Docker
大约 4 分钟
Docker
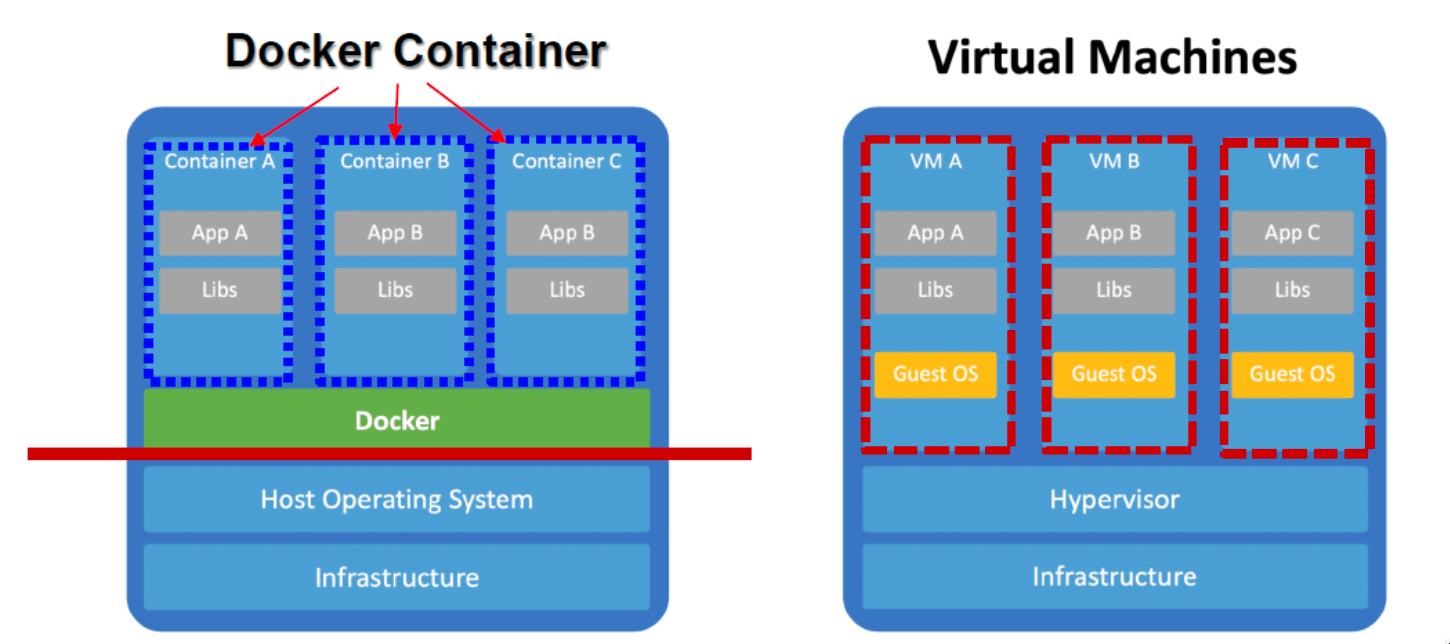
Container
- "Container":OS-Level Virtualization
- 操作系统级虚拟化:在操作系统之上对服务器进行虚拟化。
- Examples: Docker, LXC (LinuX Containers), LXD,Solaris "Zones'", Google Containers,…

- 容器:实例化「Each Container Operates like a Real Server}速度极快,每个实例的内存占用较小,并且单个主机上的密度较高。
- 缺点:容器提供的隔离性比虚拟机弱。
每个容器都像真正的服务器一样运行
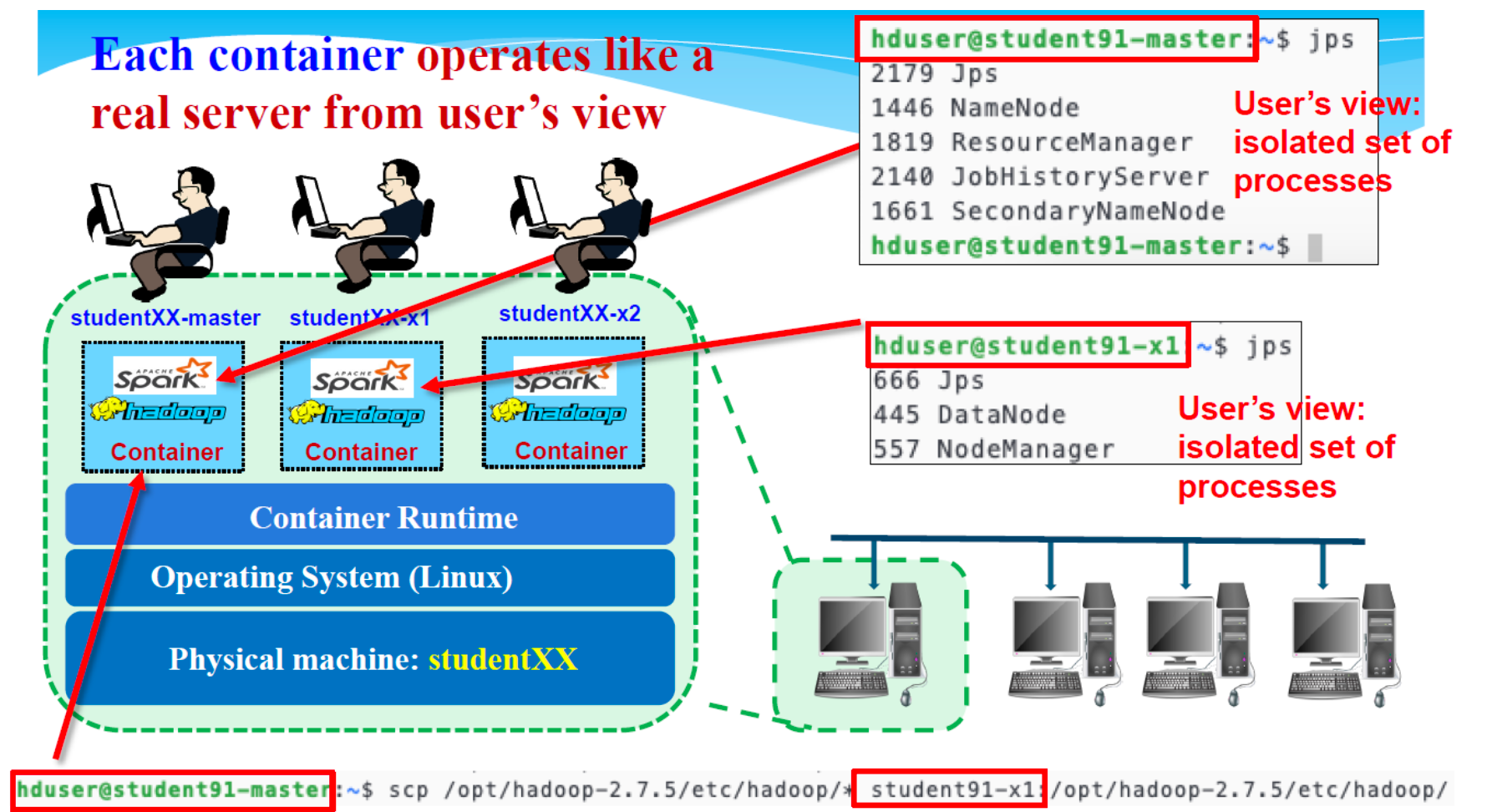
Simplistic view:a container can be seen as an isolated set of processes,interacting within an isolated set of file folders and device networks.

What is Docker?
Docker is a containerization platform that
- packages your application and all its dependencies together in the form of a docker container
- to ensure that your application works seamlessly in any environment.
Core Techniques used

Docker relies on two major Linux kernel features:
- Namespaces to isolate an application's view of the operating environment, including process frees, network, user IDs and mounted file systems → 'limits what you can see"
- Control Groups (cgroups):"limits what you can use"(e.g.,CPU time,system memory,network / disk bandwidth)
Each container runs in a separate namespace and its access is limited to that namespace.

Docker uses Linux Namespaces
- pid 命名空间:进程隔离限制你在容器中看到的进程 ID
- net 命名空间:管理网络接口(.NET:网络)--("你能看到的网络)
- ipc 命名空间:管理对 IPC 资源的访问(IPC:进程间「InterProcess」通信)
- mnt 命名空间:管理文件系统挂载点(MNT:Mount)--限制 "你能看到的文件系统"
- uts 命名空间:隔离内核和版本标识符。(UTS:Unix 分时系统「Unix Timesharing System」)。
Timesharing
分时是在许多任务或用户之间共享计算资源。它支持单个用户执行多任务或支持多用户会话。