Searching Algorithms
大约 7 分钟
Searching Algorithms
Goal
Given an array A of n numbers (in ascending order)
- Find the position of a key k from the array A
- return –1 if not found
A: | 1 | 3 | 8 | 12 | 17 | 23 | 35
Algorithm 1: Linear search
Assume k appears at most once in the array. Once k is found, the algorithm stops.
- Best Case: K is in the first element
- Worse Case: K is in the last element; element not found
- Average case: Half of the array is searched
for(int i=0;i<n;i++){
if(A[i]==target){
returni;
}
else{
return-1;
}
- Worse Case: O(n): K is in the last element/element not found
- Best Case: O(1): K is in the first element
- Average case: O(n): Half of the array is searched
- Overall, the running time of linear search is O(n): Most of the time we are interested in the worse case: You know for certain that the algorithm must perform at least that well「总体而言,线性搜索的运行时间为O(n):在大多数情况下,我们对最坏的情况感兴趣:您可以肯定地知道该算法至少必须表现得很好」
Algorithm 2: Binary search
- Suppose someone picks a number k between 1 and 100
- You are allowed to ask questions of the form “Is k greater than x”, where x is an integer you choose
- Ask as few questions as possible
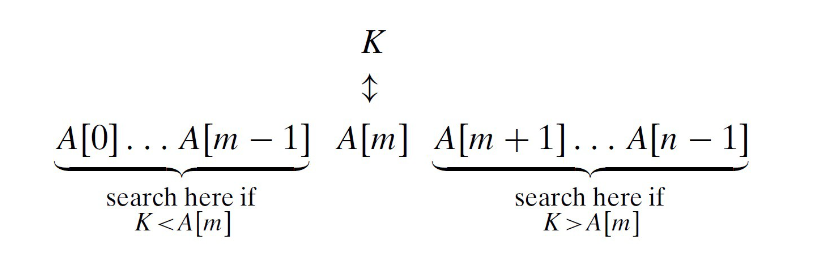
Binary search for a sorted array
- Comparing a search key K with the array’s middle element A[m]「将搜索键K与数组的中间元素A [m]进行比较」
- If they match, the algorithm stops;「如果它们匹配,则算法停止」
- Otherwise, the same operation is repeated for the first half of the array if K <A[m] , or for the second half if K>A[m]
- When to stop: If the remaining array to be searched is empty, then the key cannot be found and return -1「如果要搜索的其余数组为空,则找不到键并返回-1」
Code
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main() {
//init the array and target value
int arr[10] = {5,98,62,90,90,76,90,12,7,5};
int target = 12;
// sort the array
const int ARRAY_SIZE = 10;
int* data = arr;
int insert;
for (int next = 1; next < ARRAY_SIZE; next++) {
insert = data[next];
int moveItem = next;
while ((moveItem > 0) && (data[moveItem - 1] > insert)) {
data[moveItem] = data[moveItem - 1];
moveItem--;
}
data[moveItem] = insert;
}
// show the sorted array
for(int i = 0;i<10;i++){
cout << data[i] << " ";
}
// search
int l = 0,r= ARRAY_SIZE,m;
while (l <= r){
m = (l+r)/2;
if(target == data[m]){
cout << endl << m;
break;
} else if(target < data[m]){
r = m - 1;
} else{
l = m + 1;
}
}
return 0;
}
Example


Time complexity of binary search
- Basic operation: The number of times the search key is compared with an element of the array「搜索键与数组元素进行比较的次数」
- Assume three-way comparison: after one comparison of K with A[m], the algorithm can determine whether K is smaller, equal to, or larger than A[m]「在将K与A [m]进行一次比较之后,该算法可以确定K是小于,等于还是大于A [m]」
- Worse case: The key is not in the array「密钥不在数组中」

引用
- COMP1011 @ PolyU's PowerPoint