Data Center Network
Data Center Network

- Three-Tier DCN
- Fat Tree DCN
- Dcell
Data Center Networking (DCN)
- 是关于如何连接服务器和交换机等设备,以便在数据中心内实现高效的信息交换
- 随着数据中心的设备数量增加到数以万计,构建和维护这些网络变得十分困难
Three-Tier DCN

The three-tier DCN architecture follows a multi-rooted tree based network topology 「基于多根树的网络拓扑」composed of three layers of network switches, namely access 「接入层」, aggregate 「汇聚层」, and core layers「核心层」.

From a Vertical Traffic Model「垂直交通模式」 to a Horizontal Traffic Model「水平交通模型」.

- Past: 传统数据中心 80% 的流量是 "北向南"(或垂直流量)(外部用户和内部服务器之间的数据转发)。
- Now: 云计算数据中心 70% 的流量是 "东向西 "的
- (Facebook、Google、Amazon)-在内部服务器之间转发的数据。例如,搜索、MapReduce、VM 迁移
Three-Tier DCN: Key Weakness
- Unable to handle the growing demand of cloud computing (We Move From a Vertical Traffic Model to a Horizontal Traffic Model)
- The higher layers of the three-tier DCN are highly oversubscribed 「高度超额认购」 -> become the bottleneck「瓶颈」.
- "高度订阅"在这里指的是,网络的这一部分有大量的数据流需要处理,但是处理能力有限,无法满足所有的需求。因此,这就成为了约束整个网络性能的瓶颈。
- 接入层负责连接服务器,汇聚层负责汇集接入层的数据,而核心层负责处理汇聚层汇集的数据。
如果核心层和汇聚层的处理能力不足,那么就会出现瓶颈,限制了整个网络的性能。
- Other Issues: scalability, fault tolerance, energy efficiency,and cross-sectional bandwidth
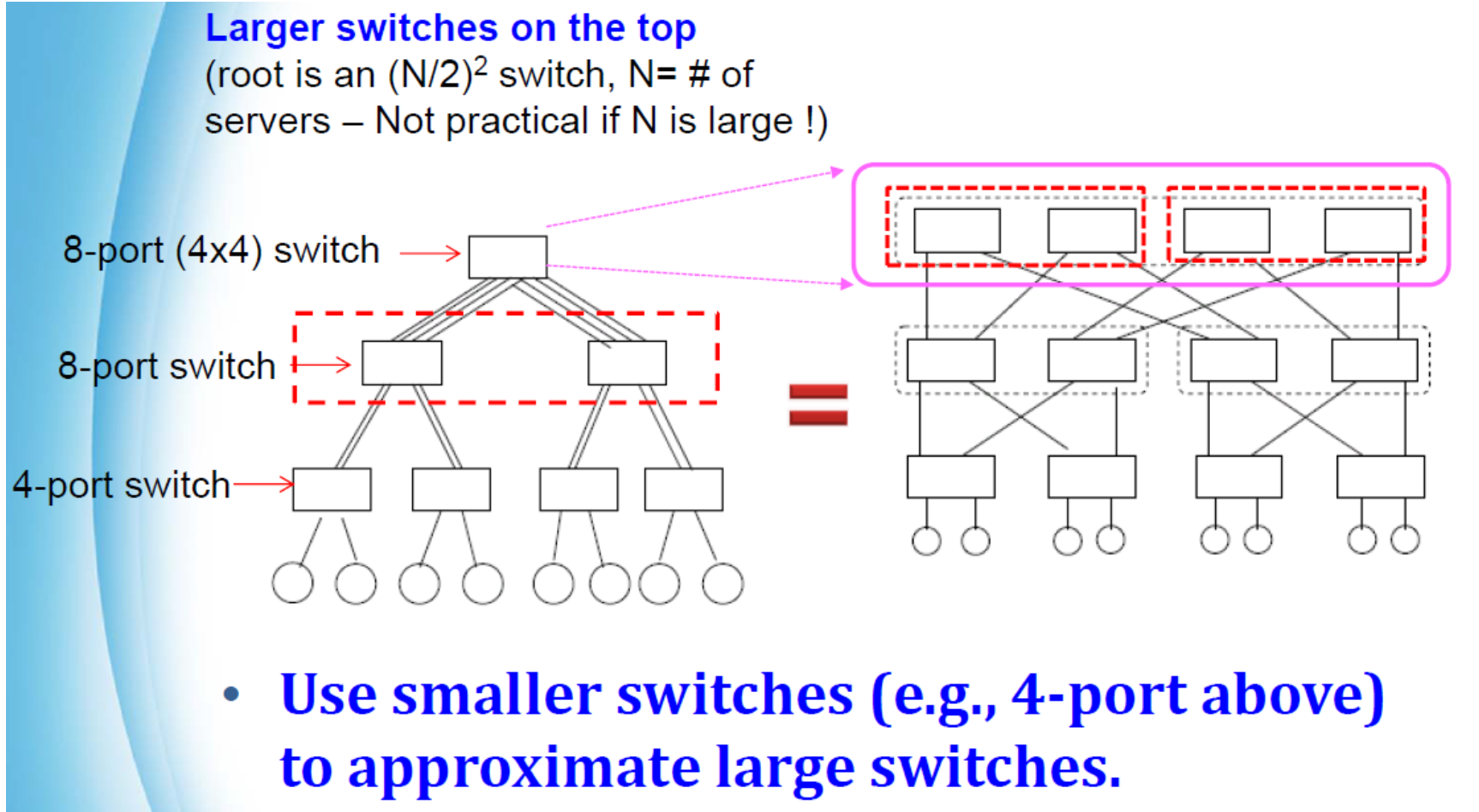
Fat-Tree Architecture
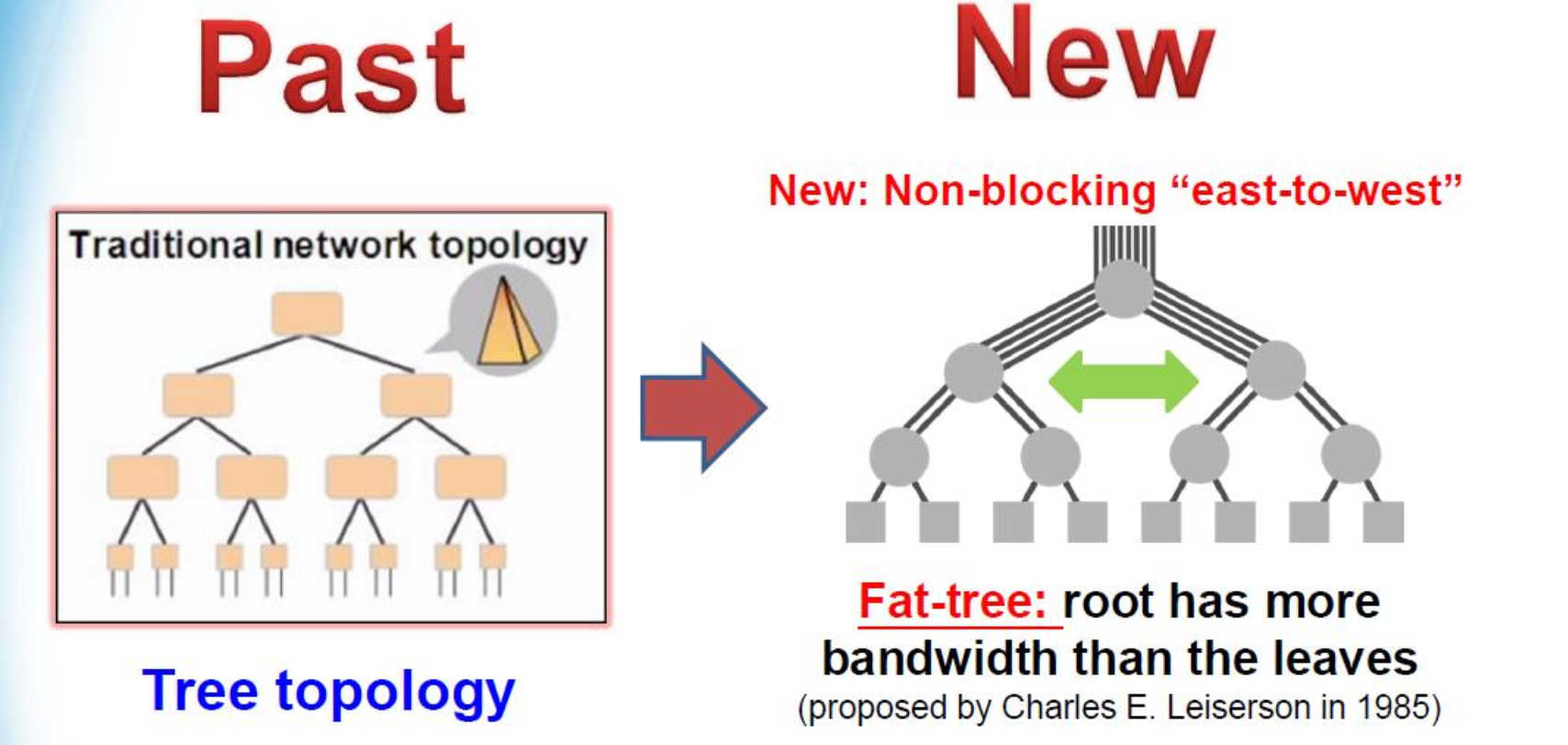
Practical Fat-Tree Architecture
Fat-Tree DCN Architecture
Fat-Tree:一种特殊类型的 Clos Networks
K-ary fat tree: three-layer topology (edge,aggregation and core)
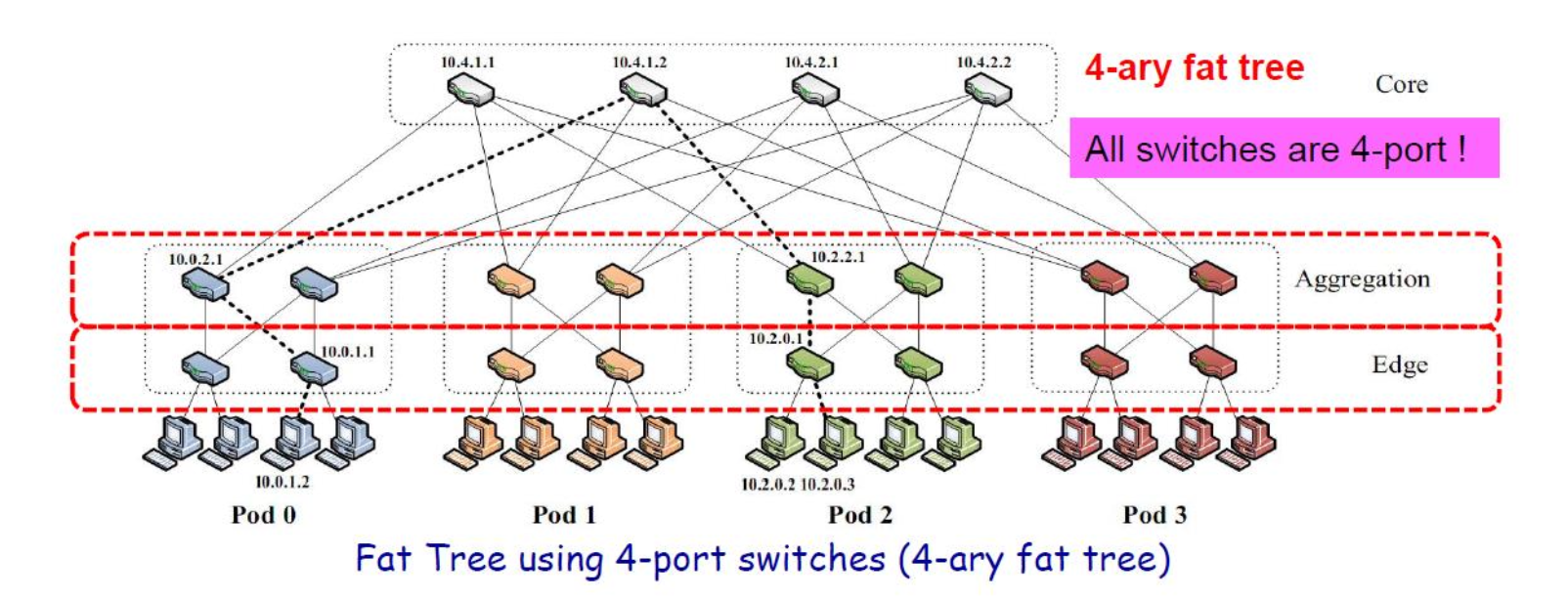
假设一个 k-ary(每个节点有不超过 k 个子节点)的三层 Fat-Tree 拓扑:
- Core 个数 = (k/2)^2
- POD 个数 = k
- 每个 POD 的 Aggregation 交换机 = k/2
- 每个 POD 的 Edge 交换机 = k/2
- 每个 Edge 连接 k/2 个 终端
- 每个 Edge 剩余 k/2 个口连接 POD 内 k/2 个 Aggregation 交换机
可以计算出,支持的服务器个数为 k * (k/2) * (k/2) = (k^3)/4
不同 POD 下服务器间等价路径数 (k/2) * (k/2) = (k^2)/4
提示
上图 为最简单的 k=4 时的 Fat-Tree 拓扑,连在同一个接入交换机下的服务器处于同一个子网,他们之间的通信走二层报文交 换。不同接入交换机下的服务器通信,需要走路由。
Fat-Tree 的缺陷
- Fat-Tree 的扩展规模在理论上受限于核心层交换机的端口数目,不利于数据中心的长期发展要求;
- 对于 POD 内部,Fat-Tree 容错性能差,对底层交换设备故障非常敏感,当底层交换设备故障时,难以保证服务质量;
Clos Network
旧貌换新颜
Clos 网络是一种多级电路交换网络,由 Charles Clos 于 1952 年首次正式提出。
- Clos networks have 3 stages
- Each stage is made up of a number of crossbar switches (r-m-r)
- Completely non-blocking if m >= 2n-1
Fat-Tree DCN
Why Fat-Tree?
- Full bisection「二分法」 bandwidth (non-blocking east-to-west)
- 每一层的聚合带宽相同(上行链路数与下行链路数相同)
可使用廉价/较小的交换机构建统一容量的交换机
- 每个端口支持与终端主机相同的速度
- 如果数据包沿可用路径均匀分布「distributed uniform」,所有设备都能以线速传输
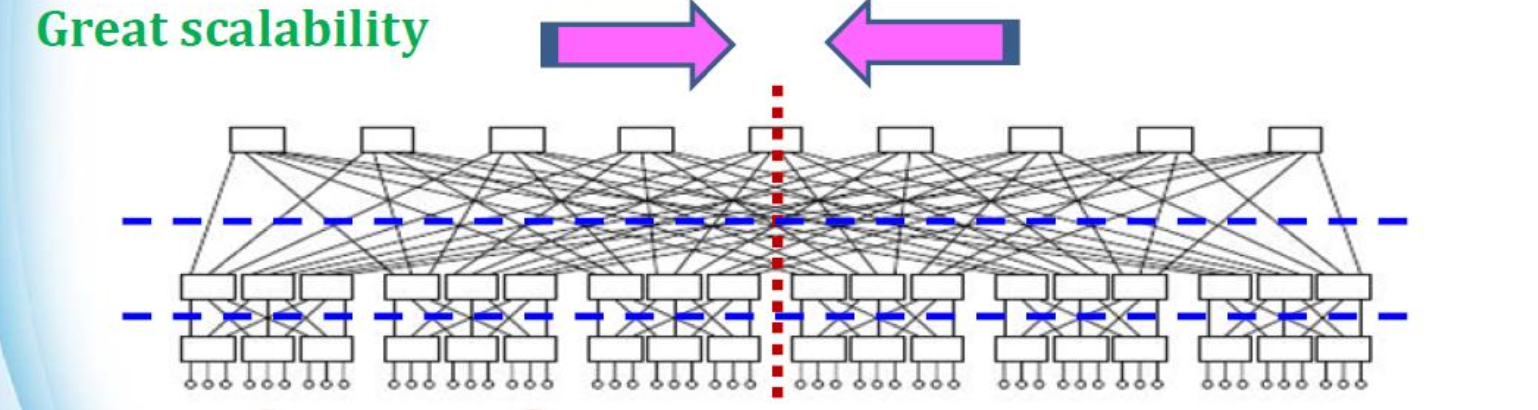
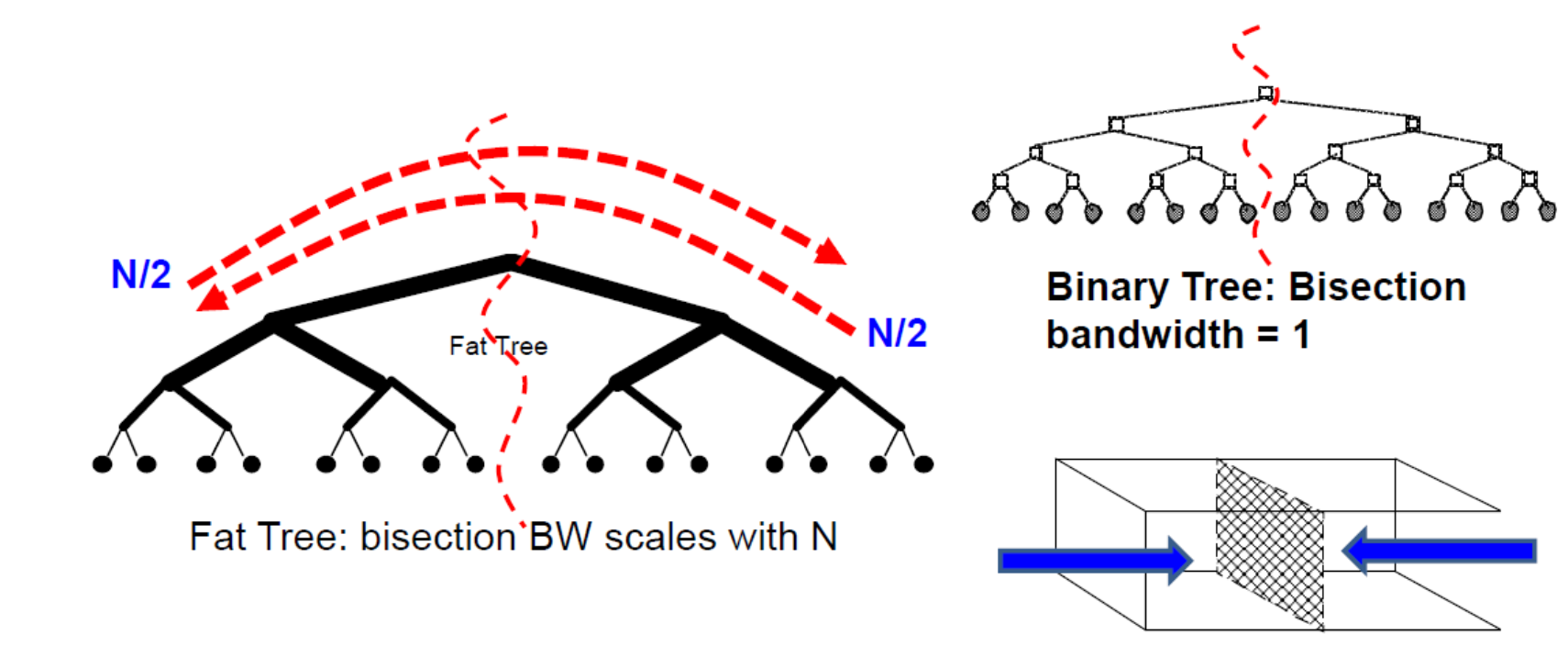
Fat-Tree DCN Bisectional Bandwidth
将 N 个节点分成两组,每组 N/2 个节点,使得这两组之间的带宽最小:即二分「Bisectional」带宽
DCell DCN
DCell 是一种以服务器为中心的混合 DCN 架构,其中一台服务器直接连接到许多其他服务器(即服务器同时充当路由器)。
高层DCell由许多低层DCell构成,同一层的DCell之间是全连接的。
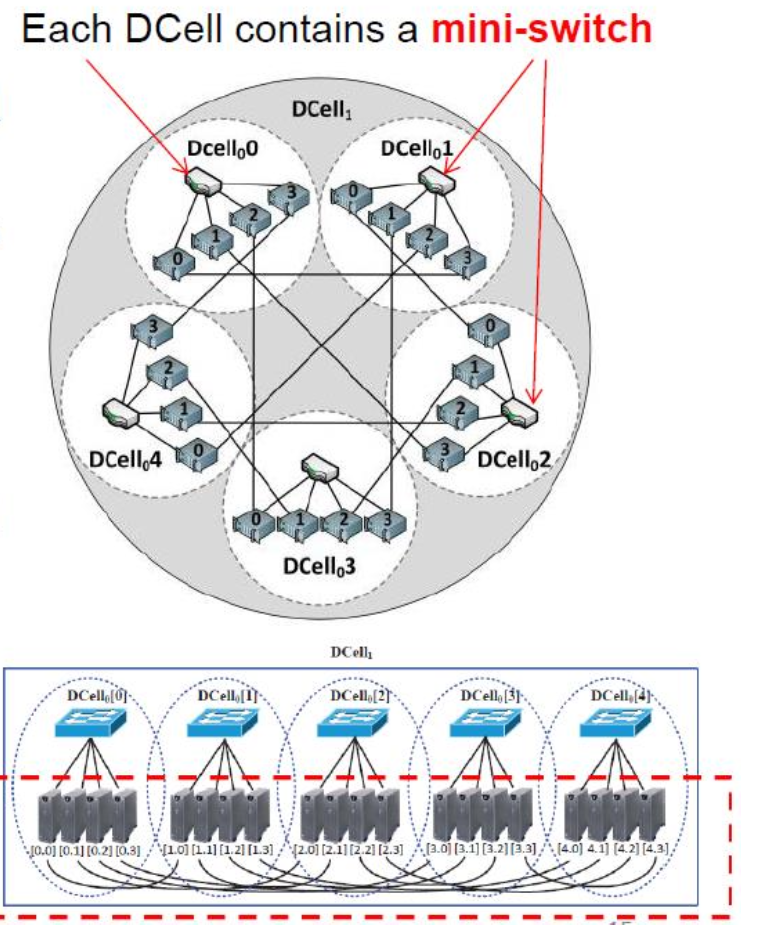
DCell offers immense scalability
- Best performance under switch failures
- Near shortest-path routing even in the presence of severe link or node failures. 「即使出现严重的链路或节点故障,也能接近最短路径路由。」
Weakness:
- 在网络负荷较重、流量模式为 "一对多 "的情况下,性能极差。
- DCell assumes a server has four or more NICs → cabling complexity「布线复杂性」
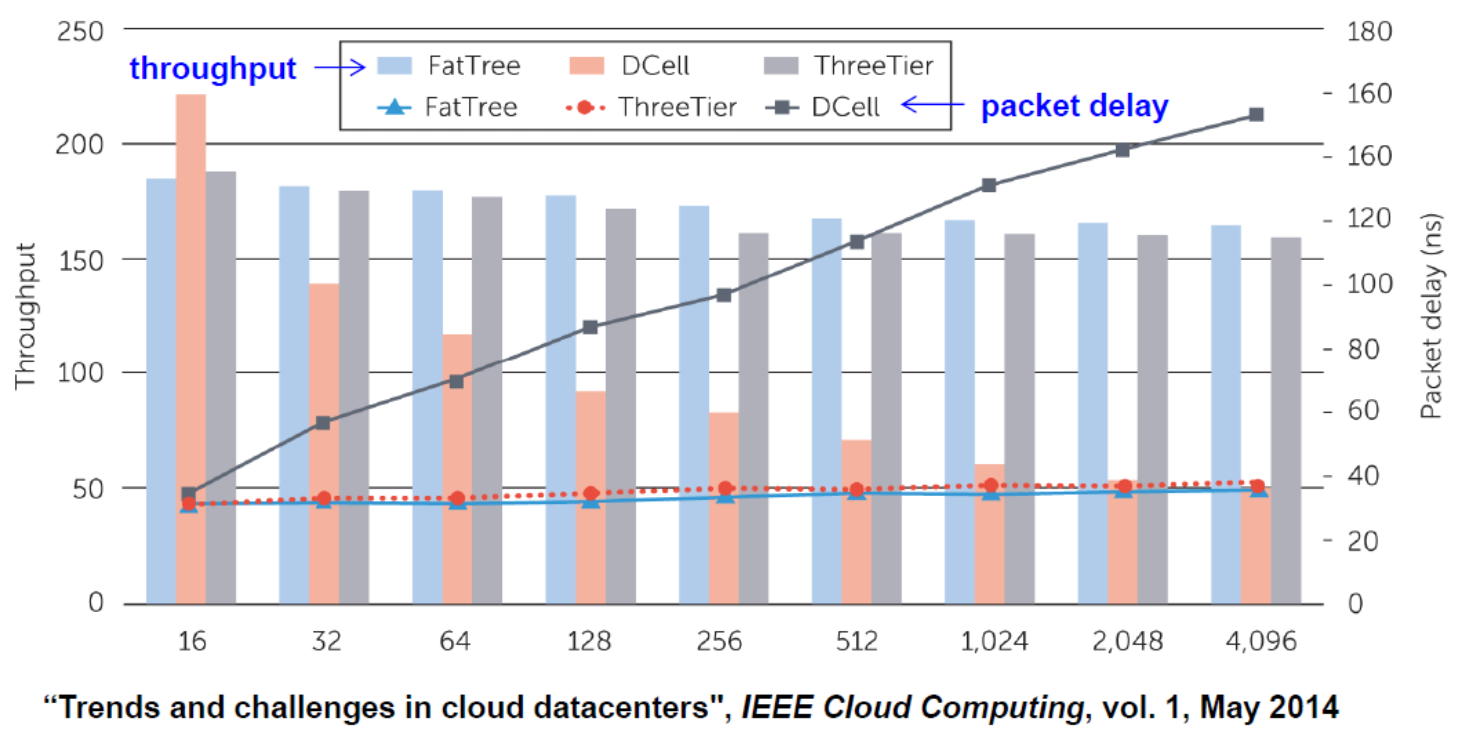
DC Networking Evaluation
As the number of nodes within the DC architecture increases, DCell experiences higher network delays and low throughput.(Fat Tree is better)
Summary
The tree-based ones are still dominant「dominant」 in the existing operational DCs.
- The traditional topology used so far is Fat Tree topology.
- 虽然 DCell 看起来很有前景,但在现实世界的云计算环境中,DCell 的实施却相当困难(而且有限)。
- 需要添加大量主机来扩展基础设施