Introduction
大约 12 分钟
Introduction
Types of Money
- Token money「代币资金」
- represented by a physical article (e.g., cash)
- can be lost
- Notational money「记名货币」
- a kind of scriptural money「经文货币」, can be electronic
- e.g., bank accounts, frequent flyer miles
- Hybrid money
- e.g., check, telephone card
| Token 代币 | Notational 记名票 | Hybrid | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Fiduciary (信托货币) | Cash: 现金 Govt. Bearer Bond:政府持票人债券是一种无记名债券,持有人可以随时兑现其面值。 | Account with a Central Bank:中央银行账户是指商业银行在中央银行开设的账户,用于存放准备金和进行清算。 | Government Check:政府支票是一种由政府机构签发的支票,用于支付政府开支或退税等。 |
| Scriptural (记账货币) | Certified Check:保付支票是一种由银行认证的支票,确保支票金额已被冻结,确保收款人能够收到款项。 Traveler Check:旅行支票是一种预付的支票,通常用于旅行时代替现金使用。 | Bank Account:银行账户是一种由银行为客户提供的账户,用于存储和管理资金。 Frequent-Flyer Miles:常旅客里程是一种航空公司为鼓励乘客频繁乘坐其航班而提供的奖励积分。 | Personal Check:个人支票是由个人签发的支票,用于支付日常开支。 Gift Certificate:礼品券是一种预付的礼券,可以在指定商店或网站上兑换商品或服务。 |
- Money order「汇票」: only the named person can claim money
- Traveler’s check: spendable by only one spender
Desirable/Ideal Properties of Money
- Universal acceptance
- Transferability, portability
- Safety (unforgeable, unstealable)「安全性(不可伪造、不可窃取)」
- Privacy (no one except parties「当事人」 know the amount)
- Anonymity「匿名性」 (no one can identify the payor「付款人」)
- Work off-line (no need for on-line verification)「离线工作(无需在线验证)」
- Divisible into change (pay for $10 item with $100 bill)「可分割为零钱(用 100 美元的钞票购买 10 美元的商品)」
- Arbitrary denominations (consider $689.14)「任意面额(考虑 689.14 美元)」
The Bitcoin Revolution
- 去中心化 点对点支付系统
- 作为货币使用:有价值单位
- 可以兑换成 "真钱"。
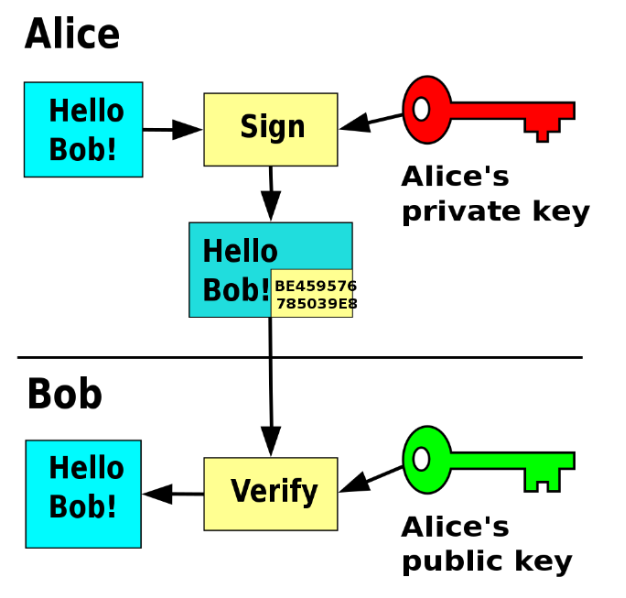
Digital Signatures
Started from a probabilistic 「概率性的」algorithm “KeyGen” that generates a key-pair:
- A pair of public key and private key
- 它们必须一起生成并且它们是“相关的”
- 要签名,请使用私有(签名)密钥 sk
- 要进行验证,请使用公共(验证)密钥 pk
E-Cash Issuance
Centralized Solution
- An e-coin is a digital signature issued by a central bank. 「电子币是由中央银行发行的数字签名。」
- 电子硬币现在由一堆字节表示。
- The merchant「商家」 verifies a coin w.r.t. the cert. of the bank
- 每个人都可以复制这些字节,并将其用于其他地方。
- Each needs a (signed) serial number # like paper money
- This will be useful for double-spending detection.
- But the merchants are not connected to each other.
- They need confirmation (with bank) that it hasn’t been spent
- Connectivity issue for the merchant, privacy issue for the payer
- Privacy issue: The bank can link the coin # with the withdrawal and spending!
E-Cash Solutions
Blind Signatures
盲签名(Blind Signatures)是一种密码学协议,允许一方在不知道消息内容的情况下对其进行签名。该技术由David Chaum在1983年提出,主要用于保护用户隐私。
The notion of Blind Signatures
- Bank can sign on serial number sn without knowing it
- User pick sn, blinds it sn’ = C(sn)
- 用户选择一个序列号(sn),然后通过某种加密函数(C)将其进行“盲化”处理,得到盲化后的序列号(sn’)。
- 这个过程确保了银行无法知道原始的序列号。
- Bank signs on sn’, user unblind the signature to get sig(sn)
- 银行对盲化后的序列号(sn’)进行签名
- 用户接收到签名后,通过反盲化过程将其还原为对原始序列号(sn)的签名(sig(sn))。
How about spending?
- 接收方需要与银行核对序列号(sn)是否已经被使用过,以防止重复使用。
- “Real system” is more complex [e.g., Compact E-Cash「紧凑型电子现金」]
- 因此,这种系统无法完全实现类似现金的隐私保护,因为每次交易都需要与银行进行核对。
Double spending?
- the payee「收款人」 must deposit with a bank「收款人必须将收到的电子现金存入银行。」
- the bank holds the list of spent coins (consensus needed if 2+ banks 「如果有 2 家以上银行,则需要达成共识」)
- [目标] 追踪并抓住双重花费者。
- zero-knowledge proofs to encrypt ID when spending
Zero-knowledge proof
零知识证明是一种密码学技术,
- 允许一方(证明者)向另一方(验证者)证明某个陈述为真,
- 而无需透露任何其他信息。
它确保了信息的隐私和安全。
假设你想证明你知道某个秘密密码,但不想透露密码本身。通过零知识证明,你可以向对方证明你确实知道密码,而不揭示密码的任何细节。