x86汇编语言基础2
x86汇编语言基础2
Processor states (x86-64, partial)
Information about currently executing program「有关当前执行程序的信息」
- Temporary data:( %rax, … )
- Location of runtime stack:( %rsp )
- Location of current code control point「Location of current code control point」:( %rip, … )
- Status of recent tests「Status of recent tests」:( CF, ZF, SF, OF )
这些信息放在寄存器内
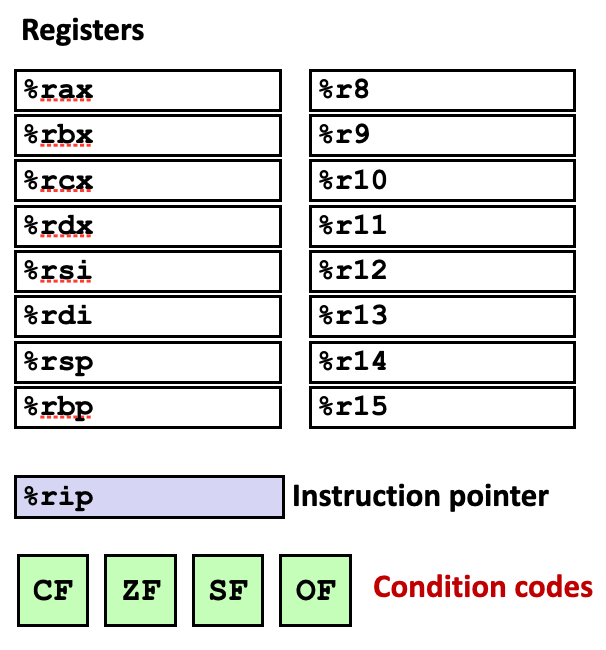
Condition codes
Single bit registers
条件码长 1bit,置放在三个寄存器中。
- CF Carry Flag (for unsigned)
- SF Sign Flag (for signed)
- ZF Zero Flag
- OF Overflow Flag (for signed)
Implicitly set (as side effect) by arithmetic operations
「通过算术运算隐式设置(作为副作用)」
Example: addq Src,Dest ↔ t = a+b
- CF set if carry out from most significant bit (unsigned overflow)
- ZF set if t == 0
- SF set if t < 0 (as signed)
- OF set if two’s-complement (signed) overflow
- a>0 && b>0 && t<0) || (a<0 && b<0 && t>=0)
Note: leaq does not alter any condition codes
注:像add、sub、xor这样的算数指令或者二进制计算指令都会通过隐式设置改变condition code
Explicit Setting by Compare Instruction
cmpl/cmpq Src, Dest
cmpl b,a like computing a-b without setting destination, but no actual subtraction is really conducted, i.e., the value of dest is not changed
- CF set if carry out from most significant bit (unsigned overflow)
- ZF set if t == 0
- SF set if t < 0 (as signed)
- OF set if two’s-complement (signed) overflow
- a>0 && b>0 && t<0) || (a<0 && b<0 && t>=0)
Explicit Setting by Test instruction
testl/testq Src, Dest
testl b,a like computing a&b without setting Dest with the computing result
Sets condition codes based on value of Src & Dest
Useful to have one of the operands be a mask「掩码」
ZF set when a&b == 0
SF set when a&b < 0
Reading condition codes
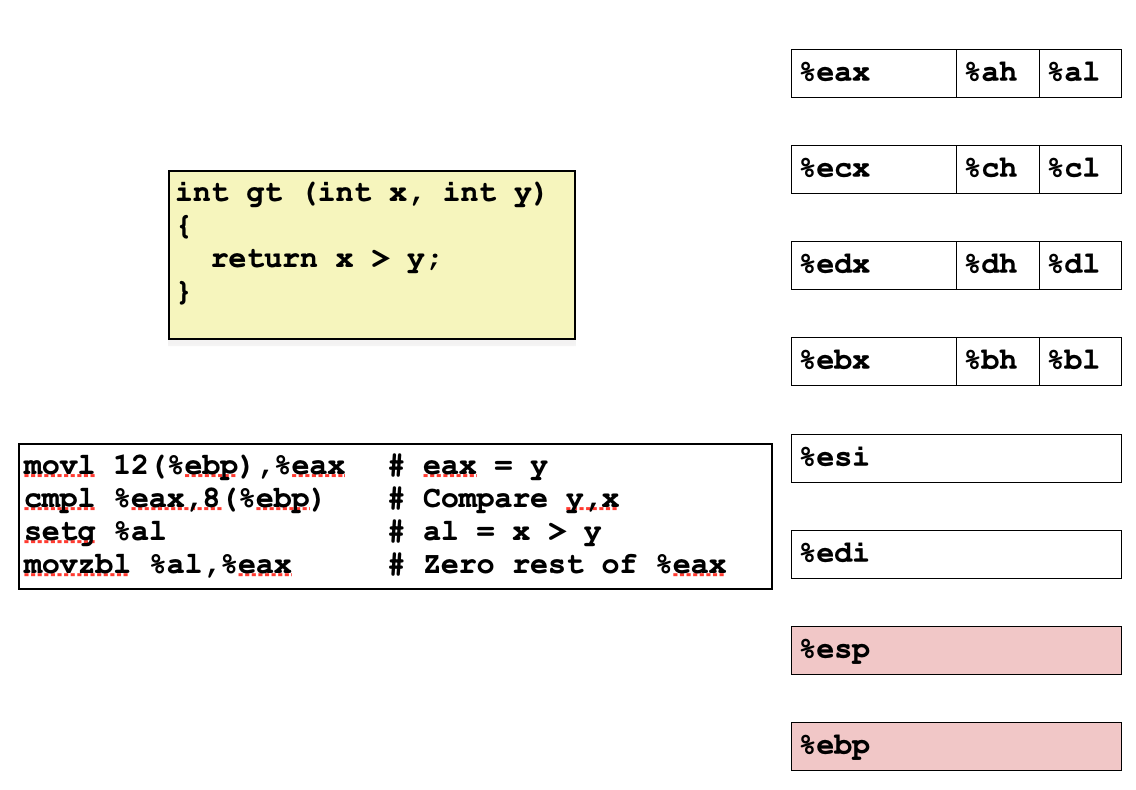
SetX Instructions
Set single byte based on combinations of condition codes
| SetX | Condition | Description |
|---|---|---|
| sete | ZF | Equal / Zero |
| setne | ~ZF | Not Equal / Not Zero |
| sets | SF | Negative |
| setns | ~SF | Nonnegative |
| setg | (SF^OF)&ZF | Greater (Signed) |
| setge | ~(SF^OF) | Greater or Equal (Signed) |
| setl | (SF^OF) | Less (Signed) |
| setle | (SF^OF)|ZF | Less or Equal (Signed) |
| seta | CF&ZF | Above (unsigned) |
| setb | CF | Below (unsigned) |
批注:一般为 setX reg;如果condition成立,reg将变成1,反之则为0;
SetX Instructions: Set single byte to (0 or 1) based on combination of condition codes「根据条件代码的组合将单字节设置为(0或1)」
addressable byte registers or memory「可寻址字节寄存器或存储器」
- Does not alter remaining 3 bytes
- Typically use movzbl to finish job
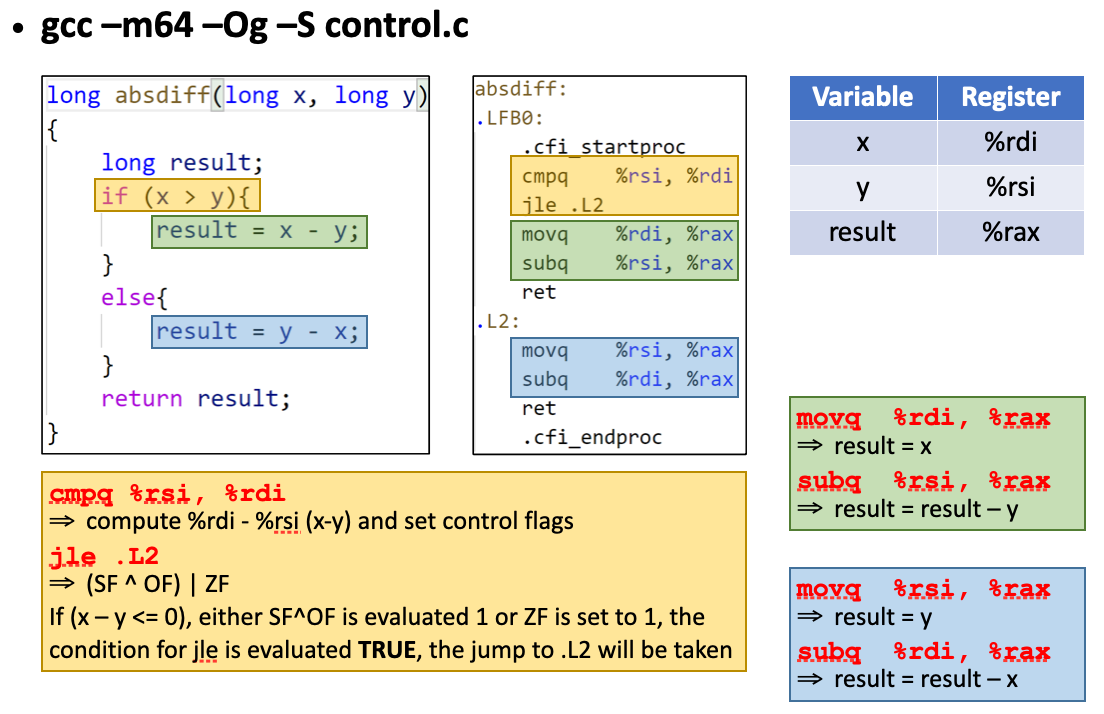
Conditional branches
Jump instructions
Jump instructions – change the control flow
jX instructions
- Change the instruction sequence by jumping to a target address either specified by absolution address or by a value in some register or memory
- Unconditional (jmp) and conditional (jX other than jmp)
| jX | Condition | Description | cmp a, b |
|---|---|---|---|
| jmp | 1 | Unconditional | --- |
| je | ZF | Equal / Zero | b == a |
| jne | ~ZF | Not Equal / Not Zero | b != a |
| js | SF | Negative | b < a |
| jns | ~SF | Nonnegative | b >= a |
| jg | (SF^OF)&ZF | Greater (Signed) | b > a |
| jge | ~(SF^OF) | Greater or Equal (Signed) | b >= a |
| jl | (SF^OF) | Less (Signed) | b < a |
| jle | (SF^OF)|ZF | Less or Equal (Signed) | b <= a |
| ja | CF&ZF | Above (unsigned) | b > a |
| jb | CF | Below (unsigned) | b < a |
注:即condition成立的时候,将会执行跳转,否则将不执行。
Implementing
Implementing conditional branches with jX
goto
- We use the C goto statement to illustrate the control flow of jump in a more readable way
- Try to avoid using goto when you are doing C programming
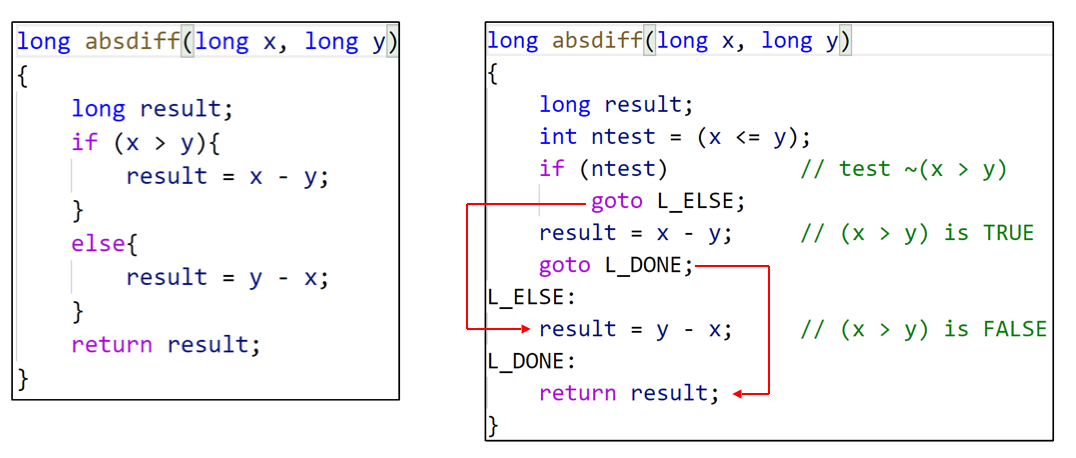
General form of expressing if-then-else
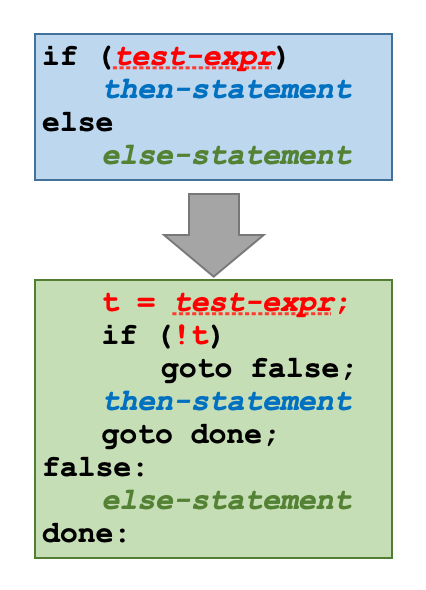
Conditional moves
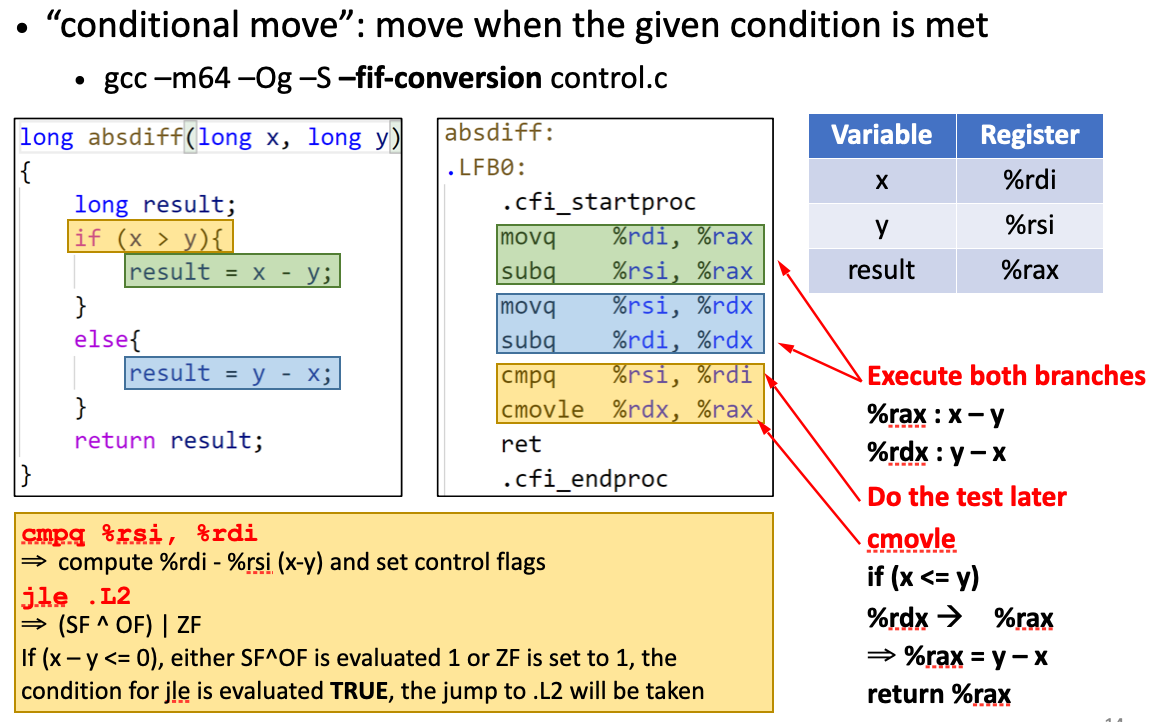
Why using conditional moves?
Modern processors use pipelines to execute a sequence of instructions「现代处理器使用流水线执行一系列指令」
Branching operation may cause the pipeline to stall「Branching operation 可能会导致管道停顿」
As a result, executing both branches will be faster then “test and jump”
Conditional branches by conditional moves

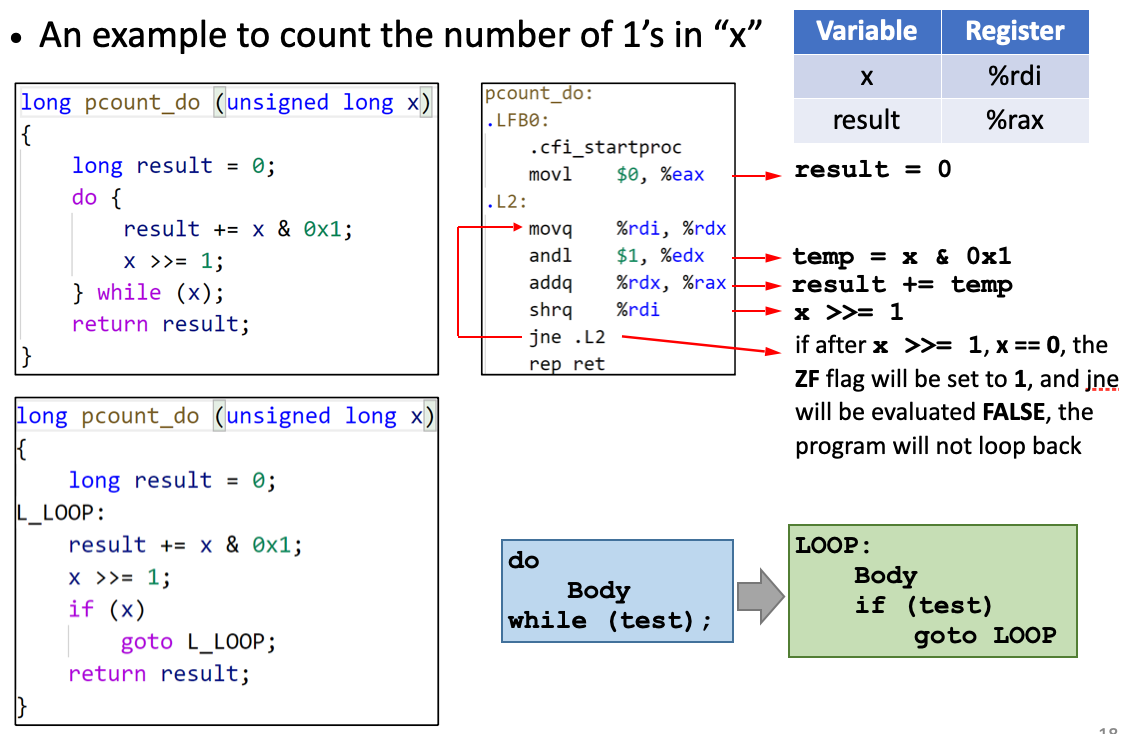
Implementation of some statements
do-while loop
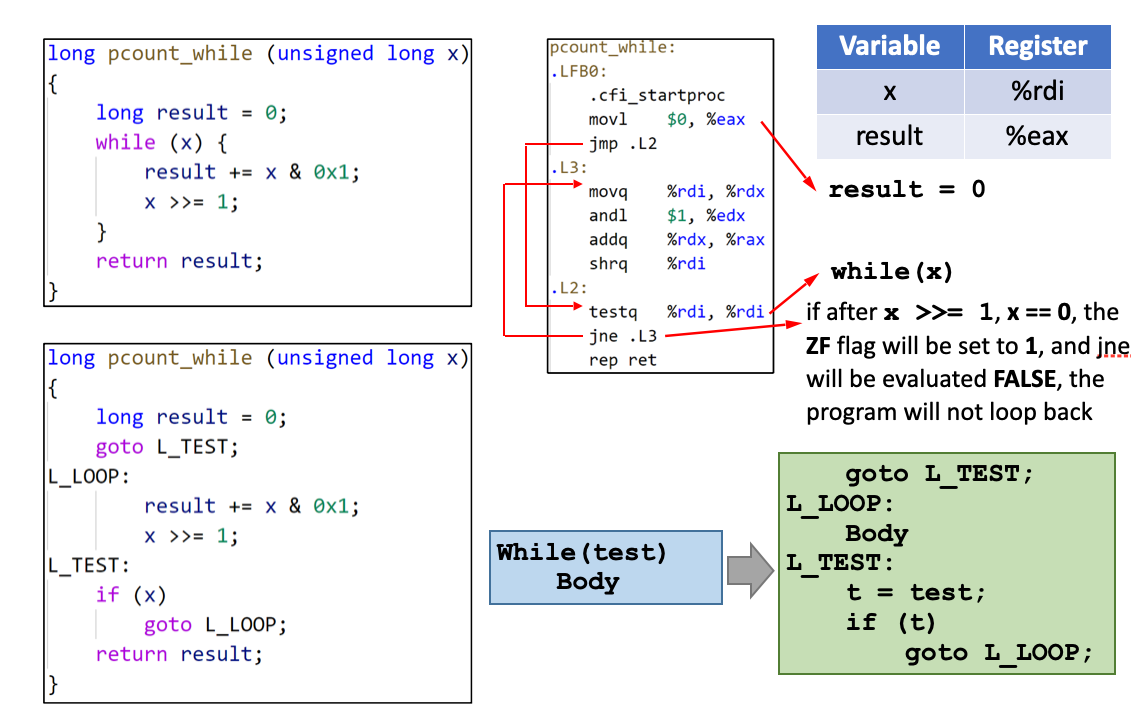
while loop
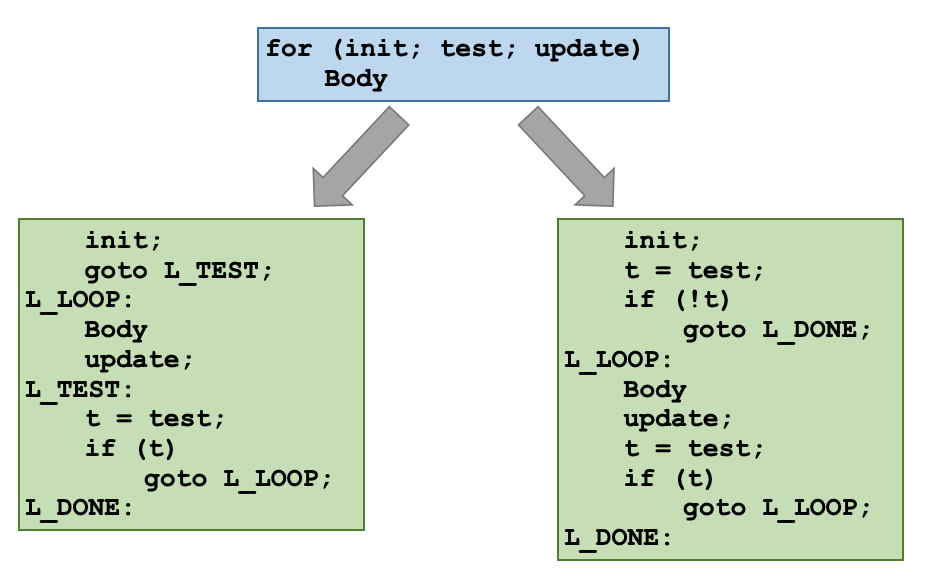
for loop
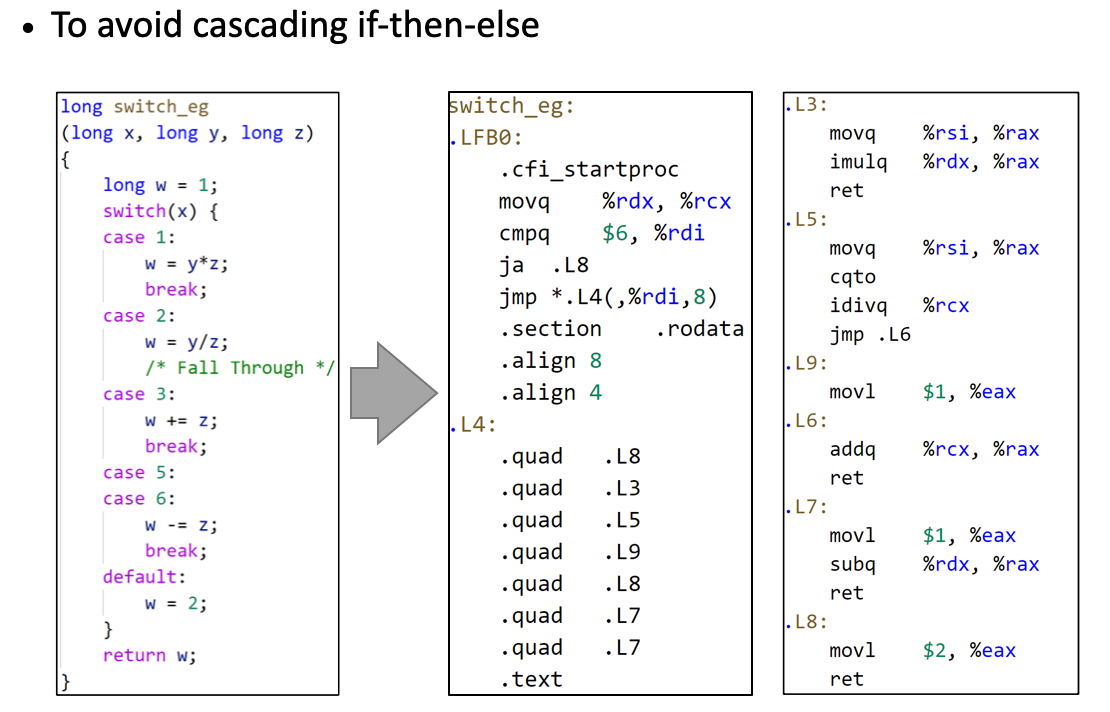
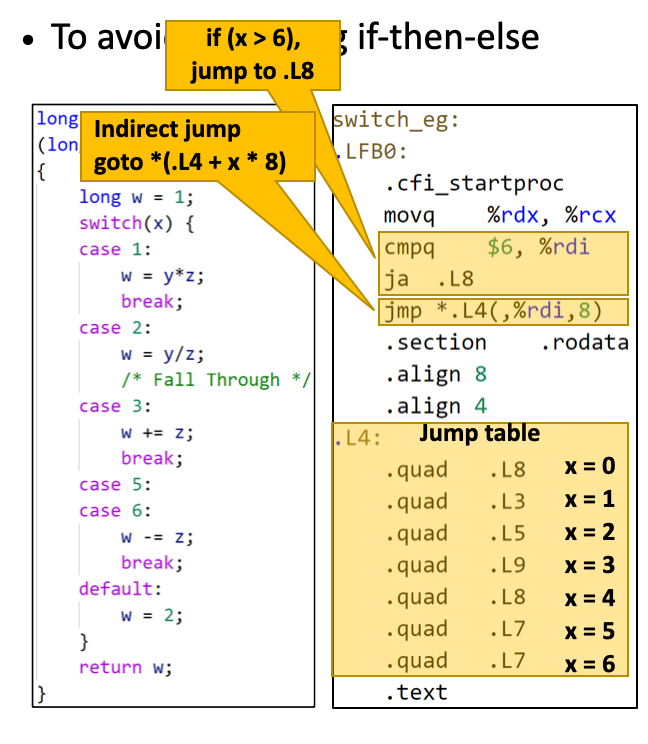
switch statement
*8 的原因是 标签 是 64bit 长 的地址,而且标签是相邻的。
引用
- COMP1411@Polyu PowerPoint