Input: Perception
Input: Perception
- 物理接收:眼睛接收光线并将其转化为电能
- 神经节细胞检测模式和运动
- 视网膜包含用于弱光视觉的杆状物和用于彩色视觉的锥状物
Brightness
- 对光的水平的主观反应
- 受物体亮度的影响
- 用明显的差异来衡量
- 视觉敏锐度随着亮度的增加而增加,闪光也是如此。
Pattern filters
神经节细胞「ganglion cells」
- 某些神经元作为模式过滤器工作
- 滤波器对中频的通过率比对高频和低频的通过率更好
- 互相压制 (来自单个细胞的随机噪声被较大的群体所纠正)
Color
- 色调「hue」(基于光的波长)
- 强度(较浅/较深)
- 饱和度(颜色中色调的纯度)
- 饱和度越高,颜色就越纯。
- 锥体对颜色的波长敏感
- 同样,相互抑制
- 蓝色敏锐度最低
- 8%的男性和1%的女性是色盲
相关信息
- 颜色不是光的物理学属性
- 颜色是人类对击中细胞的不同能量频率(短波、长波)的解释
Perception
- CT 扫描是物体的切片,显示几个层次。人眼也是如此
- 然而,由于电子眼是一个球体,视网膜上的图像是颠倒的。
- 此外,它还缩小了(视网膜上的尺寸不是实际尺寸)。
注
- 提醒你,你有两只眼睛,所以有两个颠倒的图像。
- 这两个图像是从不同的角度拍摄的
- 为了将它们合二为一,它们进入了视丘。
- 图像被分割:左边是右边,右边是左边
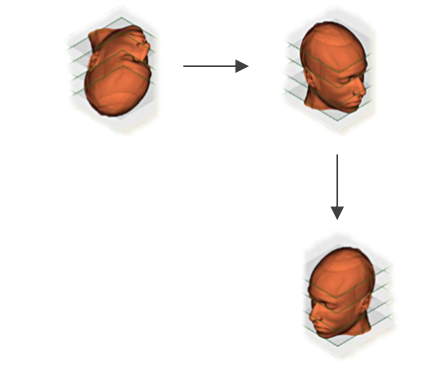
但在图像从视觉皮层传递到下一站之前,它必须:翻转、旋转和调整大小\
3D
3D视觉不是视网膜上图像的属性(它是2D的)。深度的错觉是如此强烈,以至于它敦促我们的大脑调整物体的大小,以适应我们对环境的概念性解释。
- 尺寸和深度
- 视觉角度表明物体占据视野的多少
- 与眼睛的大小和距离有关
- 视觉敏锐度是指感知精细细节的能力「Visual acuity is ability to perceive fine detail」
- "尺寸不变定律"「Law of size constancy」是指尽管视觉角度发生变化,熟悉的物体仍被视为尺寸不变。
- 像 "重叠"「overlapping」这样的线索有助于对大小和深度的感知
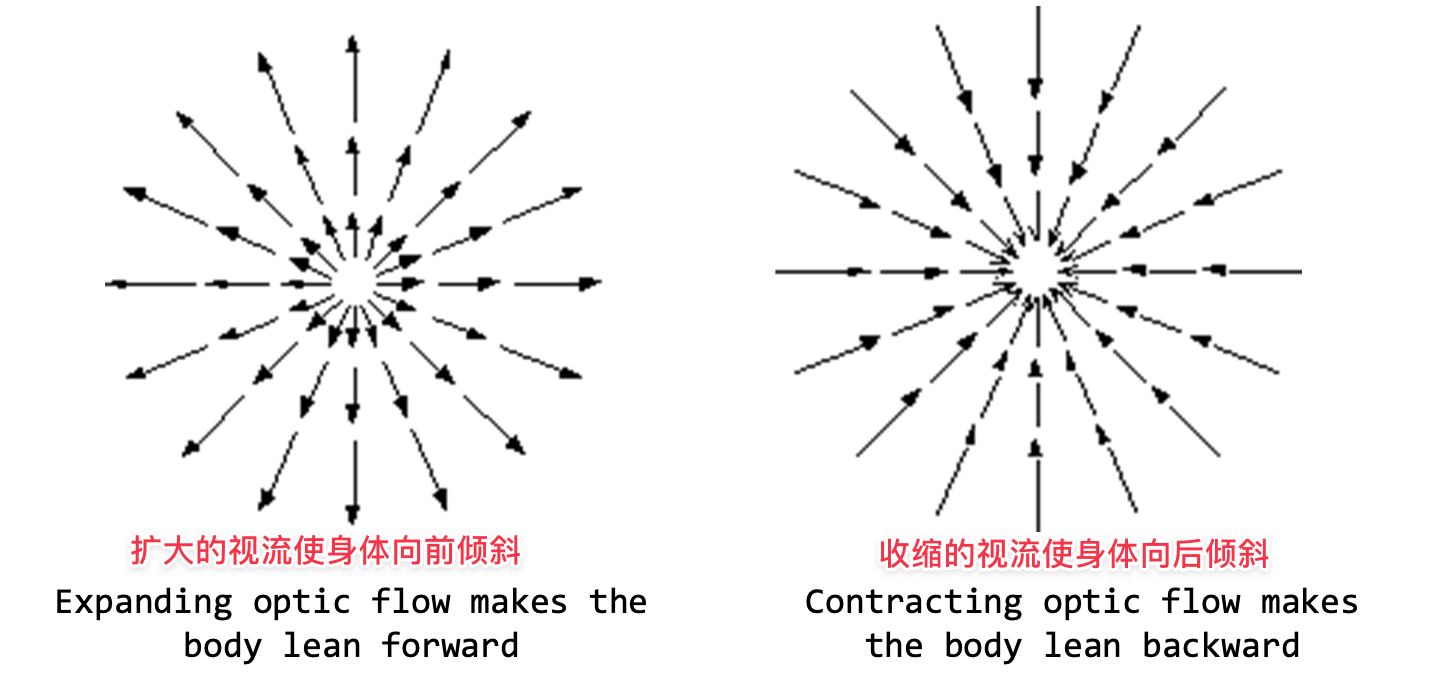
视力流是大脑的的提示,以计算在空间中的位置空间。视流「 Optic flow」是大脑计算空间位置的线索,通过运动进行定位「motion」。
- 头部移动时通过运动看到3D
- 大脑将其解释为:短路径在长路径后面;因此,一定有深度。
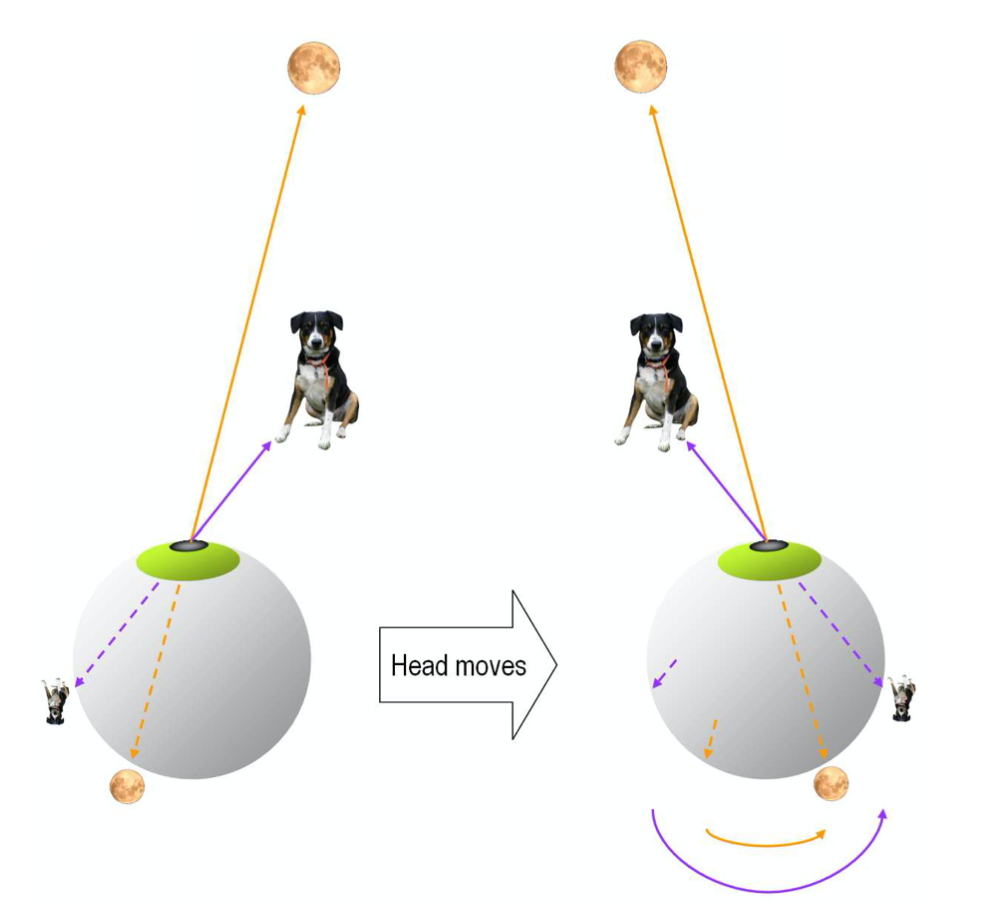
Motion parallax「运动视差」:物体离开视野的方向表示物体在物理世界中的运动方向,月亮与你同行(这可能不是真的)。
因此,3D视觉不是视网膜上图像的属性(它是2D的)。
- Visual angle indicates object size「视觉角度显示物体大小」
- Related to size and distance from eye「尽管视觉角度有变化,但尺寸不变」
- Expanding optic flow indicates ‘we go forward’「扩大光流表明“我们前进”」
- Contracting optic flow indicates ‘backward’「收缩的视网膜流表示 "向后"。」
- Long retinal path indicates ‘close by’「长的视网膜路径表示“靠近”」
- Short retinal path indicates ‘far away’「短的视网膜路径表示“很远”」
- Side of leaving visual half field indicates motion direction「离开视觉半区的一侧表示运动方向」
Pattern Recognition
Pattern recognition: Similarity
相似的物品往往被归类在一起
Most people will see columns of squares and circles,rather than rows of alternating shapes 「大多数人看到的是一列列的正方形和圆形,而不是一排排的交替形状。」
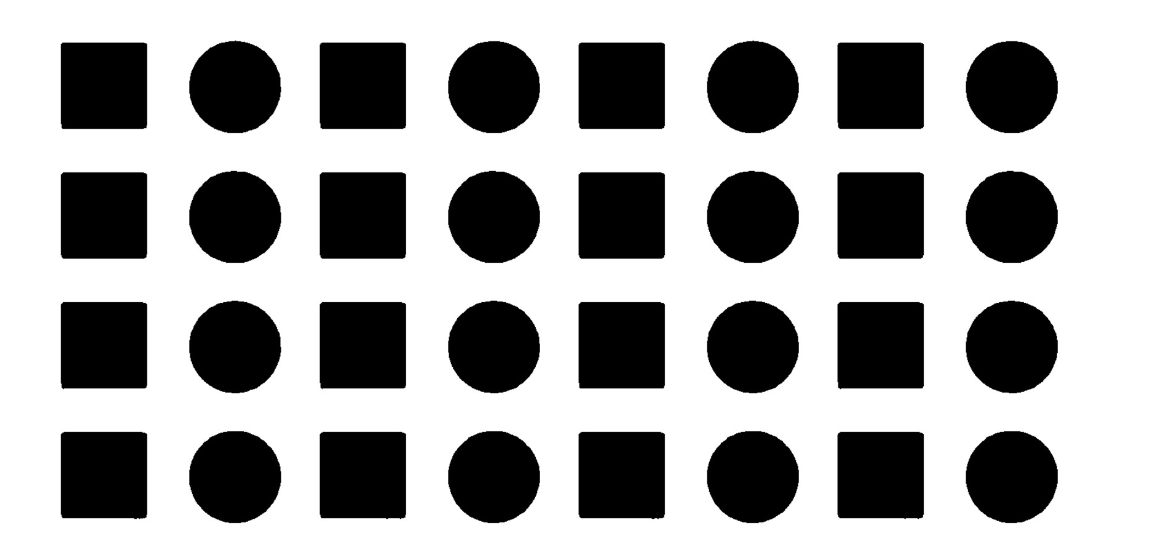
人类倾向于识别模式,即使在没有模式的地方。
Example
具有相同背景颜色的选项被用户自动 "捆绑 "在一起
相互靠近的物体往往被归为一组:我们最可能看到左边的圆圈被分成两列,右边的圆圈被分成两行。
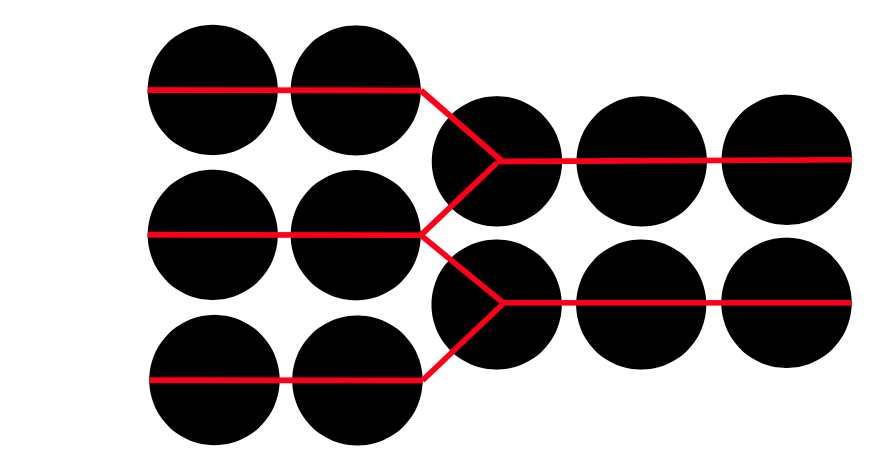
Pattern recognition: Proximity
接近
Pattern recognition: Symmetry
对称性
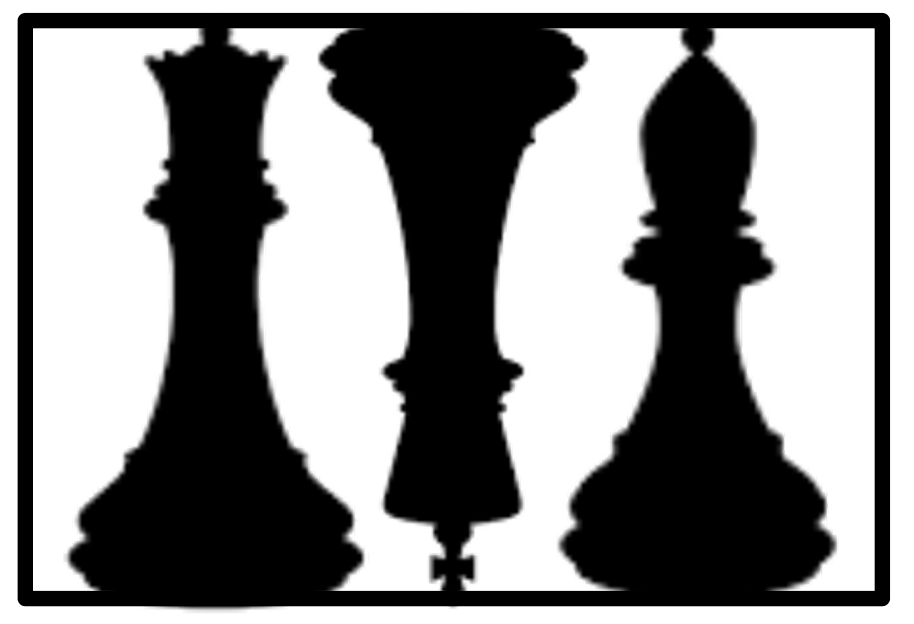

在矩形中,我们最有可能感知到白色背景下的三个黑色对称图形(而不是黑色背景下的四个不对称的白色物体)。
Pattern recognition: Continuity
- 连续性
- 线条被视为遵循最平滑的路径
Pattern recognition: closure
被组合在一起的物体被看作是一个整体。我们倾向于忽略空隙和完整的线条


Pattern recognition: Surroundedness

被其他地区包围的地区往往被看作是独立的人物
Consequences
- 因此,模式识别不是数据的属性(计算频率可能也是如此)。
- To turn data into information, the following happens: DATA ->INFORMATION
Summary
- 某些神经元作为模式过滤器工作(例如,通过中频比通过高频和低频更好「pass middle frequencies better than higher and lower frequencies」)。
- Random noise from individual cells is corrected by the larger group
- Brightness is subjective reaction to levels of light「亮度是对光线水平的主观反应」
- 锥体对光的波长敏感。颜色不是光的物理属性,而是人类对击中细胞的不同能量频率(短波、长波)的解释。
- 3D processing. 3D is NO property of the retina’s 2D image「三维处理。三维是视网膜的二维图像的无属性」
- slicing up (eye fixations)「切片(眼睛注视)」
- imputing missing data from memory (concept-driven percept)
- shrinking images
- taking them from different angles
- splitting them up「拆分它们」
- left goes right, right goes left
- merging
- flip
- rotate「旋转」
- resize (blow up)
- Size and depth are derived from visual angle, distance from eye, and image overlap
- Sizes of known objects are assumed to have constant size despite changes in visual angle
- Position in space is derived from motion (expanding = forward, contracting = backward)
- The direction in which an object leaves the visual field indicates the direction of object motion
- the side of your direction means object goes with you,opposite side of your direction means object stays behind
- Patterns are formed according to:
- similarity rather than dissimilarity
- proximity rather than distance
- symmetry rather than asymmetry
- continuity rather than discontinuity
- closure rather than openness
- small things rather than big things (which form 'the background')
- data that are surrounded by different data indicate an individual event rather than an integral part
The eye filters,selects,and changes data so to make an interpretation of the world about us.
- Color is not a property of light but of the eye's receptors.
- 3D vision results from manipulations by the brain to create a depth illusion.
The brain uses heuristics such as similarity, continuity,and proximity to make sense of information that passes the eye.
Patterns are not the result of recognition but rather of human construction. 「模式不是识别的结果,而是人类构造的结果」