Cleaning Data in Python
Cleaning Data in Python
PD dateframe 类型转换
Why do data types matter?
- Affects which operations you can perform
- Avoid storing data as strings (when possible)
- int , float : enables mathematical operations
- datetime : enables date-based a ributes and methods
- category : uses less memory and runs faster
- bool : enables logical and mathematical operations
Series 查看类型
In [7]:
ride_sharing["station_A_id"].dtype
Out[7]:
dtype('int64')
- object : Python strings (or other Python objects)
- bool : True and False values
- Other types: int , float , datetime , category
dataFrame 查看类型
print(ri.dtypes)
<script.py> output:
stop_date object
stop_time object
driver_gender object
driver_race object
violation_raw object
violation object
search_conducted bool
search_type object
stop_outcome object
is_arrested bool
stop_duration object
drugs_related_stop bool
district object
stop_datetime datetime64[ns]
dtype: object
to object
new_column = ride_sharing["station_A_id"].astype("object")
airlines['dest_region'].str // check string
to int
new_column = ride_sharing["station_A_id"].astype("int")
to dt.datatime
new_column = pd.to_datetime(ride_sharing['ride_date'])
to category
new_column = ride_sharing["type"].astype("category")
category 元数据
dataframe 由 series 组成。因此,每一列series有独自的元数据。就category而言,
attrition_filtered['JobRole'].value_counts()
Research_Scientist 292
Manager 102
......
Sales_Executive 0
Sales_Representative 0
Name: JobRole, dtype: int64
# Remove categories with no rows
attrition_filtered['JobRole'] = attrition_filtered['JobRole'].cat.remove_unused_categories()
Research_Scientist 292
Manager 102
Research_Director 80
Human_Resources 52
Name: JobRole, dtype: int64
Assert
断言,断言错误则直接报错
assert ride_sharing['user_type_cat'].dtype == 'category'
treat duplicate
.duplicated() method

# Get duplicates across all columns
duplicates = height_weight.duplicated()
print(duplicates)
>>>
"""
1 False
... ....
22 True
23 False
......
"""
- subset : List of column names to check for duplication.
- keep : Whether to keep first ( 'first' ), last ( 'last' ) or all ( False ) duplicate values
# Column names to check for duplication
column_names = ['first_name','last_name','address']
duplicates = height_weight.duplicated(subset = column_names, keep = False)
subset 用于圈定范围
Output duplicate values
duplicates = height_weight.duplicated(subset = column_names, keep = False)
height_weight[duplicates]
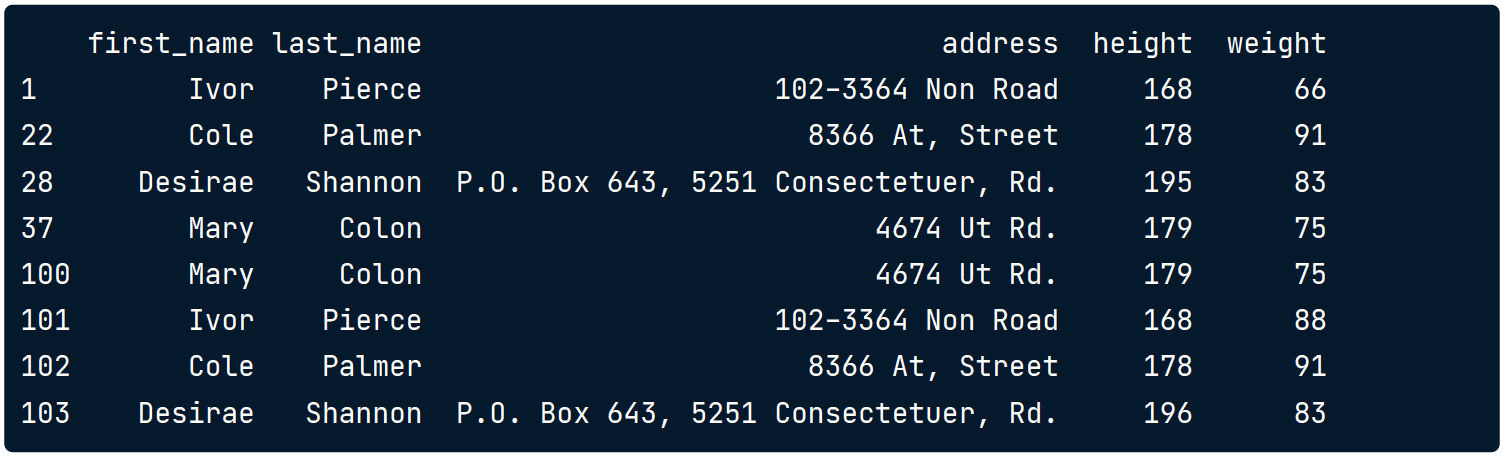
注意 duplicates 没有引号,因为 duplicates 被手动定义为 height_weight 的一部分。
Drop duplicates
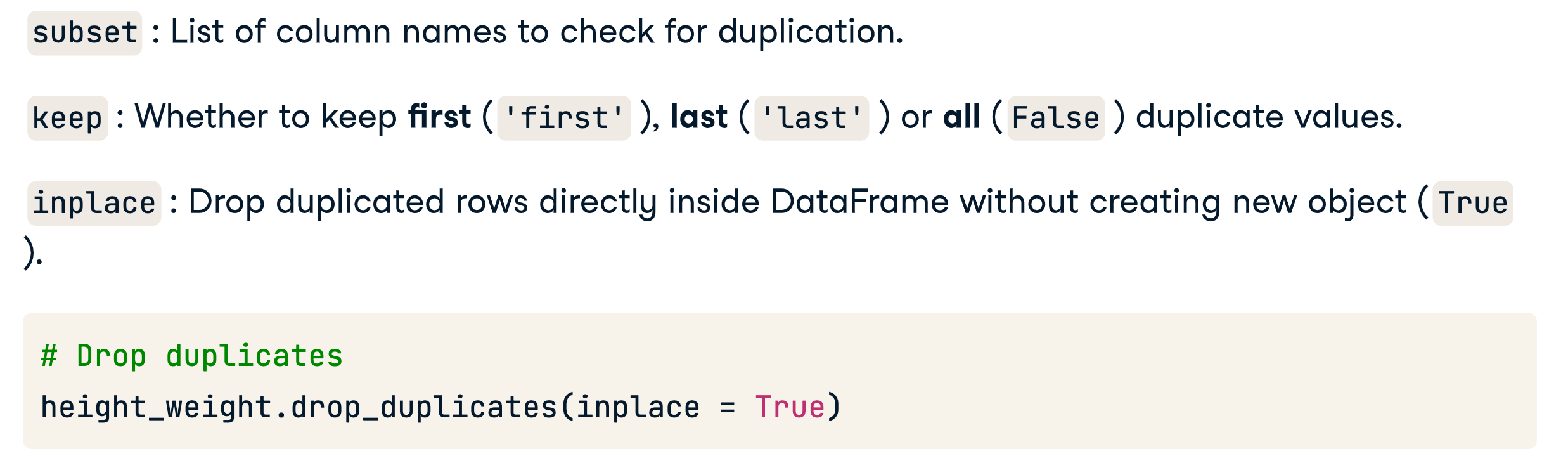
with .drop_duplicates()
height_weight.drop_duplicates(inplace = True)
with groupby
# Group by column names and produce statistical summaries
column_names = ['first_name','last_name','address']
summaries = {'height': 'max', 'weight': 'mean'}
height_weight = height_weight.groupby(by = column_names).agg(summaries).reset_index()
# Make sure aggregation is done
duplicates = height_weight.duplicated(subset = column_names, keep = False)
height_weight[duplicates].sort_values(by = 'first_name')
Unique
Print unique values
# Print unique values of survey columns in airlines
print('Cleanliness: ', airlines['cleanliness'].unique(), "\n")
print('Safety: ', airlines['safety'].unique(), "\n")
print('Satisfaction: ', airlines['satisfaction'].unique(), "\n")
difference
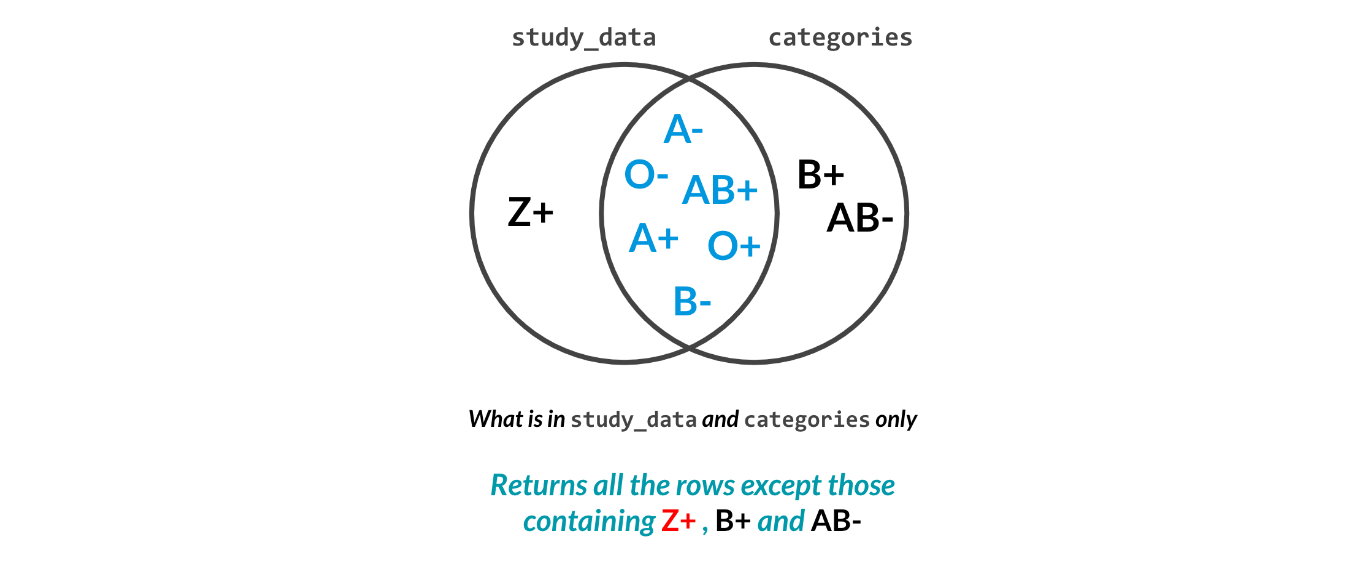
# Find the cleanliness category in airlines not in categories
cat_clean = set(airlines["cleanliness"]).difference(categories["cleanliness"])
# Find rows with that category
cat_clean_rows = airlines['cleanliness'].isin(cat_clean)
# Print rows with inconsistent category
print(airlines[cat_clean_rows])
# Print rows with consistent categories only
print(airlines[~cat_clean_rows])
Categorical variables
Value consistency
What type of errors could we have?

value_counts()
marriage_status.value_counts()
>>>
unmarried 352
married 268
MARRIED 204
UNMARRIED 176
dtype: int64
Strip all spaces
demographics = demographics['marriage_status'].str.strip()
Collapsing data into categories
将数据分为类别
pd.qcut()
Create categories out of data: income_group column from income column.
# Using qcut()
import pandas as pd
group_names = ['0-200K', '200K-500K', '500K+']
demographics['income_group'] = pd.qcut(demographics['household_income'], q = 3, labels = group_names)
# Print income_group column
demographics[['income_group', 'household_income']]
income_group household_income
0 200K-500K 189243
1 500K+ 778533
pd.cut()
# Using cut() - create category ranges and names
ranges = [0,200000,500000,np.inf]
group_names = ['0-200K', '200K-500K', '500K+']
# Create income group column
demographics['income_group'] = pd.cut(demographics['household_income'], bins=ranges,
labels=group_names)
demographics[['income_group', 'household_income']]
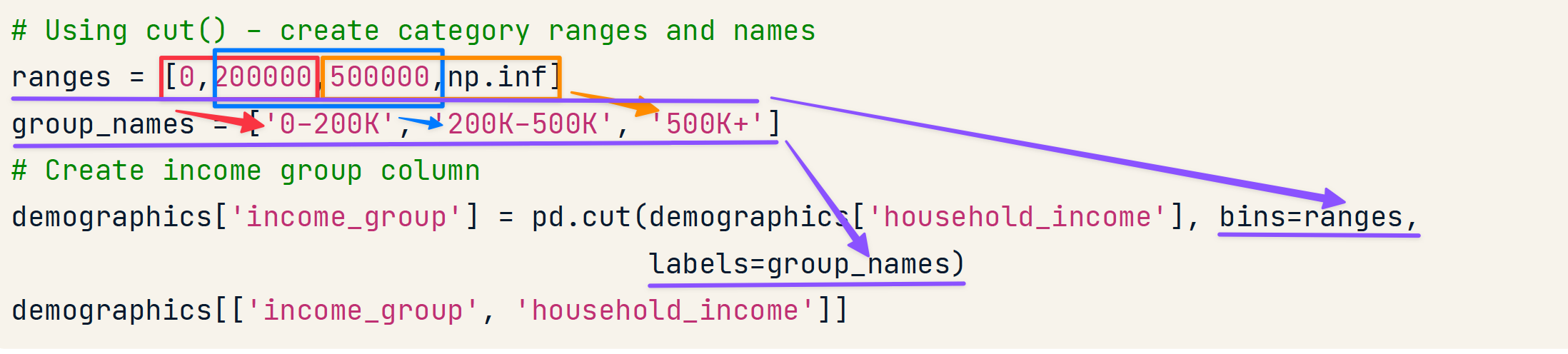
income_group Income
0 0-200K 189243
1 500K+ 778533
Replace
Create mappings and replace
# Create mappings and replace
mappings = {'Monday':'weekday', 'Tuesday':'weekday', 'Wednesday': 'weekday',
'Thursday': 'weekday', 'Friday': 'weekday',
'Saturday': 'weekend', 'Sunday': 'weekend'}
airlines['day_week'] = airlines['day'].replace(mappings)
Replace str
phones["Phone number"] = phones["Phone number"].str.replace("-","")
Replace with Regular expressions
Replace 支持使用正则表达式,正则表达式语法请参考 https://www.runoob.com/regexp/regexp-tutorial.html
phones['Phone number'] = phones['Phone number'].str.replace(r'\D+', '')
.any()
存在性
# Assert that full_name has no honorifics
assert airlines['full_name'].str.contains('Ms.|Mr.|Miss|Dr.').any() == False
assert 关键字
断言,后面跟一个布尔判断,如果后面返回 False 则会导致 Exception
Remember, assert returns nothing if the condition passes
dt.date
user_signups[user_signups['subscription_date'] > dt.date.today()]
Datetime formatting
pandas.to_datetime()
- 可以自动识别大多数格式
- 有时会出错或无法识别的格式
# Will work!
birthdays['Birthday'] = pd.to_datetime(birthdays['Birthday'],
# Attempt to infer format of each date
infer_datetime_format=True,
# Return NA for rows where conversion failed
errors = 'coerce')
格式转换
// eg1
birthdays['Birthday'] = birthdays['Birthday'].dt.strftime("%d-%m-%Y")
// eg2
ages_manual = today.year - banking["birth_date"].dt.year
Cross field validation
The use of multiple fields in a dataset to sanity check data integrity
即交叉数据验证
.sum()
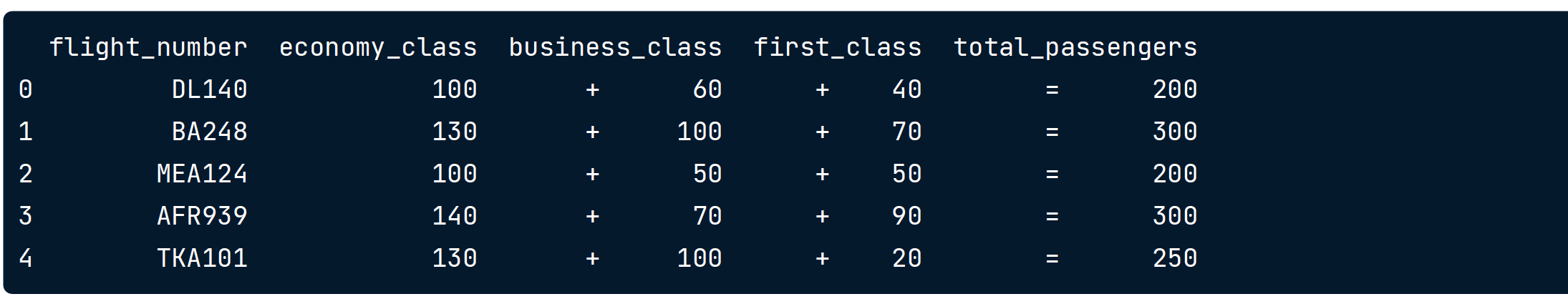
sum_classes = flights[['economy_class', 'business_class', 'first_class']].sum(axis = 1)
// axis = 1 表示横向求和,axis = 0 表示纵向求和
passenger_equ = sum_classes == flights['total_passengers']
# Find and filter out rows with inconsistent passenger totals
inconsistent_pass = flights[~passenger_equ]
Completeness
数据完整性
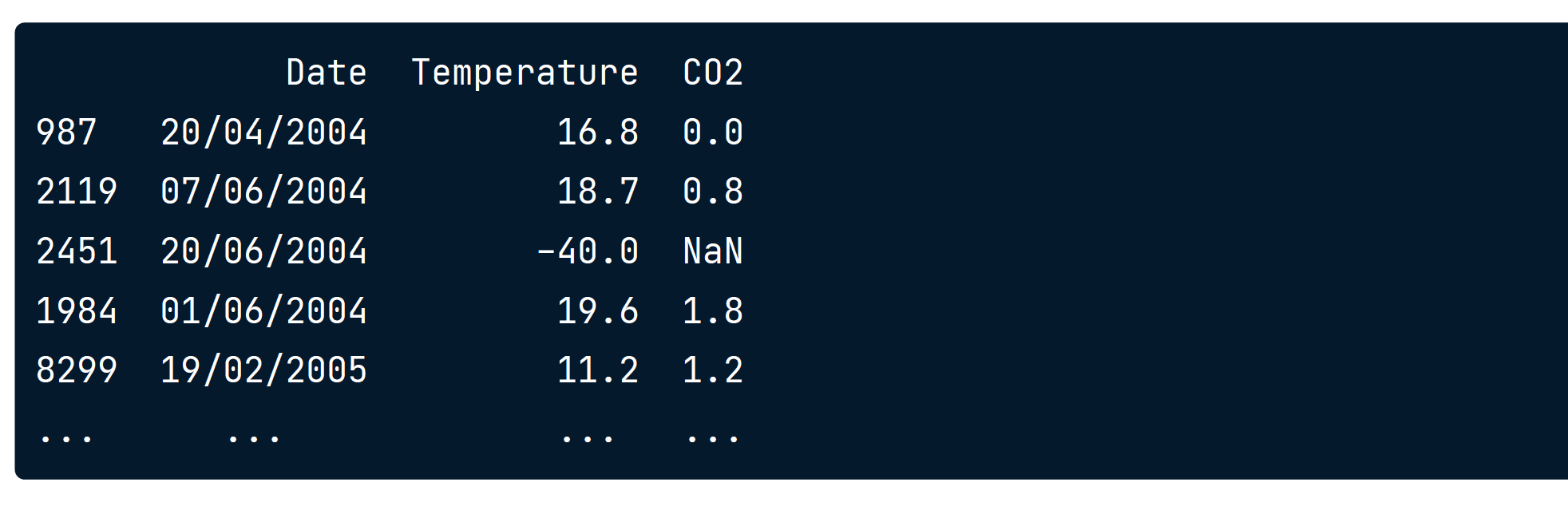
确实的数据会以NaN显示。
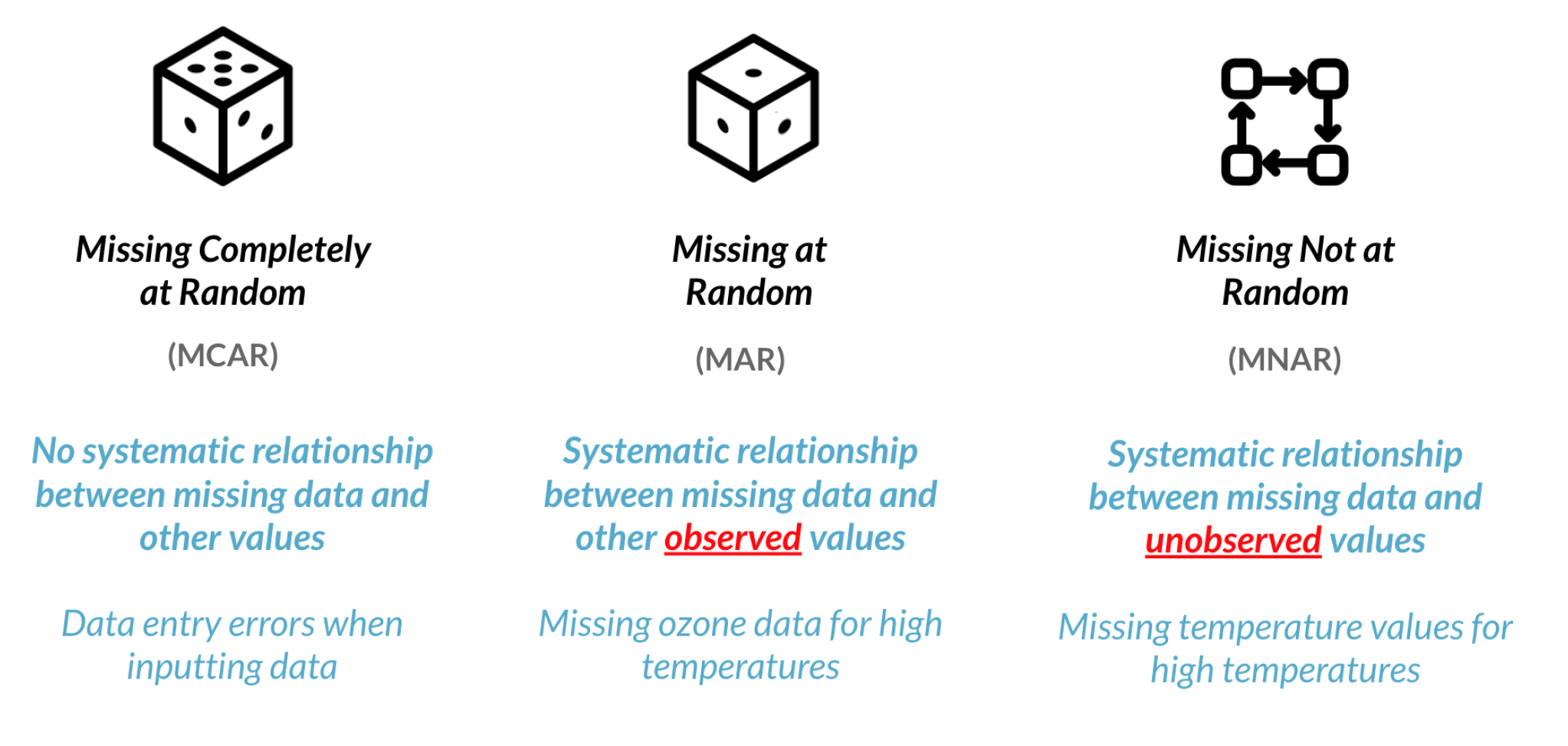
.isna()
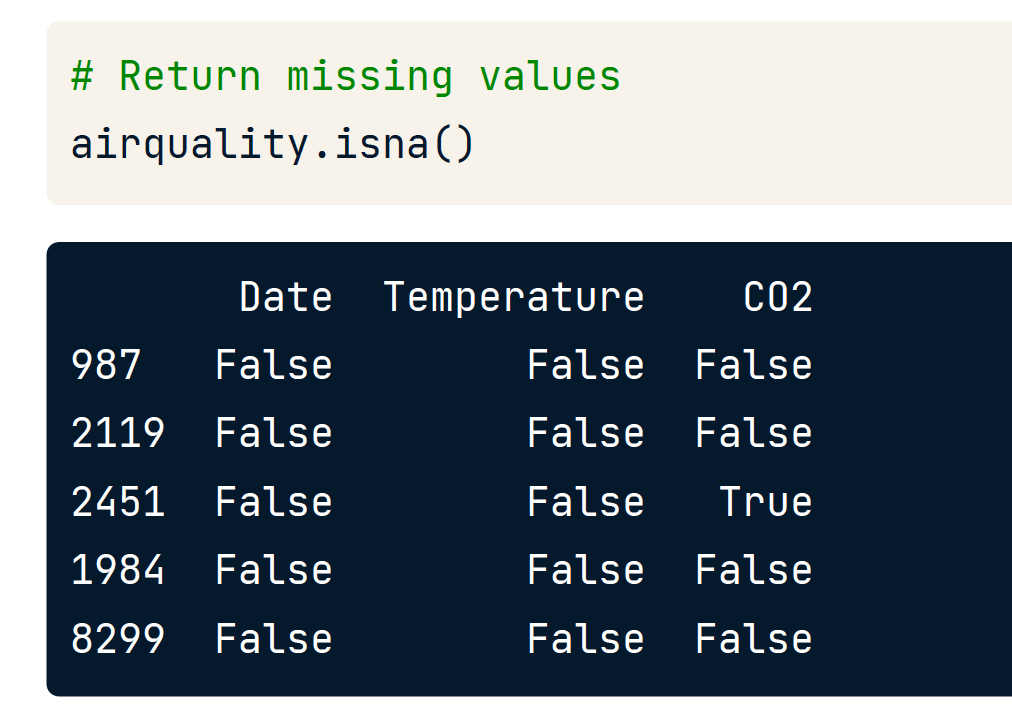
.isna().sum()
统计NaN的个数。
缺失可视化
msno.matrix(sorted_airquality)
plt.show()
Dropping missing values
# Drop missing values
airquality_dropped = airquality.dropna(subset = ['CO2'])
Treat Nan
fillna()
co2_mean = airquality['CO2'].mean()
airquality_imputed = airquality.fillna({'CO2': co2_mean})
使用平均值
np.mean()
Simple string comparison
Minimum edit distance
从一个字符串过渡到另一个字符串所需的最少步骤
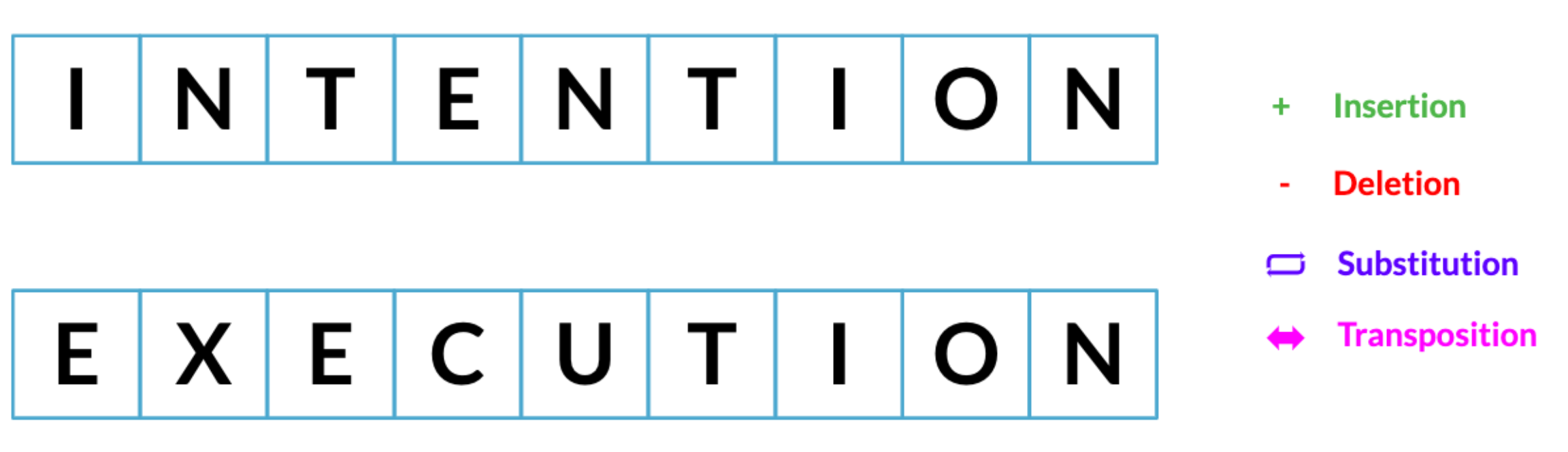
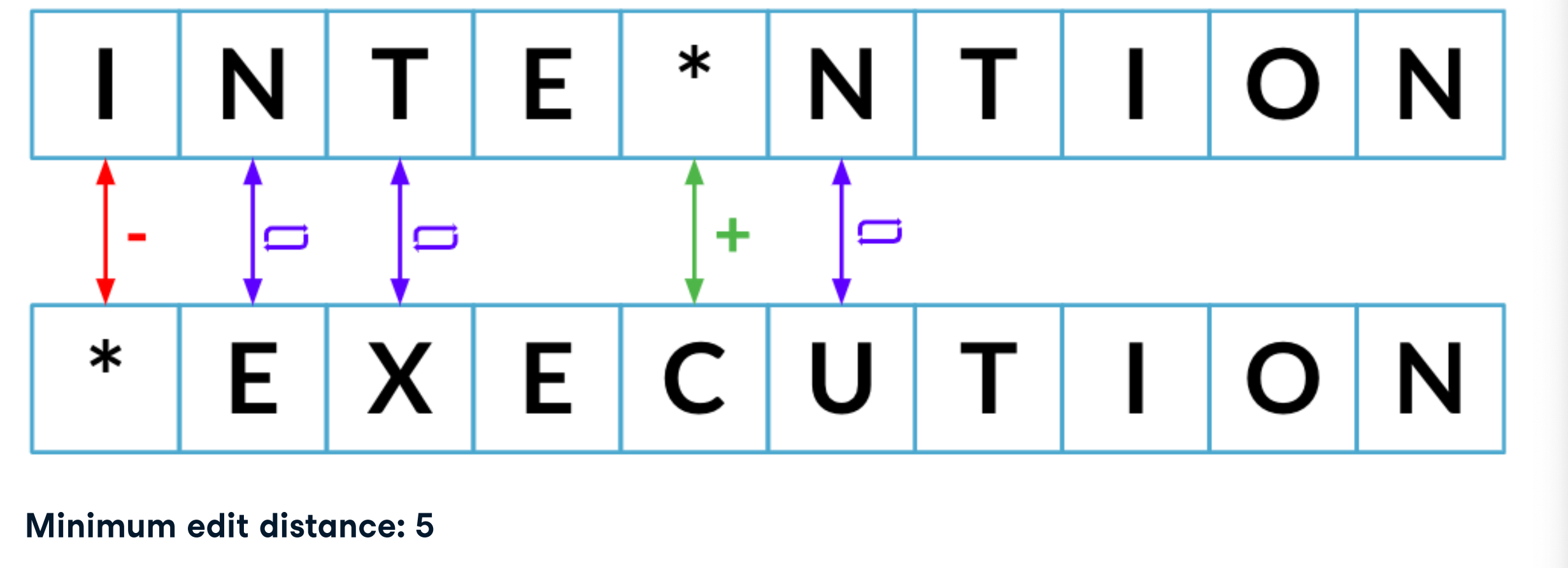

Possible packages: nltk , fuzzywuzzy , textdistance ..
相似性
# Lets us compare between two strings
from fuzzywuzzy import fuzz
# Compare reeding vs reading
fuzz.WRatio('Reeding', 'Reading')
# Partial string comparison
fuzz.WRatio('Houston Rockets', 'Rockets')
# Partial string comparison with different order
fuzz.WRatio('Houston Rockets vs Los Angeles Lakers', 'Lakers vs Rockets')
86
90
86
列表
# Import process
from fuzzywuzzy import process
# Define string and array of possible matches
string = "Houston Rockets vs Los Angeles Lakers"
choices = pd.Series(['Rockets vs Lakers', 'Lakers vs Rockets',
'Houson vs Los Angeles', 'Heat vs Bulls'])
# limit 按排名截取前几个
process.extract(string, choices, limit = 2)
[('Rockets vs Lakers', 86, 0), ('Lakers vs Rockets', 86, 1)]
与字符串匹配的折叠类别
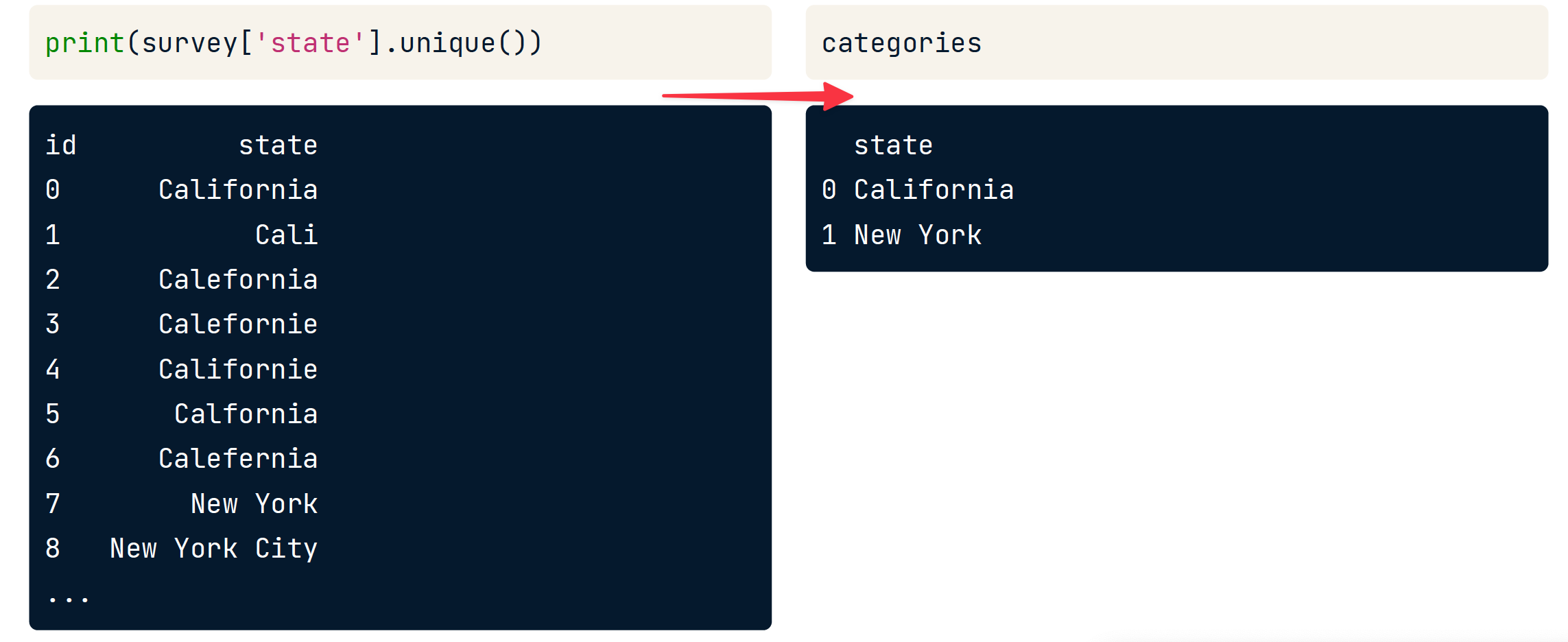
# For each correct category
for state in categories['state']:
# Find potential matches in states with typoes
# 第一个参数是标准 值 ,第二个参数是需要校准的 序列
# matches 是待校准值的unique 以及对应分数
matches = process.extract(state, survey['state'], limit = survey.shape[0])
# For each potential match match
for potential_match in matches:
# If high similarity score
# 如果待校准的值的分数大于80分,则替换为 state
if potential_match[1] >= 80:
# Replace typo with correct category
survey.loc[survey['state'] == potential_match[0], 'state'] = state
该操作是整列操作,survey['state'] 是一整列。
Append 相似追加
之前的append追加数据时,无法处理相似数据的重复问题。
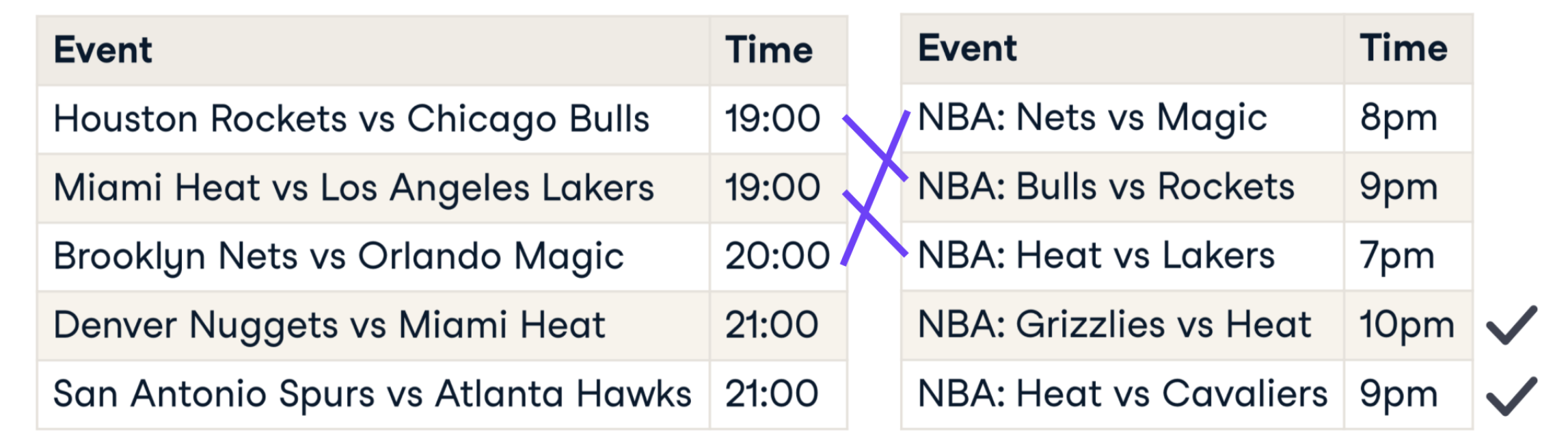
如何防止相似的数据被追加?可以按照这样一个流程
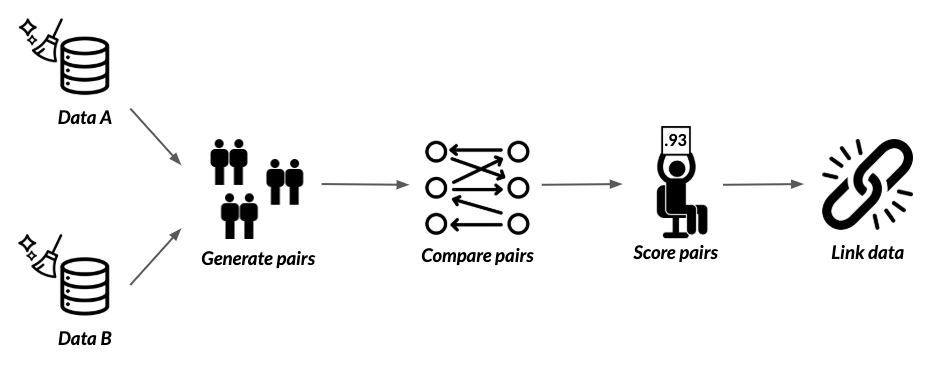
The recordlinkage package
# Import recordlinkage
import recordlinkage
# Create indexing object
indexer = recordlinkage.Index()
# Generate pairs blocked on state
indexer.block('state')
pairs = indexer.index(census_A, census_B)
print(pairs)
# 这一步产生了 Index对
MultiIndex(levels=[['rec-1007-org', 'rec-1016-org', 'rec-1054-org', 'rec-1066-org',
'rec-1070-org', 'rec-1075-org', 'rec-1080-org', 'rec-110-org', 'rec-1146-org',
'rec-1157-org', 'rec-1165-org', 'rec-1185-org', 'rec-1234-org', 'rec-1271-org',
'rec-1280-org',...........
66, 14, 13, 18, 34, 39, 0, 16, 80, 50, 20, 69, 28, 25, 49, 77, 51, 85, 52, 63, 74, 61,
83, 91, 22, 26, 55, 84, 11, 81, 97, 56, 27, 48, 2, 64, 5, 17, 29, 60, 72, 47, 92, 12,
95, 15, 19, 57, 37, 70, 94]], names=['rec_id_1', 'rec_id_2'])
# Create a Compare object
compare_cl = recordlinkage.Compare()
# Find exact matches for pairs of date_of_birth and state
compare_cl.exact('date_of_birth', 'date_of_birth', label='date_of_birth')
compare_cl.exact('state', 'state', label='state')
# Find similar matches for pairs of surname and address_1 using string similarity
compare_cl.string('surname', 'surname', threshold=0.85, label='surname')
compare_cl.string('address_1', 'address_1', threshold=0.85, label='address_1')
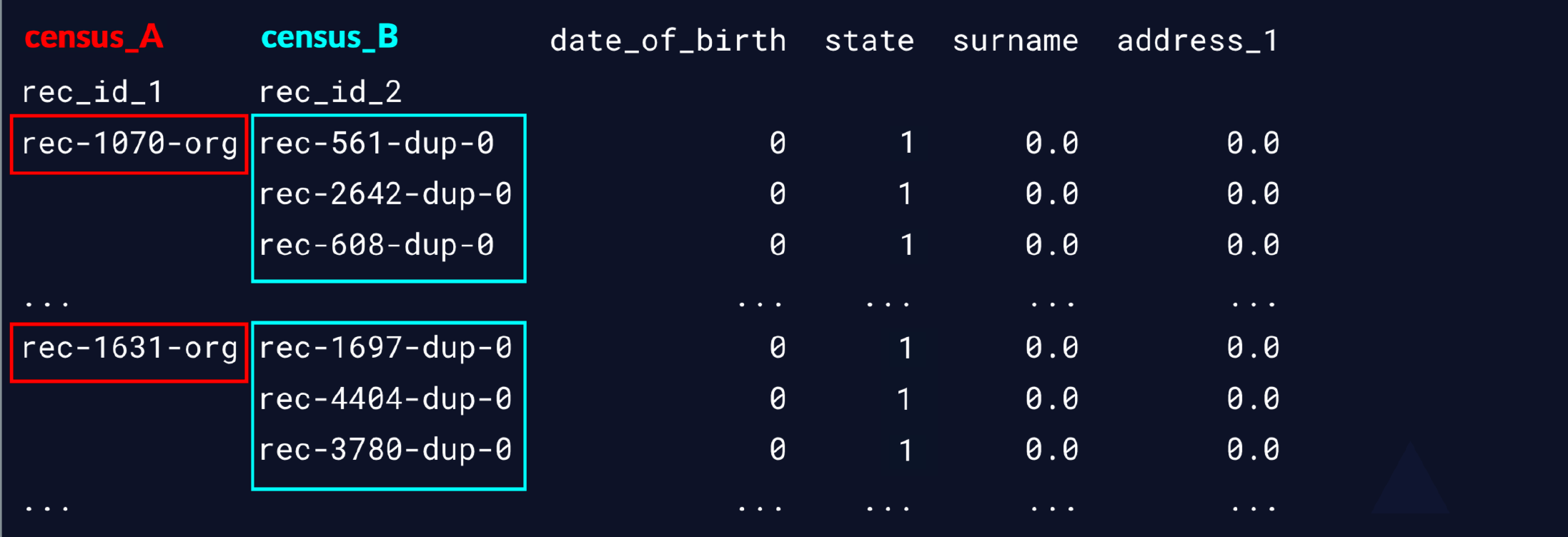
# Find matches
potential_matches = compare_cl.compute(pairs, census_A, census_B)
# print
print(potential_matches)
下面结果中,1表示符合,0表示不符合
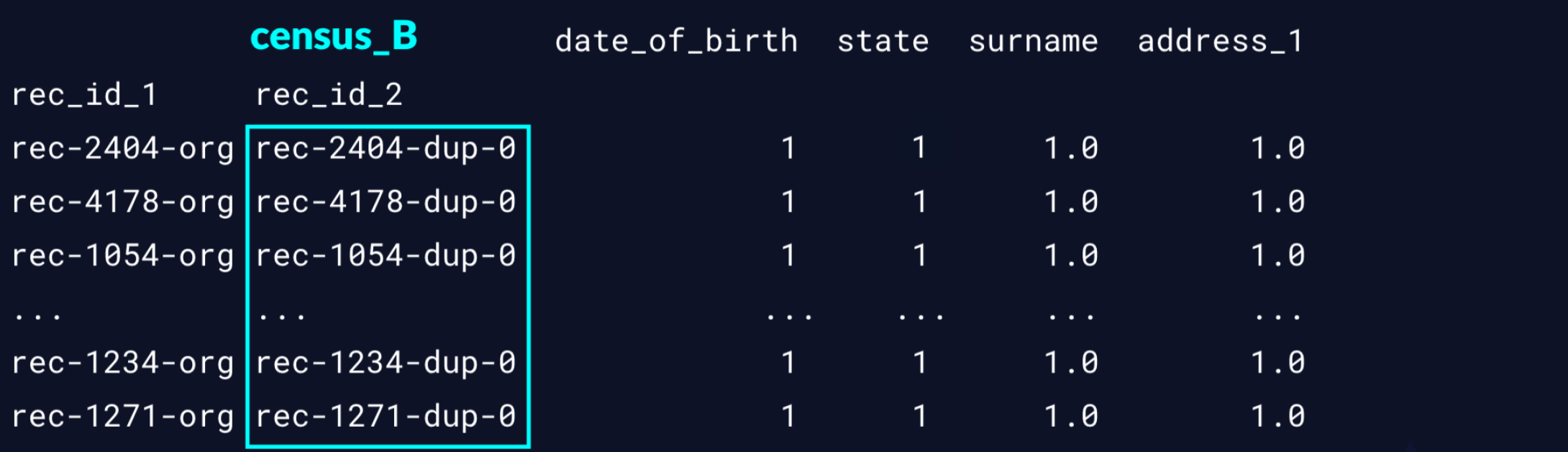
下一步 筛选出来我认为是相似的数据条目
# 我们设定 当某一行的值的和 >= 3时,认为是相似的
potential_matches[potential_matches.sum(axis = 1) => 3]
print(matches)
>>> matches.index
MultiIndex(levels=[['rec-1007-org', 'rec-1016-org', 'rec-1054-org', 'rec-1066-org',
'rec-1070-org', 'rec-1075-org', 'rec-1080-org', 'rec-110-org', ...
接下来只需要
# Get indices from census_B only
duplicate_rows = matches.index.get_level_values(1)
print(census_B_index)
# drop duplicates
census_B_new = census_B[~census_B.index.isin(duplicate_rows)]
# Link the DataFrames!
full_census = census_A.append(census_B_new)
np.non
可以使用NaN值替代异常值。NaN元素位于 Numpy, 应当先导入 Numpy as np
# 用NaN代替 98, 99
pounds = pounds.replace([98, 99], np.nan)
str操作
series.str.cat()
# Concatenate 'stop_date' and 'stop_time' (separated by a space)
combined = ri.stop_date.str.cat(ri.stop_time, sep = " ")
将 date 列 和 time 列的字符串拼接。
区分 .cat
- series.str.cat() 是 处理 str 元素的,用于拼接的方法
- series.cat 表示看做 category处理,类似于 series.str
Strip
去除指定字符后的字符,适用于对DataFrame 整列进行操作
总结