Google Kubernetes
Google Kubernetes

Container Management and Orchestration Tools -> How to build and manage a container cluster?
Google Kubernetes (K8s)
- Kubernetes Architecture
- Kubernetes Pods,Namespace Quota
- Kubernetes Volume
Kubernetes 又称 K8s,是一个开源系统,用于自动化部署、扩展和管理容器化应用程序。
- 它将组成应用程序的容器分组为逻辑单元,以便于管理和发现
- Kubernetes 建立在 Google 15 年运行生产工作负载的经验之上,并结合了社区的最佳理念和实践。
Kubernetes 是一个跨节点集群管理容器化应用程序的系统。Kubernetes 可以协调 Docker 容器、Rkt 容器等!
Container orchestration is all about managing the lifecycles of containers, especially in large, dynamic environments (e.g.,a big cluster). Existing tools:
- Kubernetes (2015:Google open sourced,short for "K8S")
- Amazon's Elastic Container Service (ECS)
- Amazon Elastic Kubernetes Service (EKS)
- Azure's Container Service (AKS)
CaaS
- CaaS 通常是指一个完整的容器环境,包括协调工具、镜像目录、集群管理软件以及一套开发者工具和 APls。
- Container Orchestrators
- 自动化容器的生命周期;
- 在虚拟机上创建服务、调度任务和 pod。

Container Orchestration (Case: Deployment)

Task done by Orchestrator
- Provisioning「调配」 and deployment of containers
- Redundancy and availability of containers
- 扩展或移除容器,以便在主机基础设施上均匀「evenly」分布应用程序负载
- 在主机资源短缺或主机死亡的情况下,将容器从一台主机转移到另一台主机
- Allocation of resources between containers
- Load balancing between containers
- Health monitoring of containers and hosts
- Configuration of an application in relation to the containers running it
通常在 YAML(如 deploy.yaml)或 JSON 文件中描述应用程序的配置。
Architecture
master-slave architecture
容器位于 Pod 内。
Components
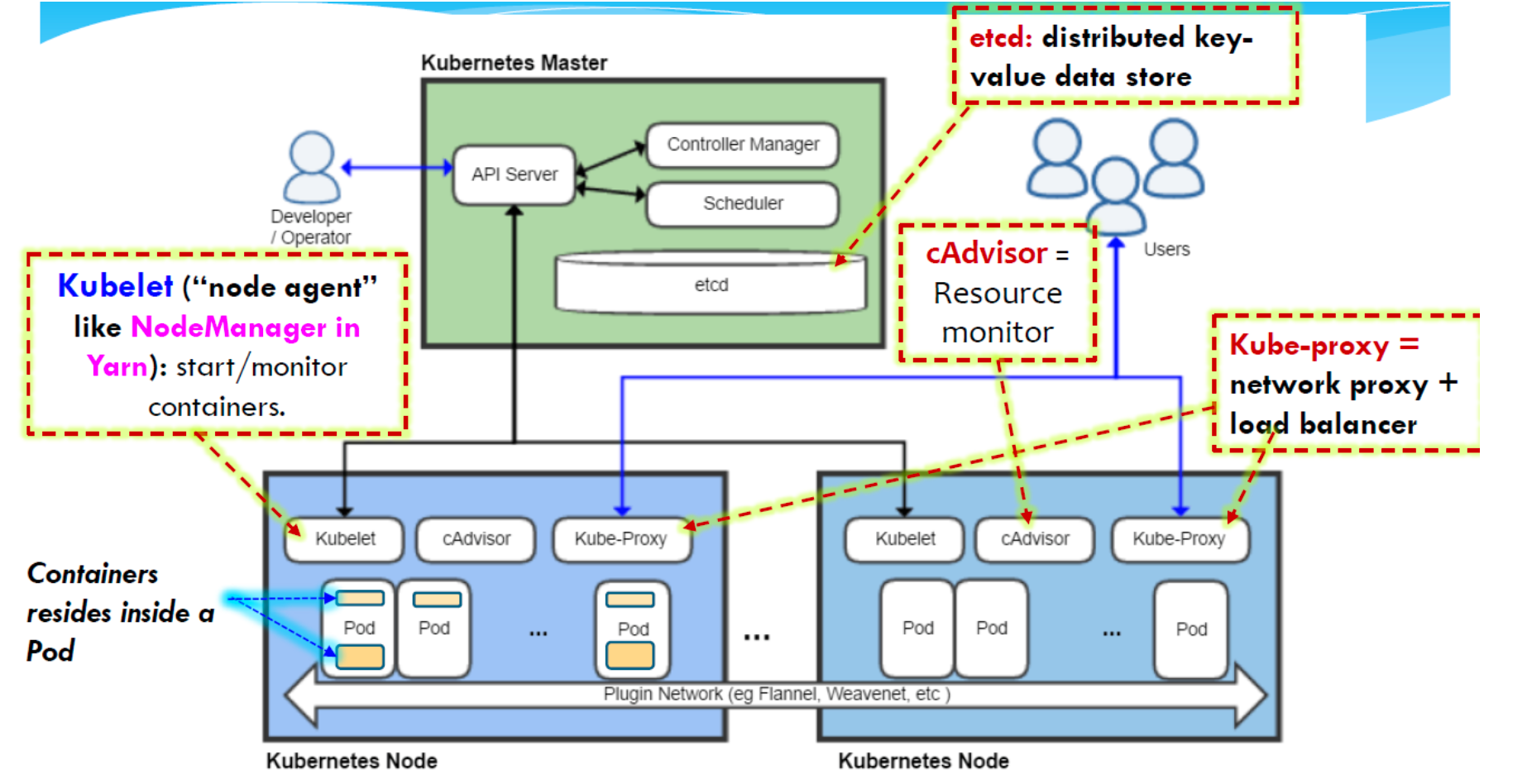
- Kubernetes Master: runs on a single node in your cluster
- 类似于 Yarn 的 ResourceManager
- Kubelet: the primary "node agent"that runs on each node
- 类似于 Yarn 的 NodeManager
- creating pods and make sure they are all running
- Kubelet是在Kubernetes集群中每个节点上运行的主要“节点代理”
- 它负责维护和管理该节点上的Pods(Pod是Kubernetes中的最小部署单元)。
- Kubelet接收一组由各种机制(主要是通过apiserver)提供的PodSpecs,然后确保这些PodSpecs中描述的容器正在运行并且是健康的。它还负责报告节点的状态以及运行中的Pod的状态。
- Kube-proxy: a network proxy and load balancer (packet forwarding) that runs in each node.
- etcd: a distributed, key-value data store for the master node to store the configuration data of the cluster.
- cAdvisor: provides a metric monitoring capability

Workflow

- 用户通过 kubectl 命令行工具向 Kubernetes 发送命令。kubectl 会将用户的命令翻译成一个声明式的 Deployment 对象。Deployment 是 Kubernetes 的一个高级 API,它支持滚动更新。
- kubectl 将 Deployment 对象发送到运行在集群中的 Kubernetes API 服务器(kube-apiserver)。
- kube-apiserver 将 Deployment 对象存储在 etcd 中。etcd 是一个运行在集群中的分布式键值存储系统,kube-apiserver 会向 kubectl 响应。
- Kubernetes 控制器管理器(kube-controller-manager)异步地监听 Deployment 事件,从 Deployment 创建一个 ReplicaSet,并将其发送到 kube-apiserver。ReplicaSet 是 Deployment 的一个版本。在滚动更新过程中,会创建一个新的 ReplicaSet,并逐步扩展到期望的副本数量,同时旧的 ReplicaSet 会逐步缩减到零。
- kube-apiserver 将 ReplicaSet 保存到 etcd 中。
- kube-controller-manager 从 ReplicaSet 创建两个(或更多,如果我们扩展)Pods,并将它们发送到 kube-apiserver。Pod 是 Kubernetes 的基本单位,它代表一个或多个共享 Linux cgroup 和命名空间的容器。
- kube-apiserver 将 Pods 保存到 etcd 中。
- Kubernetes 调度器(kube-scheduler)异步地监听 Pod 事件,更新每个 Pod 以将其分配给一个 Node,并将它们发送回 kube-apiserver。
- kube-apiserver 将 Pods 保存到 etcd 中。
- 最后,运行在分配的 Node 上的 kubelet(始终在监听)实际启动容器。

客户端发送一个部署请求到 API Server。这个请求通常由
kubectl create -f deployment.yml命令发送。API Server 将部署信息持久化到 etcd 数据库中。etcd 返回 200 状态码给 API Server,然后 API Server 返回 200 状态码给客户端。这个时候,部署的创建工作并没有完成,还有许多后台的异步操作需要进行。
Controller Manager 对 API Server 设置了监听 (watch),当它看到有新的部署创建时,会将这个部署的信息填充到 SharedCache 中。
Deployment Controller 看到新的部署后,会从队列中取出它,然后创建一个 ReplicaSet,并将 ReplicaSet 对象持久化到 API Server 和 etcd 中。
对 ReplicaSet 重复步骤 3。
ReplicaSet Controller 看到新的 ReplicaSet 后,会从队列中取出它,然后创建指定数量的 Pods,并将 Pods 对象持久化到 API Server 和 etcd 中。
对 Pods 重复步骤 3,但这次是由 Scheduler 来执行。
Scheduler 看到未调度的 Pods 后,会执行其业务逻辑,将 Pods 的 Spec 中的 nodeName 字段填充为可调度的 Node 的名称,并将调度后的 Pods 对象持久化到 API Server 和 etcd 中。
对 Pods 重复步骤 3,但这次是由 Kubelet 来执行。
Kubelet(在被调度的节点上)看到它应该在其机器上运行一个 Pod,然后与容器运行时(如 Docker)进行交互,使得 Pod 能在其机器上运行。
Kubernetes Container Runtime
Docker 并非唯一选择
The container runtime is responsible for
- pulling the container image from a registry
- unpacking the container images
- running the application.
Kubernetes 支持的容器运行时:Docker、containerd、cri-o、Frakti、rktlet 和 Kubernetes CRI(容器运行时接口)的任何实现。
容器运行时接口(CRI) - 一个插件接口,使 kubelet 能够使用各种容器运行时
Kubernetes Pod
A pod consists of one or more containers
- Pod 是 Kubernetes 中最小的可部署单元
- 同一 pod 中的容器位于同一位置,并调度在同一台机器上。
- Network: Each Pod is assigned a unique IP address
- Pod 中的所有容器共享相同的 IP 地址和端口空间。
- 存储:Pod 中的应用程序可访问共享卷( = 本地磁盘空间或网络磁盘)。
提示
In terms of Docker concept, a Pod is just a group of Docker containers with shared namespaces and shared filesystem volumes.
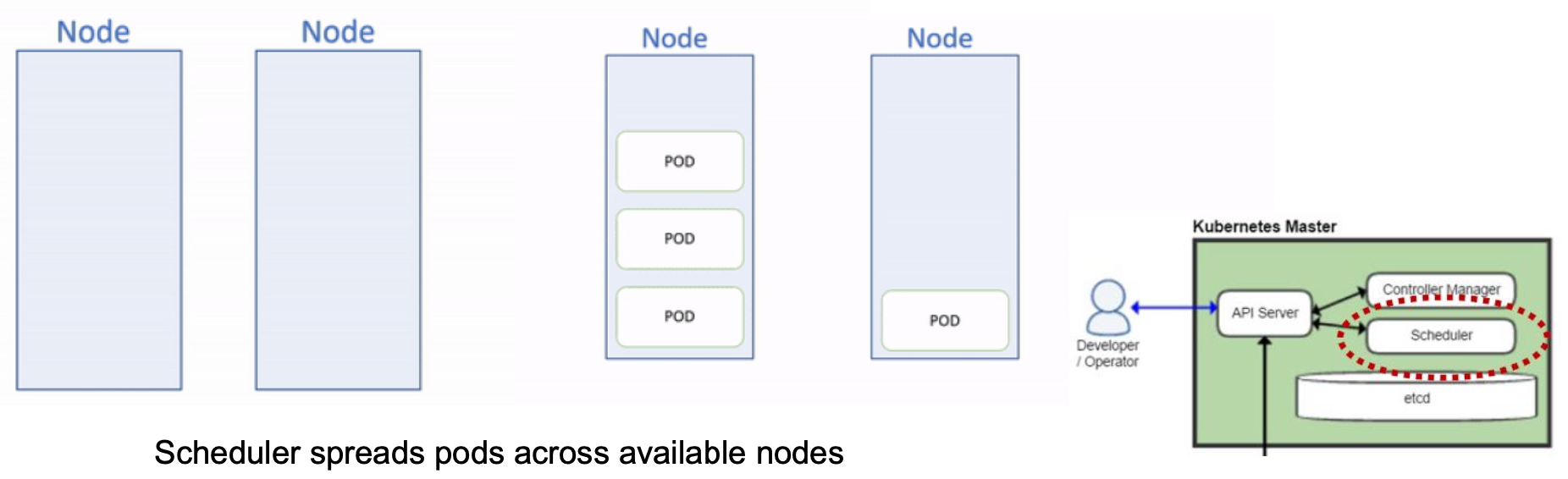
Kubernetes Scheduler
Scheduler is a component in a master node,which is responsible for deciding which worker node should run a given pod.
2-step operation:
- Filtering (e.g.,enough resource?)
- Scoring (pick the one with the highest ranking)
Scheduler spreads pods across available nodes 「调度程序将 Pod 分散到可用节点上」
Kubernetes cAdvisor
- cAdvisor (容器顾问)是一种开源容器资源使用情况收集器,作为 Kubelet 二进制文件的一部分。
- cAdvisor auto-discovers all containers in the given node and collects CPU,memory,filesystem,and network usage for those containers.
- Kubelet 可直接从 cAdvisor 提取容器资源使用指标「metrics」,并根据这些指标做出决策。
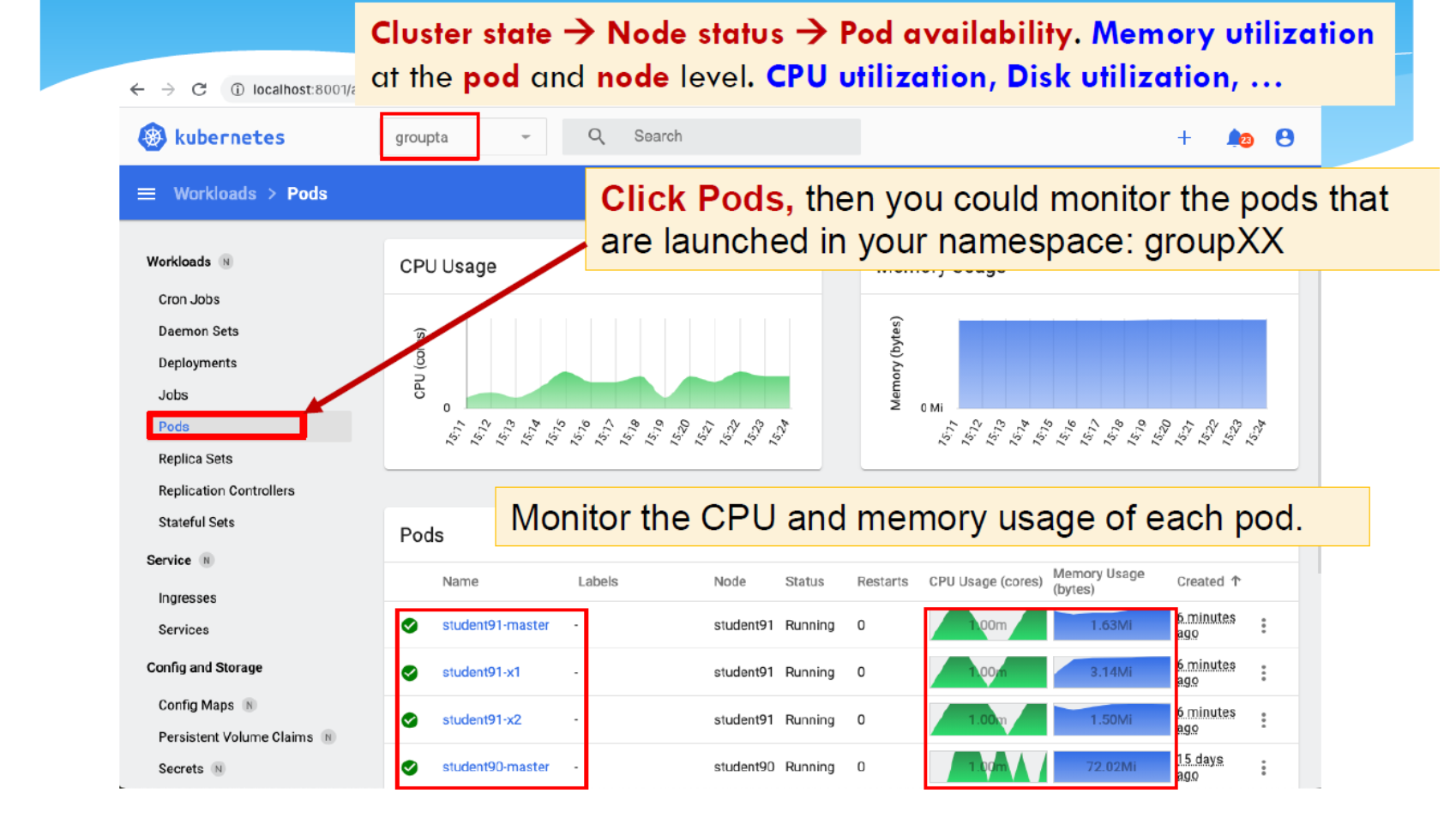
Kubernetes Dashboard
用于观察 Kubernetes 中容器的默认基于 Web 的用户界面。
- 在 pod 中部署应用程序
- pod 中运行的应用程序概览。
- 对 Pod 中正在运行的应用程序进行故障排除「Troubleshoot」。
- 允许您更改集群所需的资源量。
- 监控每个 Kubernetes pod 的 RAM 和 CPU 利用率
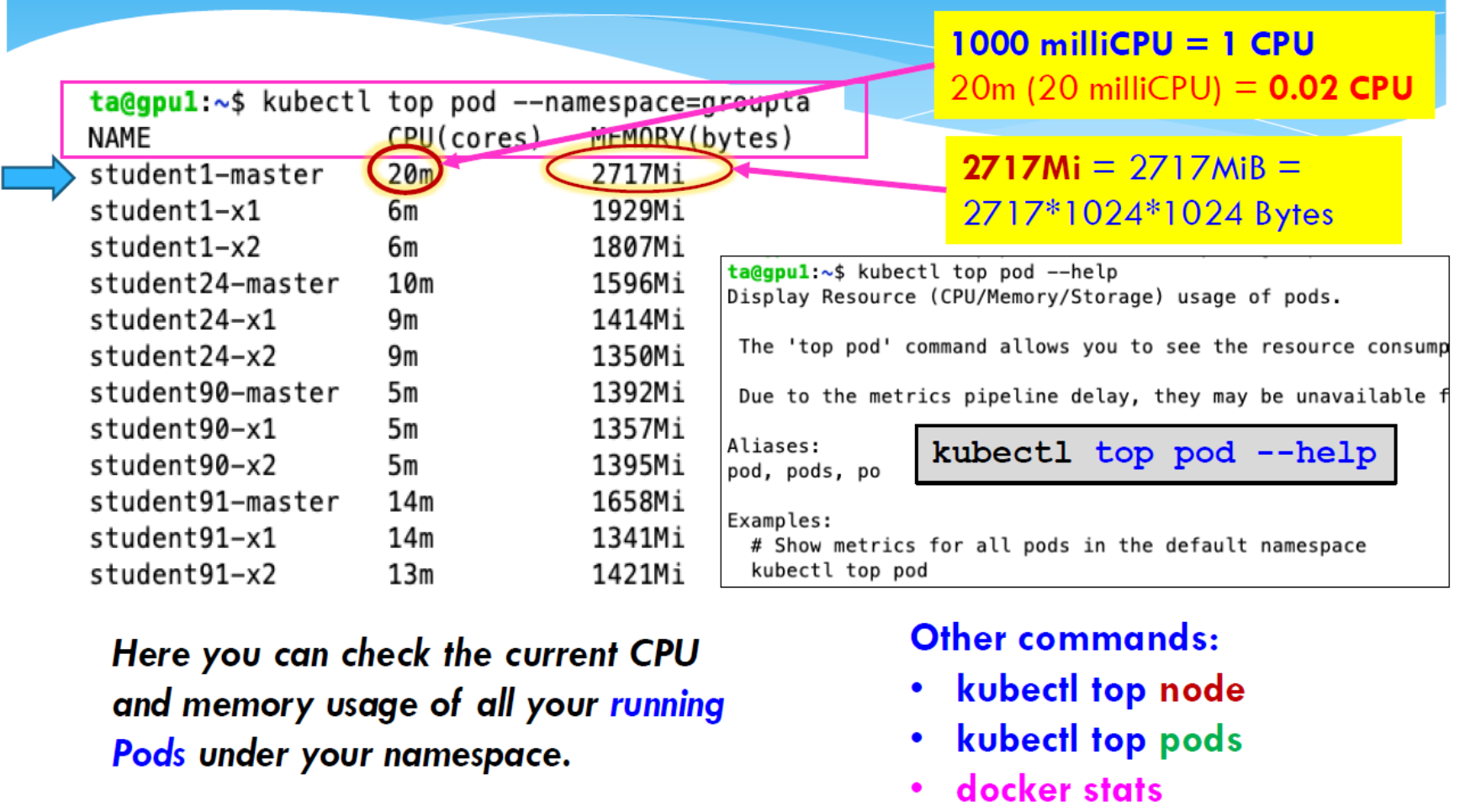
Check Current Resource Usage
Use “kubectl top” command check current resource usage
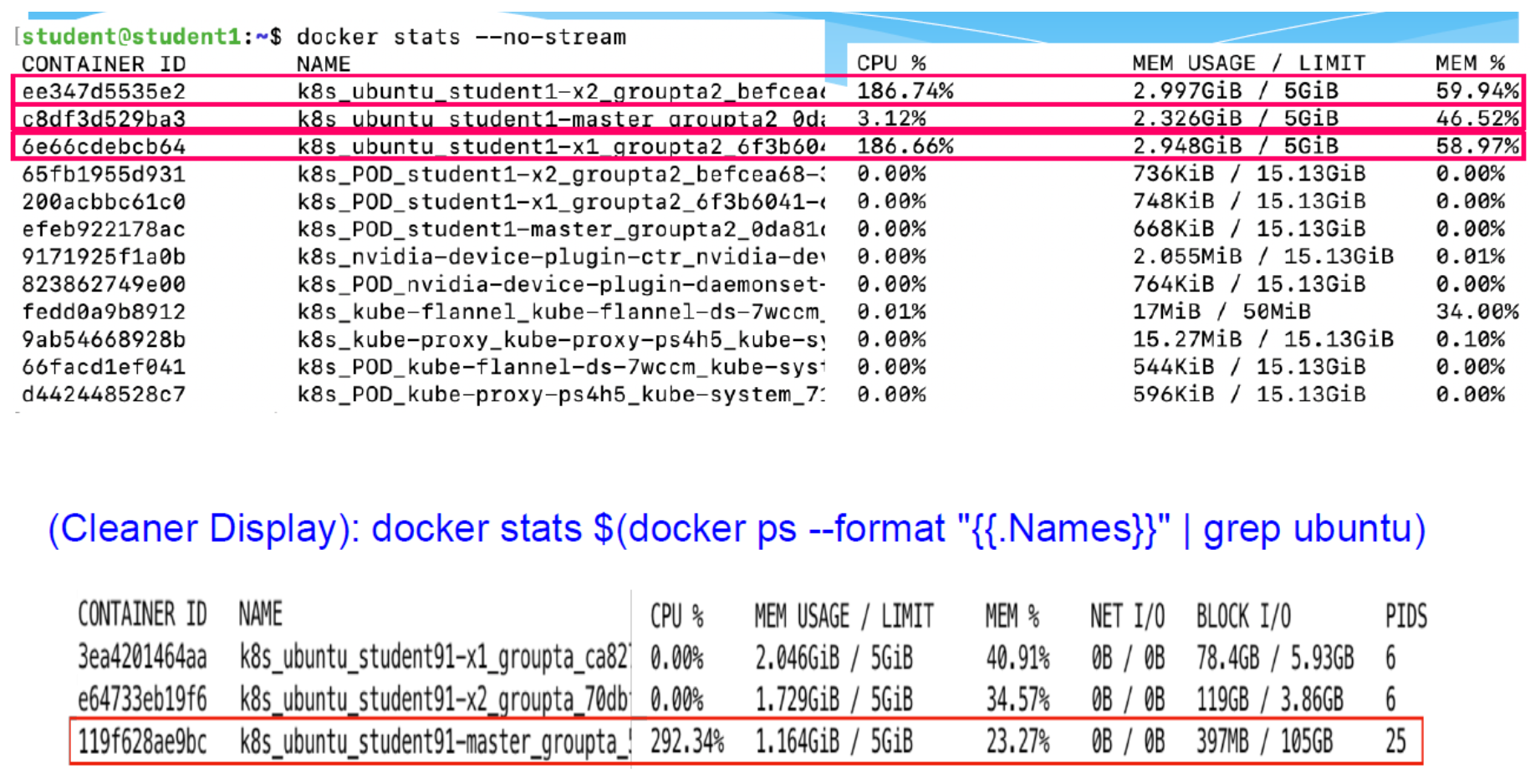
Docker Stats: Monitor CPU/Memory Usage
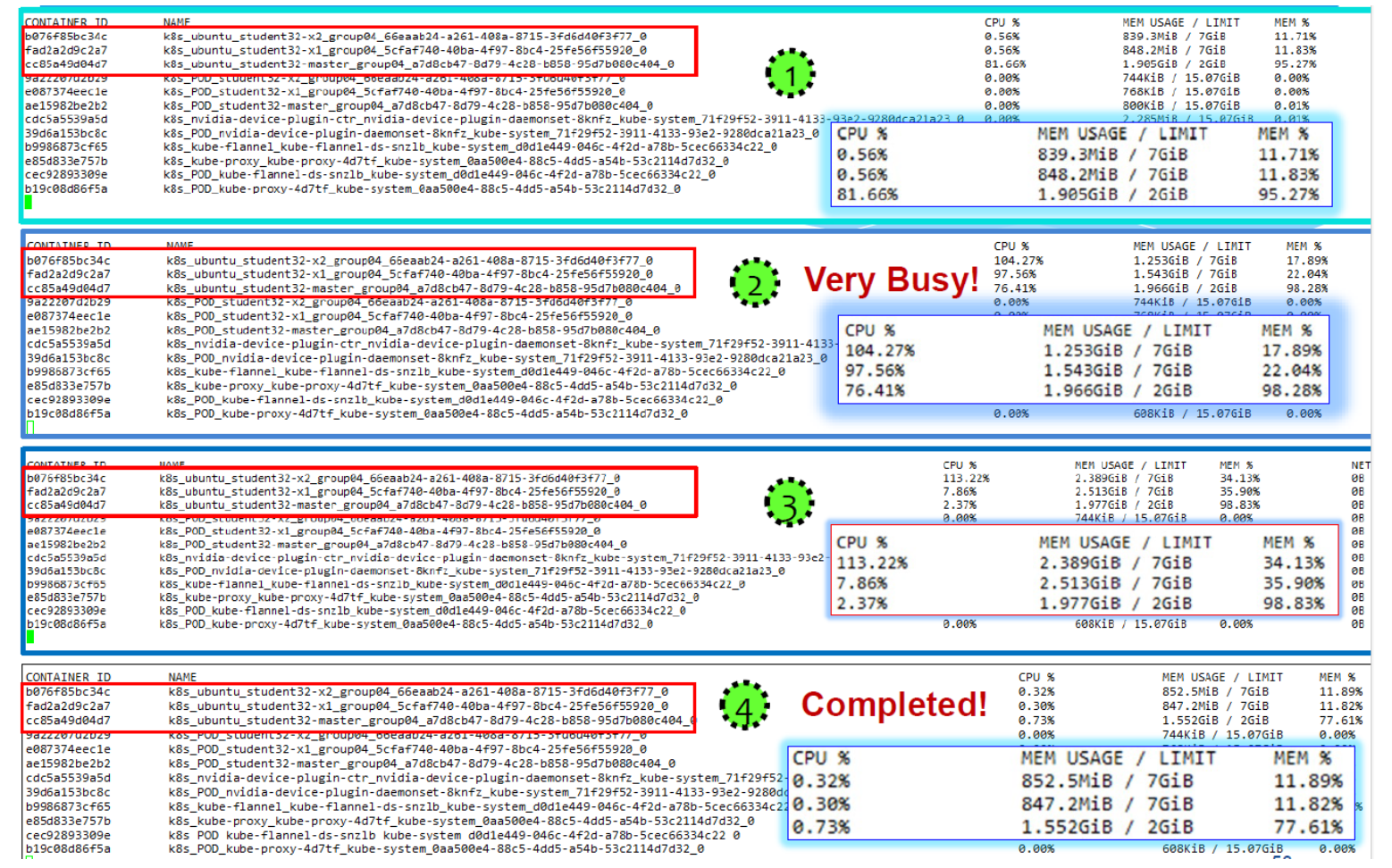
CPU/Memory Usage during Spark TeraSort
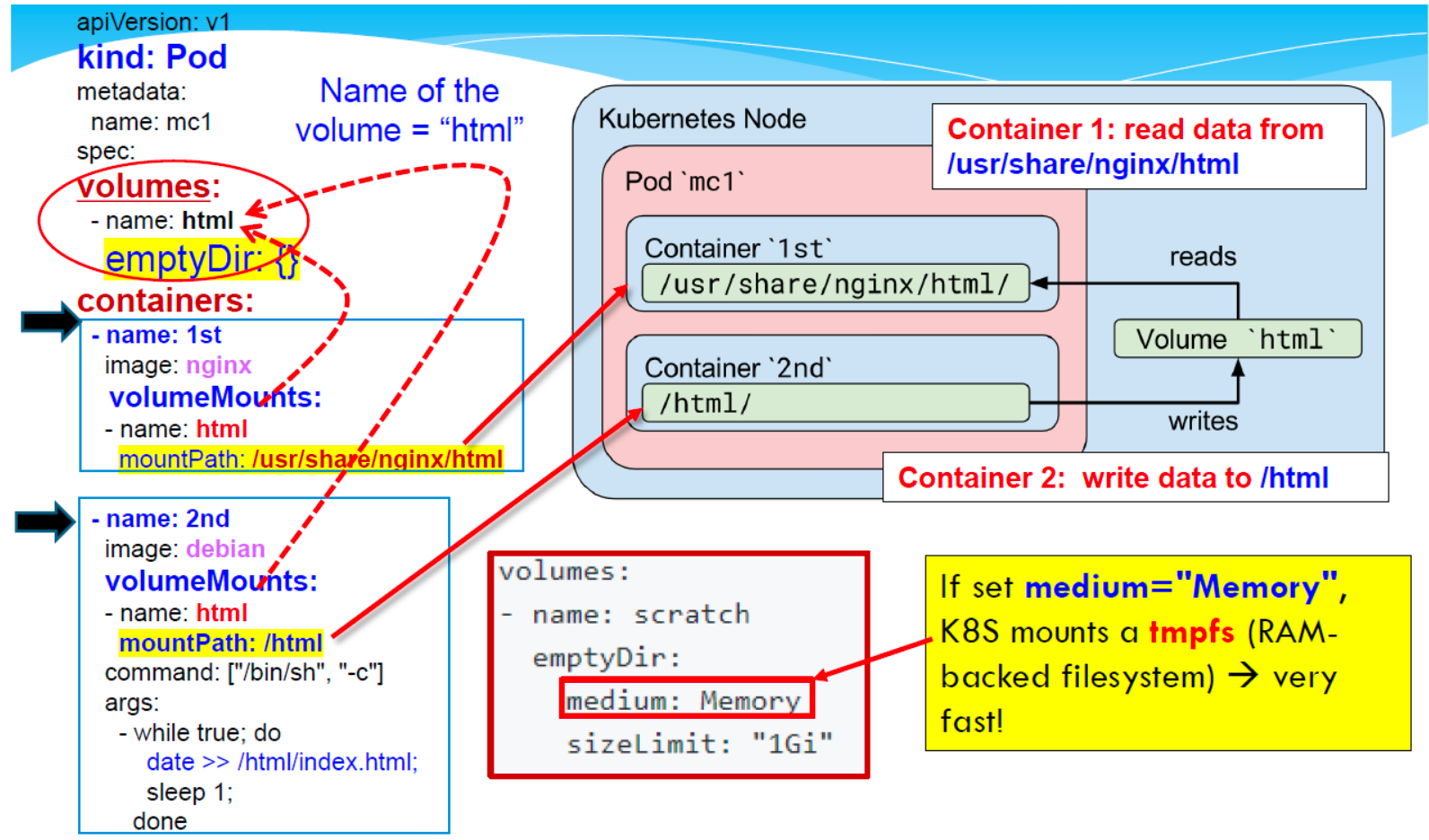
Volumes
- On-disk files in a container are ephemeral「短暂的」.
- 当容器崩溃时,kubelet 会重新启动容器,但处于干净状态(之前的所有更改都会丢失)。
- 为了获得独立于容器的更一致的存储,可以使用卷「Volume」。
A Pod uses a Volume for storage
- Volumes can be used by all containers in pod, but they must be mounted in each container that needs to access them first.
- Each Container in the Pod's configuration must independently specify「指定」 where to mount each volume
Two basic types of Volumes:
- Ephemeral「临时的」 volume:具有 pod 的生命周期。当 pod 不再存在时,Kubernetes 会销毁临时卷。例如,emptyDir、configMap、secret 等。
- Persistent volume: 在 Pod 的生命周期之外存在(即使 Pod 崩溃或被删除也能生存)。例如,hostPath、perpetitiveVolumeClaim、awsElasticBlockStore、azureDisk、gcePersistentDisk
对于给定 pod 中的任何卷,数据都会**在容器(而非 Pod)**重启时保留。
Type of Kubernetes
- Node-local
- emptyDir:当 pod 被分配给一个节点时创建的初始空卷;即使 pod 中的容器终止并重新启动,该卷也会在 Pod 的生命周期内持续存在。
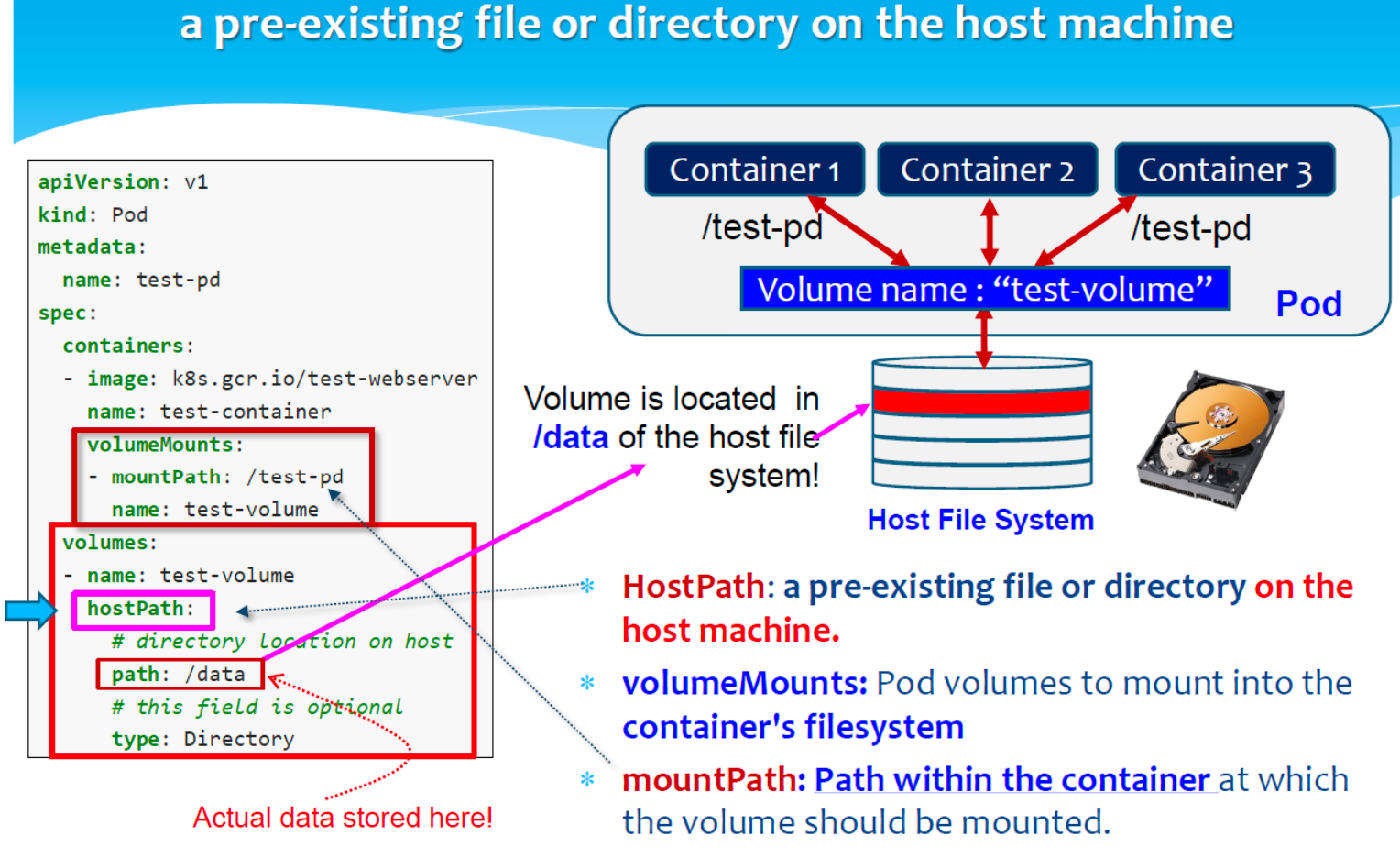
- hostPath:将主机节点文件系统中的文件或目录挂载到 pod 中
- nsf:将现有的 NFS(网络文件系统)挂载到 pod 中。
- permanentVolumeClaim:将 PersistentVolume 挂载到 pod 中,并在 pod 的生命周期结束后持续存在。
- 分布式文件系统:CephFS、rbd、Glusterfs
- 特定于云提供商的 awsElasticBlockStore(AWS)、gcePersistentDisk(Google Cloud)和 azureDiskVolume(Azure)。
emptyDir
“empty” at Pod startup
HostPath
a pre-existing file or directory on the host machine