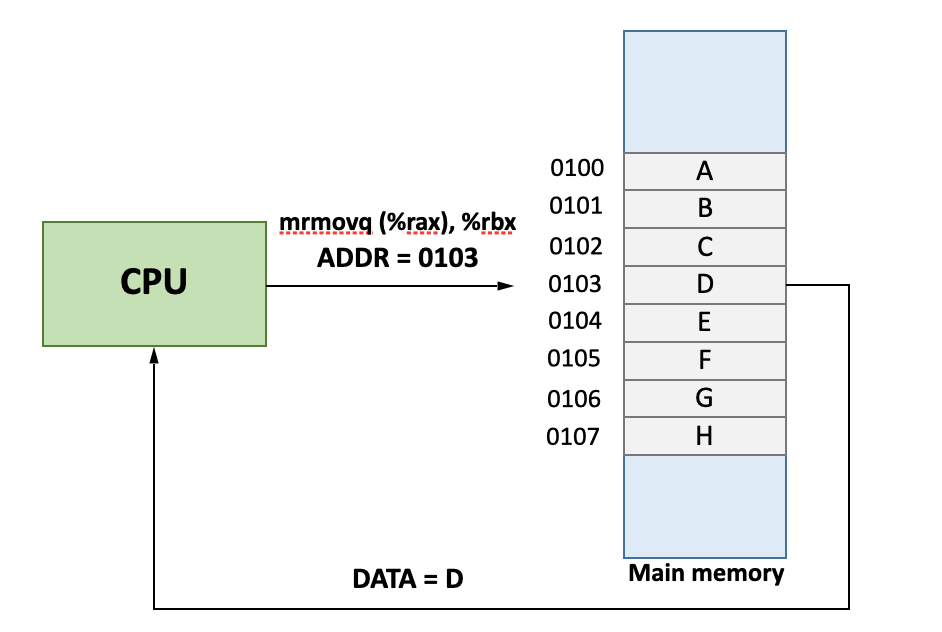
If I want to use a data item in my executable file, which has been loaded to main memory, how do I know the physical address of the data item?「如果要在可执行文件中使用已加载到主存储器中的数据项,我如何知道该数据项的物理地址?」
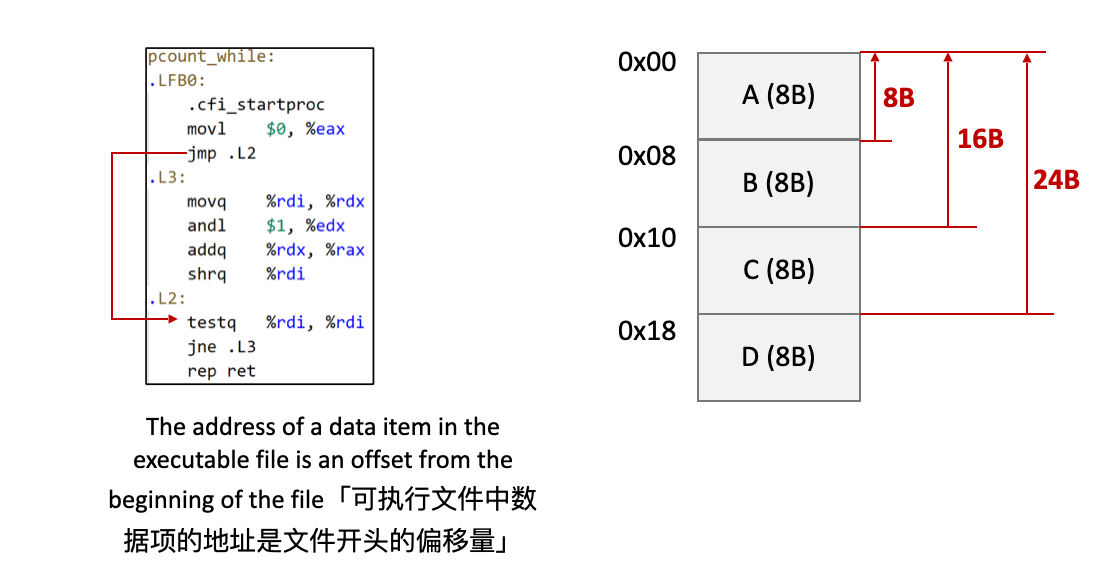
To access “G” in physical main memory
- That is, to determine the physical address of “G”
- Which page is “G” in? -> page 1
- Where is page 1 loaded to? -> frame 3
- What’s G’s offset in page 1? -> 0x10 away for the start of page 1
- Physical address = start address of frame 3 + G’s offset
- 0x0100 + 0x10 = 0x0110
- Go to main memory with address 0x0110, you will get data item G
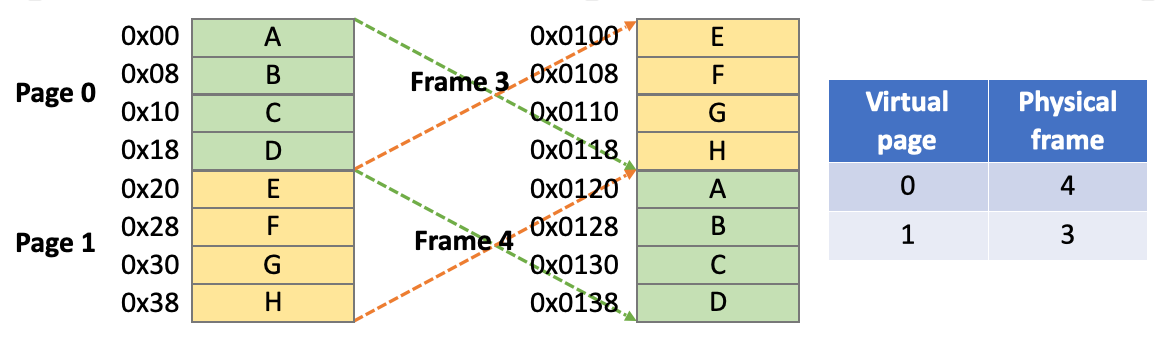
General steps
我们在系统层面看到的都是虚拟地址。
- Virtual address (x) 由 page number (x) 和 offset (x) 组成
- Check page table, page number (x) -> frame number (x)
- Frame number (x) -> starting address (x)
- Starting address (x) + offset (x) = physical address (x)
If we want to access “b” which is in page 2. When we check the page table, do not find page 2 (page fault)
- page 2 has not been loaded into physical memory
- load page 2 into main memory
- if no space, kick out some old page
- do address translation for b, get b’s physical address
- fetch b from main memory to CPU
Example
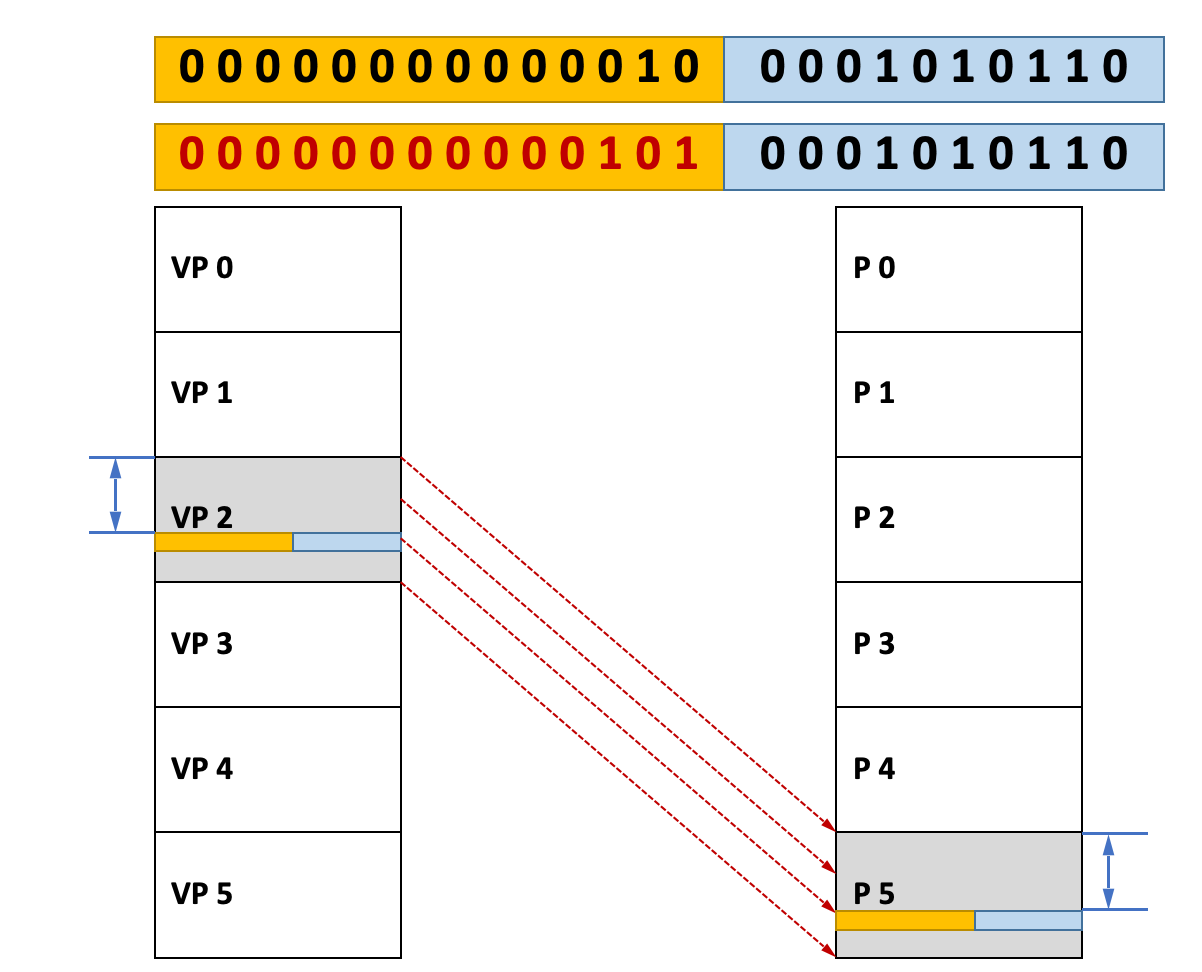
- Assume we use 24bits for an Virtual address
- Assume the first virtual page/physical page is numbered from 0
- In a paging system, the size of one page is 1KB
1KB = 1024 Bytes = 2^10 bytes 我们需要10位来存储 offset (x)
剩下的 24-10 = 14位 来存储Page number
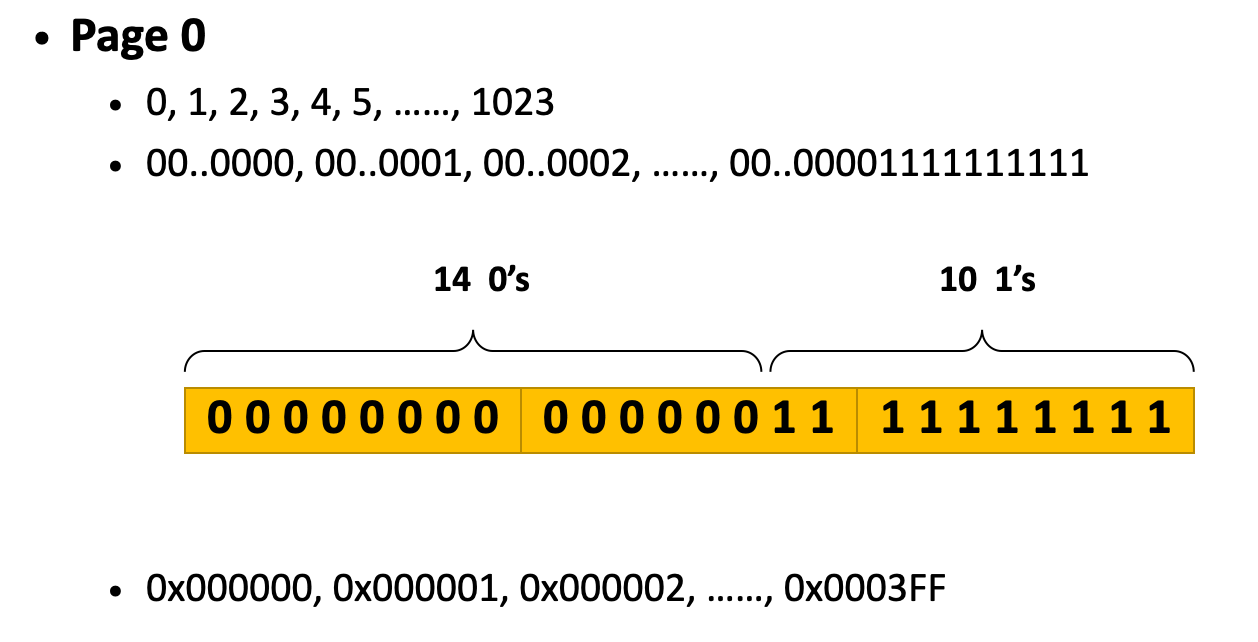
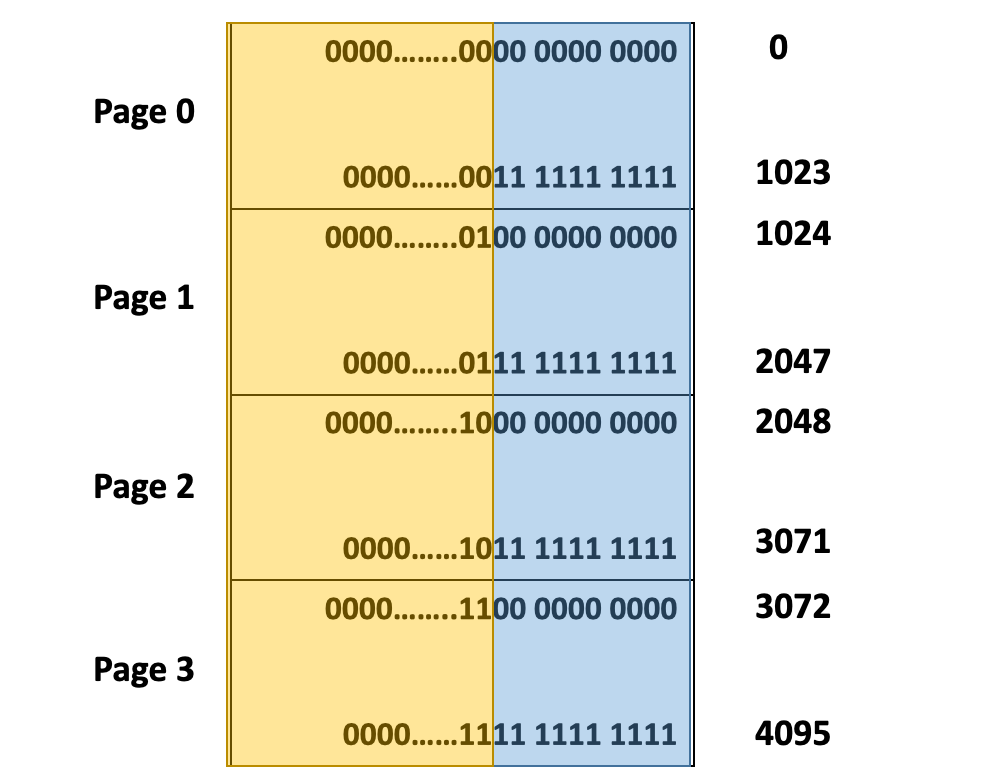
在Page Table里,我们只需记录 Virtual Page Number 。在每个Page里,每个条目的前14位相同。
offset 用于表示偏差
Memory Management Unit
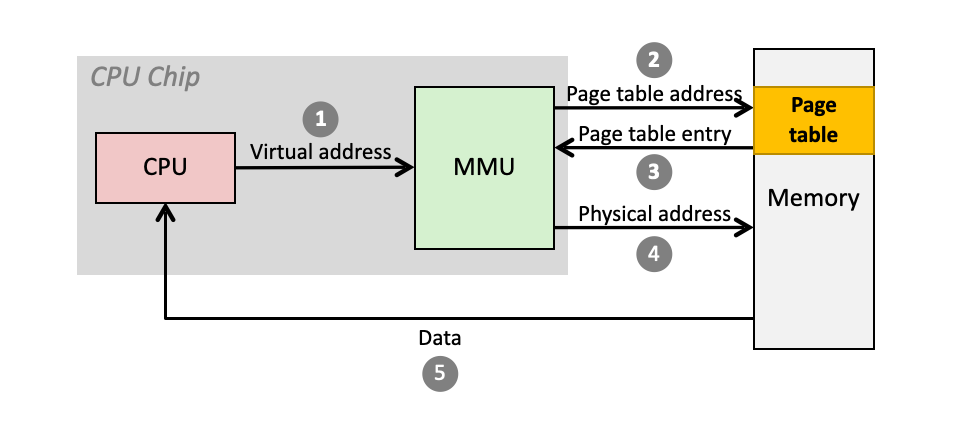
Address translation is done by a special hardware in CPU called Memory Management Unit (MMU)「地址转换由CPU中称为内存管理单元(MMU)的特殊硬件完成。」
- Address translation is too complex and slow
- We need a fast worker to do the job
Translation lookaside buffer
Accessing page table in main memory is slow
Translation lookaside buffer (TLB): a cache for page table in the CPU chip
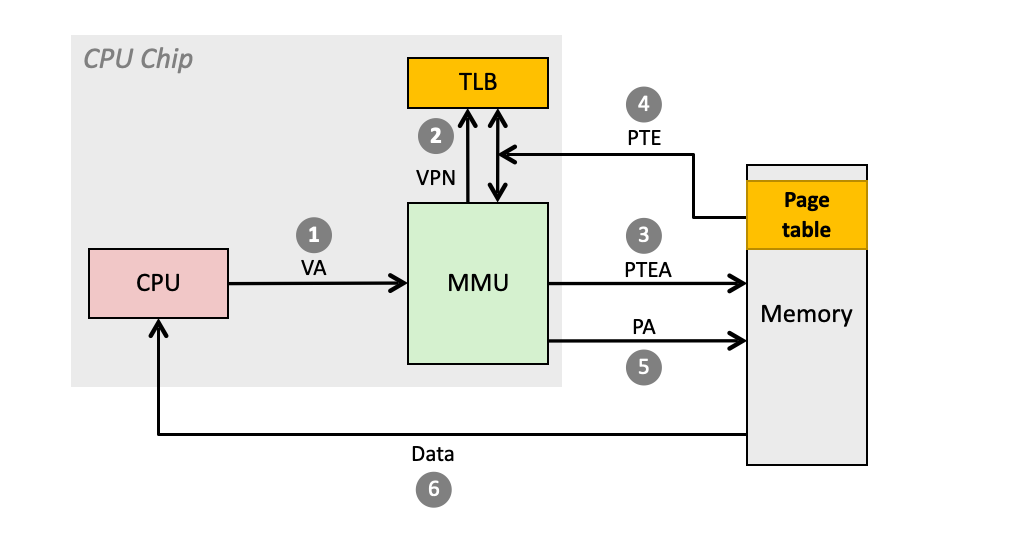
Other question
VM as a way for memory management「VM作为内存管理的一种方式」
- The need for memory management
- There are multiple processes in the system sharing the memory
- Memory space is generally insufficient for all the processes
- Targets of memory management
- How to allocate memory space to concurrent processes?「如何为并发进程分配内存空间?」
- Space efficiency
- How to provide protection so that process A cannot access the data of process B?「如何提供保护,以使进程A无法访问进程B的数据?」
- How to allocate memory space to concurrent processes?「如何为并发进程分配内存空间?」
Memory allocation to multiple processes
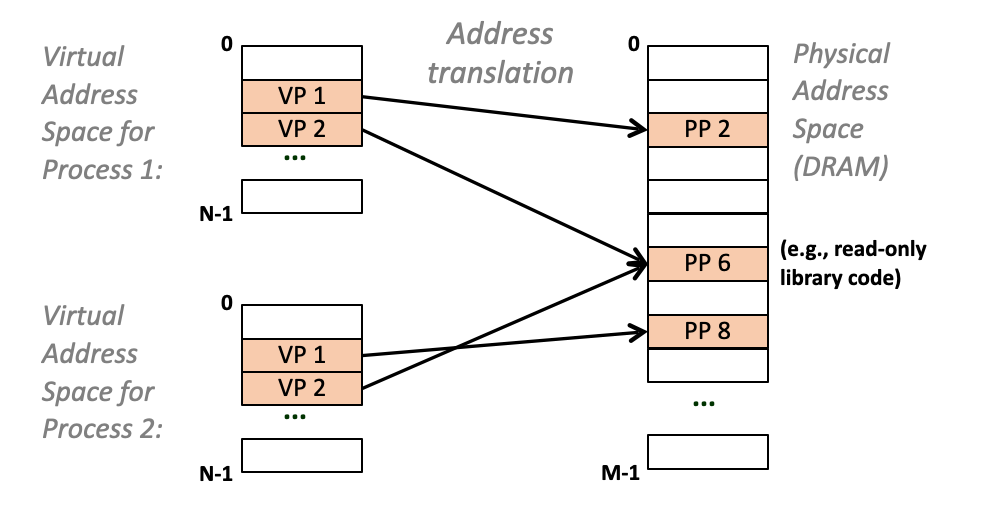
Memory allocation for multiple processes「多个进程的内存分配」
- Each process can use a specific amount of physical pages「每个过程可以使用特定数量的物理页面」
- Each virtual page can be mapped to any physical page「每个虚拟页面都可以映射到任何物理页面」
- A virtual page can be stored in different physical pages at different times「虚拟页面可以在不同时间存储在不同的物理页面中」
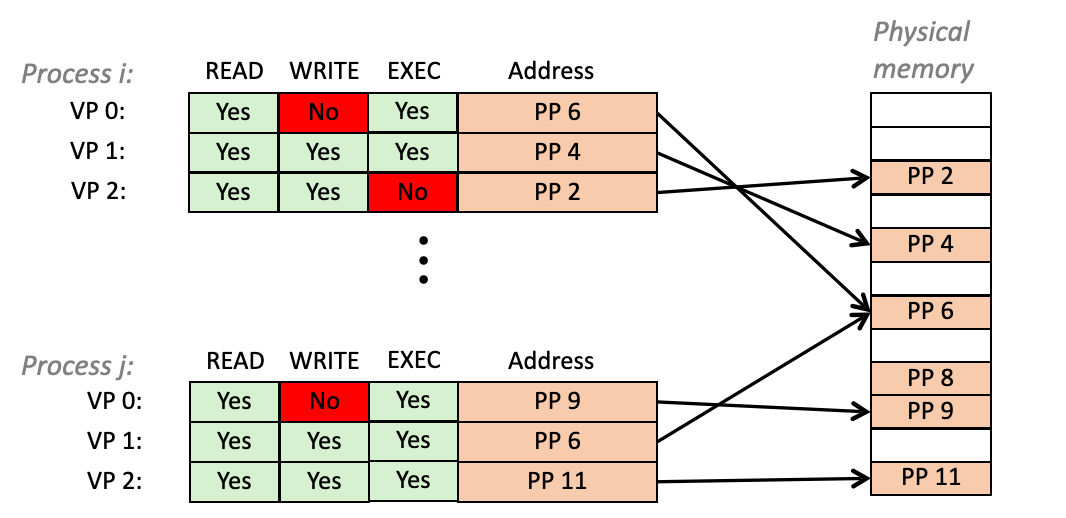
Memory protection
- Extend page table entries with permission bits
- MMU will check these bits on each access
引用
- COMP1411's PowerPoint