CPP面向对象编程入门
CPP面向对象编程入门
Structure
Allow programmers to create a container for a collection of data items (variables) which can be different types.「允许程序员为可能是不同类型的数据项(变量)的集合创建一个容器。」
Such container is regarded as a new data type.「这样的容器被视为一种新的数据类型。」
The definition of a structure is a blueprint「蓝图」 of what variables the structure should contain.「结构的定义是该结构应包含哪些变量的蓝图。」
Struct 的实质是“容器”。可以看做一个类型。每个这种类型的“盒子”里面可以包含很多变量。
Defined
To define a structure
struct structure_name {
data_type variable1;
data_type variable2;
...
};
To declare the structure (or create a variable of it)
structure_name variable_name;
Example
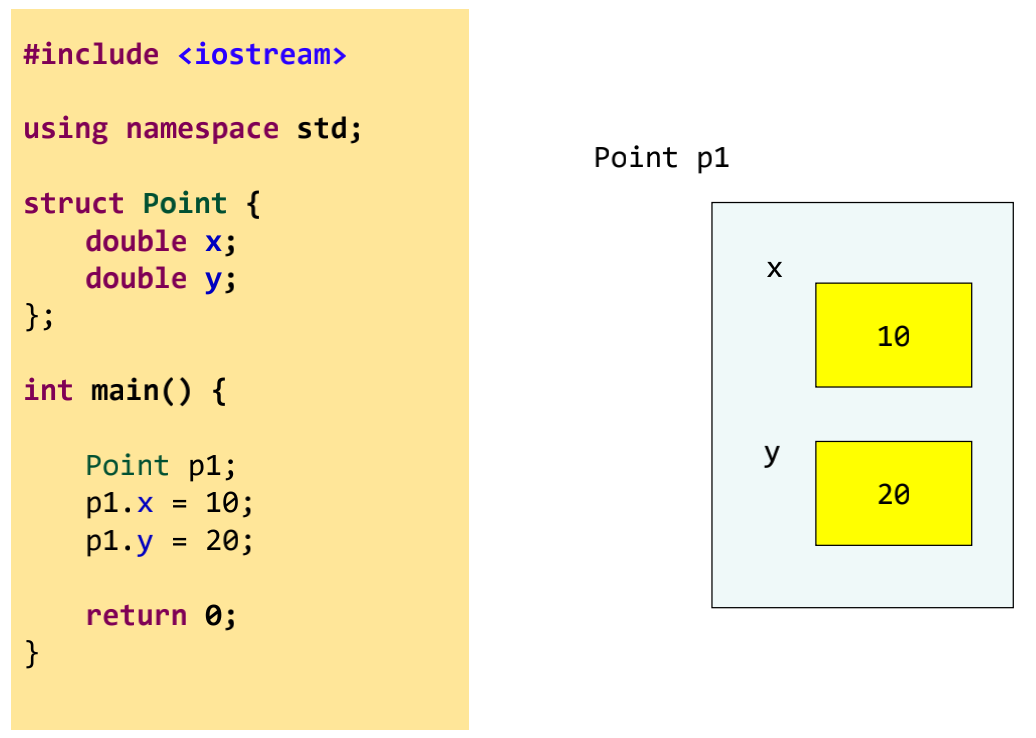
struct Point {
double x;
double y;
};
We can group the coordinates x and y into a structure called Point「我们可以将坐标x和y分组为一个称为Point的结构」
To create a Point variable
Point p1;Point sunset;Point arrayOfTimes[5];Point *pointerToTime;
To assign a value to x of p1:
p1.x = 10;To assign a value to y of p1:
p1.y = 20;To use the variable
int num = p1.x; // assign the value to another variable cout << p1.x << endl; // print p1.x out
实例应用
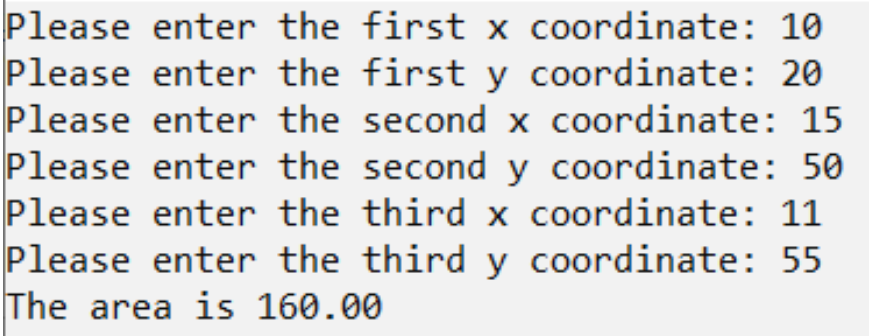
The following program computes the area of a triangle. It first reads in 3 pairs of coordinates x and y and then computes and displays the area of triangle.「以下程序计算三角形的面积。它首先读取3对坐标x和y,然后计算并显示三角形的面积。」
#include <iostream>
#include <cmath>
#include <iomanip>
using namespace std;
struct Point { // Define a point structure
double x;
double y;
};
int main() {
Point p1, p2, p3;
// Ask for inputs
cout << "Please enter the first x coordinate: ";
cin >> p1.x;
cout << "Please enter the first y coordinate: ";
cin >> p1.y;
cout << "Please enter the second x coordinate: ";
cin >> p2.x;
cout << "Please enter the second y coordinate: ";
cin >> p2.y;
cout << "Please enter the third x coordinate: ";
cin >> p3.x;
cout << "Please enter the third y coordinate: ";
cin >> p3.y;
// Calculate and display the area
cout << "The area is " << fixed << setprecision(2) << fabs((p3.y - p1.y) * (p2.x - p1.x) - (p2.y - p1.y) * (p3.x - p1.x) / 2.0) << endl;
return 0;
}
Comparison (relational operators)
To compare struct, you compare them member-wise

Array Structure
我们可以创建一个 Struct 类型的数组,比如
To declare an array of Point with a size of 3 and assign values to each set of x and y:「要声明一个大小为3的Point数组,并为每组x和y赋值:」
Point p[3];
p[0].x = 10;
p[0].y = 26;
p[1].x = 31;
p[1].y = 43;
p[2].x = 56;
p[2].y = 69;
Example
bank.cpp
#include <iostream>
#include <cstring>
using namespace std;
struct BankAccount {
int accountNo;
double balance;
};
struct BankCustomer {
char name[51];
int age;
char gender;
char address[101];
BankAccount accounts[3];
};
void deposit(BankCustomer&, int, double);
void print(const BankCustomer&);
int main() {
BankCustomer bc;
// initialize the bank customer values
strcpy(bc.name, "Dennis Liu");
bc.age = 20;
bc.gender = 'M';
strcpy(bc.address, "PQ730, Mong Man Wai Building, PolyU");
bc.accounts[0].accountNo = 1234;
bc.accounts[0].balance = 1000;
bc.accounts[1].accountNo = 0;
bc.accounts[2].accountNo = 0;
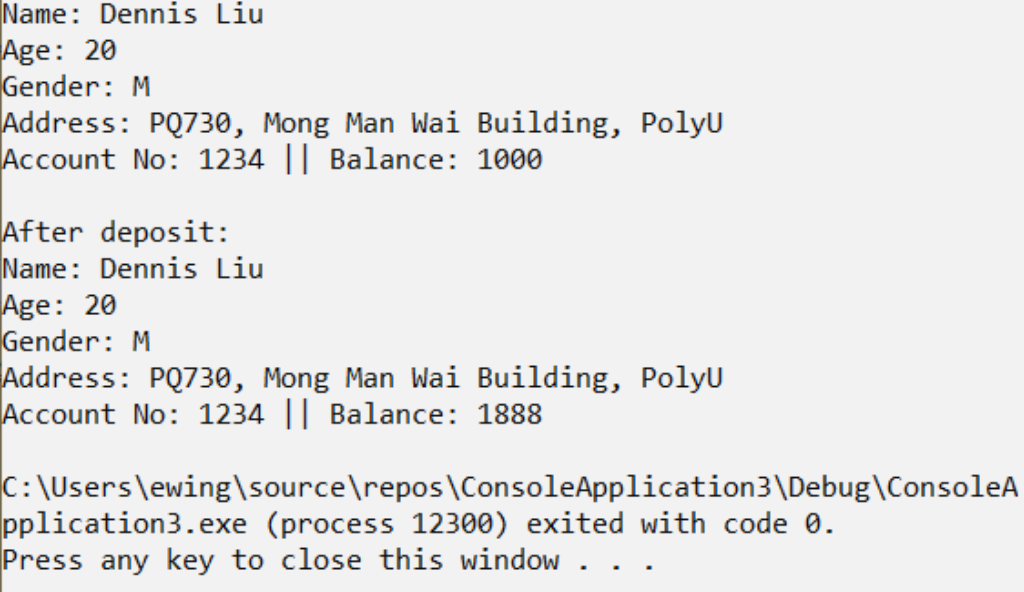
cout << "Before deposit:" << endl;
print(bc);
deposit(bc, 1234, 888);
cout << endl;
cout << "After deposit:" << endl;
print(bc);
return 0;
}
void deposit(BankCustomer &bc, int depositAcc, double amount) {
if (amount > 0) {
for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++) {
if (bc.accounts[i].accountNo == depositAcc) {
bc.accounts[i].balance += amount;
}
}
}
}
void print(const BankCustomer &bc) {
cout << "Name: " << bc.name << endl;
cout << "Age: " << bc.age << endl;
cout << "Gender: " << bc.gender << endl;
cout << "Address: " << bc.address << endl;
for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++) {
if (bc.accounts[i].accountNo != 0) {
cout << "Account No: " << bc.accounts[i].accountNo << " || Balance: " << bc.accounts[i].balance << endl;
}
}
}
Call
Call-by-value in function by default
To avoid overhead of copying the whole structure (may contain a lot of member variables and structures), we should use call-by-reference instead「为了避免复制整个结构(可能包含很多成员变量和结构)的开销,我们应该使用call-by-reference代替」
使用指针访问
Point dot;
dot.x = 10
dot.y = 15
Point* ptr = &dot
cout << dot.x << endl; // 输出 10
cout << (*ptr).y << endl; // 输出 15 (加括号的原因是 .的优先级大于 *)
cout << ptr -> x << endl; // 输出 10
注意:不可以直接 输出 dot 或者 *ptr ,因为它是一个“放置变量的容器”。
注意:只有指针变量才能使用 - > 运算符。
Object-oriented Programming
Object-oriented Programming(OOP)面向对象编程
To understand the concept of object-oriented programming, we must differentiate the following two terms「要理解面向对象编程的概念,我们必须区分以下两个术语」
- Class「类」
- Object「对象」
- method / Member Functions「方法/成员函数」
- property / Data Members「属性/ 数据成员」
注:举个例子,int是一个类(整数类);int x,x是一个对象,是int类的一个对象。再举个例子:Point 是一个类,Point y, y是一个对象,是Point类的一个对象。
注意:C++ 里面没有 method 、property 这一说法,只有 Member Functions 、Data Members 这一说法。说错了可能会被当成外行人。
Class
a framework/template/blueprint/definition of an entity
For example: Human
A normal Human has the following properties:
- Eye
- Ear
- Mouth
- Nose
In C++ terminology, the above are the attributes/data members possessed by a Human「在C ++术语中,以上是人类所拥有的属性/数据成员」
Object
An actal entity of a class「类的实际实体」
Mary is a Human:Mary is an object of the class Human
Mary has
- Eye – Beautiful
- Ear – Big
- Mouth – Small
- Nose – Hawk-liked
The green adjectives are the “values” of the attributes
In C++ terminology, an object is an instance of a class
Besides Mary, Peter is also a Human
Peter may have different “values” from Mary
- Eye – Single-edged
- Ear – Long
- Mouth – Big
- Nose – Flat
Mary is an object of Human
Peter is another object of Human
Understand
我们通过以下例子来理解OOP
We rewrite the structure Time in the previous example using the approach of writing a class Time
Time.h: Header file——So the file extension is .h
class Time {
public:
Time(); // constructor 1
Time(int, int, int); // constructor 2
void setTime(int , int, int); // set hour,minute,second
void printUniversal(); // print universal-time format
void printStandard(); // print standard-time format
private:
int hour; // 0 - 23 (24-hour clock format)
int minute; // 0 - 59
int second; // 0 - 59
};
- Contain the declaration of the class: Like the concept of prototype
- No main() function
- The file is not executable
- To be included in other source files
#include "Time.h"(注意不是< >)
注意:class 中的函数是无顺序的,class中的函数不需要按循序执行,只是按需调用。
Constructor
Time()
- Same name as the class name(如果要创建 Constructor 只需让其名称和 类的名称相同即可)
- Called once only when an object is created: Will not be called again after object creation「仅在创建对象时调用一次:创建对象后将不会再次调用」
- Mainly used for initializing data members of the class
- A class may have a number of constructors, with different input arguments「一个类可能具有许多构造函数,并且具有不同的输入参数」
- No return type
在source file里,我们可以这样使用 Constructor
Time solt1; //无参数,匹配到 constructor 1
Time solt2(9,0,0); //匹配到 constructor 2
constructor 没有return
Member Functions
Member Functions 也叫 method。
调用方式:ClassName.FunctionName()
在上述的例子里,以下是类的方法
void setTime(int, int, int);
void printUniversal();
void printStandard();
Member function 还能 被定义在 class外
Binary scope resolution operator ( :: )
- “Ties” member name to class name 「将成员名称与班级名称联系起来」
- Uniquely identify functions of particular class
- Different classes can have member functions with same name 「不同的类可以具有相同名称的 Member function」
Format for defining member functions「定义成员函数的格式」如下
ReturnType ClassName::MemberFunctionName(arguments)
{
…
}
批注:即我们可以实现在class的括号内声明方法,在class的括号外定义方法。当然没有声明和定义在哪里没有任何限制。而且即使方法定义在class的大括号外面,方法可以直接调用class中定义的属性和方法。注意使用 ClassName::MemberFunction()表示; Constructor也可以在class外定义
Data Members
Data Members 也叫 property.
调用方式:ClassName.MemberName
在上述的例子里,以下是类的属性
int hour;
int minute;
int second;
Each Time object has its own set of data members: hour, minute and second.「每个Time对象都有自己的一组数据成员:hour, minute and second」
Since these data members are private, they can only be accessible by its member functions 「由于这些数据成员是私有的,因此只能通过其成员函数进行访问」
注意:只有 public 下的 属性和方法 可以被外界函数访问;private下的属性和方法不能被外界访问;public下的函数可以操作private下面的属性和方法。详细的在之后讨论。
Invocation
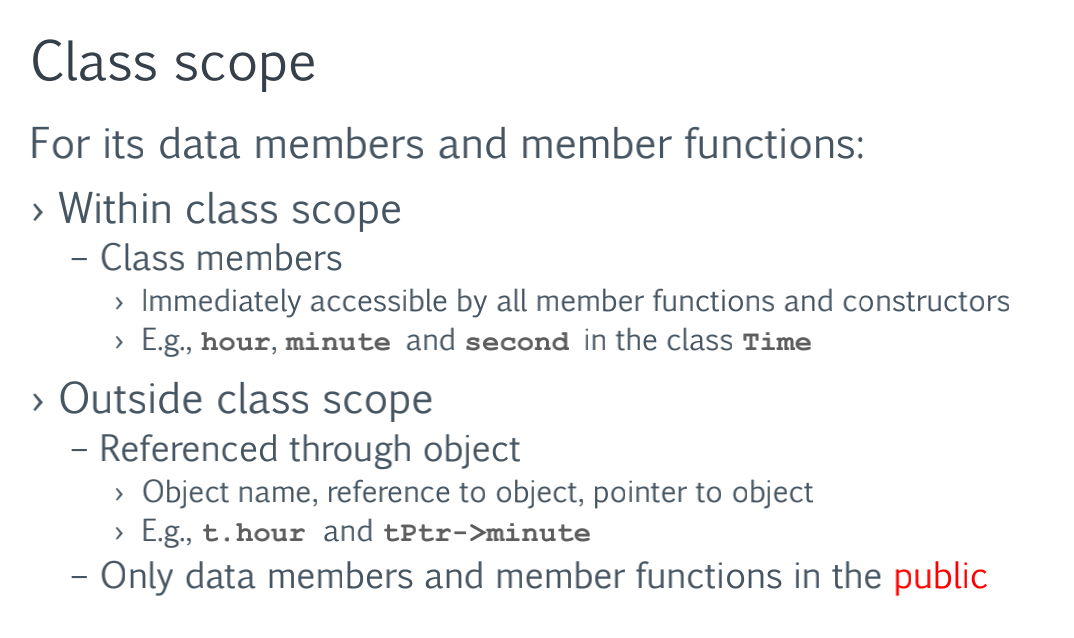
在外界可以通过 variableName.method() 或者 variableName.property 调用
t.hour
t.printUniversal();
t.printStandard();
t.setTime(13, 27, 6);
Access Specifiers
public: Accessible by the “outside world” relative to the class
private: Accessible only to constructors and member functions of class
private data members cannot be accessed (both read and write) by the “outside world”
Controlling Access to Members
- Class member access
- Explicitly set to private, and public
- Default private without Specifier
- struct member access
- Default public without Specifier
- Explicitly set to private, public, protected
- Access to class’s private data
- Controlled with access member functions
- Get function (accessor) – Read private data
- Set function (mutator) – Modify private data
- Controlled with access member functions
Scope

Advantages
- Code reuse
- A collection of classes forms the library as programming utilities
- No “re-inventing the wheel”
- Interfaces
- Data encapsulation (information hiding) and implementation hiding
注意
Struct 和 Class 里面要包含什么呢
class Entry {
private:
static int get_id(){
static int number = 0;
number += 1;
return number;
}
public:
Entry *next = nullptr;
Entry *prev = nullptr;
int id = get_id();
};
这个例子,可以看到,有一下两种语句
- 函数的定义
- 变量的声明/定义/初始化
但是,不能在 成员函数以外 进行写除了 上面两个以外 的任何语句;
Struct 和 Class 的对比
- Structure
- Contain data items only
- All data are implicitly public
- Less data integrity control capabilities
- Class
- Contain data members and object behaviours (member functions)
- Hide information using private
- More data integrity control capabilities
- Extensible
批注
含义上
- struct更适合看成是一个数据结构的实现体
- class更适合看成是一个对象的实现体。
功能上
相同点:它们都可以提供自己的接口函数,构造函数。
struct 没有 public 和private 之分,但 class 有。
struct没有继承,没有封装,要说封装只有初步封装。
struct只能叫做数据的集合,外部可以任意访问。
一个class可以由结构继承而来。
class把数据,接口可以以三种类型封装,private,public,protected;还可以继承和派生。
class就完成了封装,维护了数据安全,这就是面向对象的理念
最本质的一个区别就是默认的访问控制:默认的继承访问权限
struct是public的,class是private的。
Header file
Head file 里面放什么?
- Class definitions and member function prototypes「类定义和成员函数原型」
但是,head file 里面成员函数外面,不可以定义变量! 但可以声明。
Included in each file using class. Eg. #include "Time.h"
声明、定义和初始化
- 声明:用于向程序表明变量的类型和名字。
- 定义:用于为变量/函数分配存储空间,还可为变量/函数指定初始值。程序中,变量/函数有且仅有一个定义。
- 定义,定义的同时会完成声明。
- 变量初始化:声明+定义+变量赋值
extern int a; //声明,不是定义
int b; //声明,也是定义,未初始化
int c = 10; //声明,也是定义,也初始化了
extern double max(double d1,double d2); //声明
double max(double d1,double d2); //声明
double max(double d1,double d2);
{
XXX
} //声明+定义
Public、Protected和Private
Private, Public, Protected下的访问性不同
表现在 访问者不同 、继承特点不同
- Private:只能由该类中的函数、其友元函数访问,即只允许本类的成员函数访问
- Protected:可以被该类中的函数、子类的函数、以及其友元函数访问,但不能被该类的对象访问,即只允许子类及本类的成员函数访问
- Public: 可以被该类中的函数、子类的函数、其友元函数访问,也可以由该类的对象访问,即可以被任意实体访问
什么叫被该类的对象访问?eg. student.id
注:友元函数包括两种:设为友元的全局函数,设为友元类中的成员函数
C++类对象共享数据的实现
使用局部变量和全局变量共享数据
使用局部变量能够在调用和被调用函数之问通过参数传递实现不同函数块之问的数据共享。局部变量具有局部作用域,能很好地实现函数之间的数据隐蔽。但在传递过程中需要很大的系统开销,故一般只用于传递少量的数据。全局变量具有文件作用域。全局变量所存储的数据在程序中任何地方都可以访问,能够在程序中的所有函数之间实现数据共享。使用全局变量实现共享数据相当方便,但其副作用也相当大。因为全局变量无法对数据的访问权进行有效控制。也就是说,我们很难知道程序中数据在那些函数中共享,这样一旦共享的数据发生结构性调整,也就很难判断它到底影响到哪些函数,从而给程序维护带来相当大的困难。这种共享方式,直接影响到数据安全、程序代码重用和扩充。所以,在程序设计中,应可能少的使用这种共享方式。
通过类的数据成员共享数据
C++中类内部封装的数据成员提供了同一类的函数成员之间进行数据共享机制。这种共享方式一方面实现了类内部函数的全面共享,同时也提供了通过设置适当的访问控制属性,把共享只限制在类的范围之内,这样对类外来说,类的数据成员仍是隐藏的,达到了共享与隐藏两全,解决了全局变量和局部变量所无法克服的矛盾。
例如:一个时钟类,该类中封装了私有数据成员有Hour,Minute,Second,在类的成员函数之间实现数据共享。在类的外面,对它们的访问只能通过类自身提供的外部接口进行,无法直接访问。
class Clock //时钟类的声明
{
public:
//公有数据成员函数
void SetTime(int NewH =0,int NewM =0,int News=0);
void ShowTime();
private://私有数据成员
int Hour,Minute,Second;//在类的成员函数之间共享
}
通过类的静态成员实现数据共享
C++中使用静态成员可以实现同一类的不同对象之间共享数据 j。类的普通数据成员在类的每一个对象都有一个拷贝,就是说每个对象的同名数据成员可以分别存储不同数值,这就保证对象拥有自身区别其他对象的特征的需要。静态数据成员是类的数据成员的一种特例,采用static关键字来声明;每个类只有一个拷贝,由该类的所有对象共同维护和使用,从而实现了同一类的不同对象之间的数据共享。
如果想实现和Private的访问者限制相同的且只属于自己的属性,要在Private下使用 static 定义。
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class Entry {
private:
static int get_id(){
static int number = 0;
number += 1;
return number;
}
public:
Entry *next = nullptr;
Entry *prev = nullptr;
int id = get_id();
};
int main() {
Entry a,b;
cout << b.id << a.id << endl;
return 0;
}
静态成员变量确实起到了在不同对象间共享的作用!不过由于其是静态属性,内存是在全局/静态区域开辟的,属于栈内存区,内存大小使用受限。如果能动态从堆中申请内存,则可以使用大内存空间了。
Example
有一学生类:
class engineer
{
Private:
int ID;
char nalne;
static count;//静态数据成员,用来存放“人数”
string name;
}
Source-code files
- Member function definitions
- Compiled and linked
- File extension .cpp
附加材料
time.h
// prevent multiple inclusions of header file
#ifndef TIME_H
#define TIME_H
class Time {
public:
Time(); // constructor
void setTime(int, int, int); // set hour, minute, second
void printUniversal(); // print universal-time format
void printStandard(); // print standard-time format
private:
int hour; // 0 - 23 (24-hour clock format)
int minute; // 0 - 59
int second; // 0 - 59
};
// Time constructor initializes each data member to zero and
// ensures all Time objects start in a consistent state
Time::Time() {
hour = minute = second = 0;
}
// set new Time value using universal time, perform validity
// checks on the data values and set invalid values to zero
void Time::setTime(int h, int m, int s) {
hour = (h >= 0 && h < 24) ? h : 0;
minute = (m >= 0 && m < 60) ? m : 0;
second = (s >= 0 && s < 60) ? s : 0;
}
// print Time in universal format
void Time::printUniversal() {
cout << setfill('0') << setw(2) << hour << ":"
<< setw(2) << minute << ":"
<< setw(2) << second;
}
// print Time in standard format
void Time::printStandard() {
cout << ((hour == 0 || hour == 12) ? 12 : hour % 12) << ":" << setfill('0') << setw(2) << minute << ":" << setw(2) << second << (hour < 12 ? " AM" : " PM");
}
time.cpp (在source file里调用time.h)
#include <iostream>
#include "Time.h" // Include the header file to this source
using namespace std;
int main() {
Time t;
// output Time object t's initial values
cout << "The initial universal time is ";
t.printUniversal(); // 00:00:00
cout << "\nThe initial standard time is ";
t.printStandard(); // 12:00:00 AM
t.setTime(13, 27, 6); // change time
// output Time object t's new values
cout << "\n\nUniversal time after setTime is ";
t.printUniversal(); // 13:27:06
cout << "\nStandard time after setTime is ";
t.printStandard(); // 1:27:06 PM
t.setTime(99, 99, 99); // attempt invalid settings
// output t's values after specifying invalid values
cout << "\n\nAfter attempting invalid settings:" << "\nUniversal time: ";
t.printUniversal(); // 00:00:00
cout << "\nStandard time: ";
t.printStandard(); // 12:00:00 AM
cout << endl;
return 0;
}
运行结果如下
The initial universal time is 00:00:00
The initial standard time is 12:00:00 AM
Universal time after setTime is 13:27:06
Standard time after setTime is 1:27:06 PM
After attempting invalid settings:
Universal time: 00:00:00
Standard time: 12:00:00 AM